A 12 kVA, 208 V, 60Hz, 4-pole, three-phase, Y-connected synchronous generator has a 5 ohm synchronous reactance. The generator is supplying a rated load at unity power factor. The excitation voltage of the generator was 206 V/phase. If the field current is increased by 20% and the prime mover power is kept constant, what is the new power angle in degrees? Round your answer to one decimal place.
Answers
The new power angle of the synchronous generator, given an increased field current and constant prime mover power, is approximately 49.8 degrees when rounded to one decimal place.
The new power angle of the synchronous generator, given an increased field current and constant prime mover power, can be calculated by considering the change in the excitation voltage and the synchronous reactance.
To calculate the new power angle, we first need to determine the initial power angle. Since the generator is operating at unity power factor, the power angle is initially 0 degrees.
The power angle is related to the excitation voltage, synchronous reactance, and load impedance. In this case, the load is at the unity power factor, so the load impedance is purely resistive.
Given that the generator has a synchronous reactance of 5 ohms, the load impedance is also 5 ohms (as the load is at unity power factor). With the initial excitation voltage of 206 V/phase, we can calculate the initial current flowing through the synchronous reactance using Ohm's Law (V = I * Z). Thus, the initial current is 206 V / 5 ohms = 41.2 A.
Now, to find the new power angle, we increase the field current by 20%. The new field current is 1.2 times the initial field current, which becomes 1.2 * 41.2 A = 49.44 A.
Next, we need to calculate the new excitation voltage. The excitation voltage is directly proportional to the field current. Therefore, the new excitation voltage is 1.2 times the initial excitation voltage, which becomes 1.2 * 206 V = 247.2 V/phase.
Using the new excitation voltage and the load impedance of 5 ohms, we can calculate the new current flowing through the synchronous reactance. Thus, the new current is 247.2 V / 5 ohms = 49.44 A.
Finally, we can calculate the new power angle using the equation tan(theta) = (Imaginary part of the current) / (Real part of the current). In this case, the real part of the current remains the same, i.e., 41.2 A, but the imaginary part changes to 49.44 A. Therefore, the new power angle is arctan(49.44 A / 41.2 A) = 49.8 degrees.
Hence, the new power angle of the synchronous generator, given an increased field current and constant prime mover power, is approximately 49.8 degrees when rounded to one decimal place.
Learn more about Ohm's Law here :
https://brainly.com/question/1247379
#SPJ11
Related Questions
If a blender uses 110 volts and 20 amperes how many watts is it using?

Answers
Answer:
2200 watts
Explanation:
# of Watts = Volts × Amps
# of Watts = 110 × 20# of Watts = 2200 wattsHave a lovely rest of your day/night, and good luck with your assignments! ♡
A gas turbine power plant operates on a simple thermodynamic cycle. The ambient conditions
are 100 kPa and 24 °C. The air at this condition enters the engine at 150 m/s whose diameter
is 0.5 m. The pressure ratio across the compressor is 13, and the temperature at the turbine
inlet is 1400 K. Assuming ideal operation for all components and specific heats for air and
products separately. In addition, neglect the mass of fuel burned. Do the followings:
a) Choose the suitable thermodynamic cycle “Brayton Cycle”
b) Draw pv and Ts diagram and label it
c) Calculate the power required by the compressor
d) Determine the pressure and the temperature at the turbine exit
e) Compute the power produced by the turbine
f) Available specific work
g) The thermal efficiency.
Answers
Answer:
Heat rate. 10,535 kJ/kWh. Turbine speed. 7,700 rpm. Compressor pressure ratio. 14.0:1. Exhaust gas flow. 80.4 kg/s. Exhaust gas temperature. 543 deg C.
Explanation:
Which of the following illustrates a technological fix, in contrast to social engineering, to solve the problem of water shortage?
a. Persuading people to take shorter showers
b. Low-flush toilets
c. Wearing clothes more than once before washing
d. Disseminating public service announcements about the need to conserve water
Answers
The option that illustrates a technological fix, in contrast to social engineering, to solve the problem of water shortage is (b) Low-flush toilets.
Technological fixes involve implementing new technologies to address a problem, whereas social engineering involves changing people's behavior. Low-flush toilets are a technological fix because they are designed to use less water per flush, directly reducing water consumption. In contrast, options (a), (c), and (d) are examples of social engineering, as they involve persuading or encouraging people to change their behaviors to conserve water (e.g., taking shorter showers, wearing clothes more than once, or raising awareness through public service announcements).
Among the given options, low-flush toilets represent a technological fix to address water shortage issues. The correct option is (b) Low-flush toilets.
Learn more about social engineering visit:
https://brainly.com/question/31784802
#SPJ11
FAULT LOCATION METHODS(input-output)
Answers
Fault location techniques are used in power systems for accurate pinpointing of the fault position.
This paper presents a comparative study between two fault location methods in distribution network with Distributed Generation (DG). Both methods are based on computing the impedance using fundamental voltage and current signals. The first method uses one-end information and the second uses both ends
Nec ________ covers selection of time-delay fuses for motor- overload protection.
Answers
Nec Article 430 covers selection of time-delay fuses for motor- overload protection.
What article in the NEC covers motor overloads?Article 430 that is found in National Electrical Code (NEC) is known to be state as “Motors, Motor Circuits and Controllers.” .
Note that the article tells that it covers areas such as motors, motor branch-circuit as well as feeder conductors, motor branch-circuit and others.
Therefore, Nec Article 430 covers selection of time-delay fuses for motor- overload protection.
Learn more about motor- overload from
https://brainly.com/question/20738481
#SPJ1
When trying to prevent a rollover, it is important that the driver does not
A. overcorrect
B. grab the steering wheel
C. slam the brakes
D. undercorrect
Answers
FOR BRAINLIST HELP PLEASE IS A DCP
A- Causes of the 13t Amendment
B- Reasons for Women's Suffrage
C- Reasons for the Freedmen's Bureau
D- Causes of the Plantation System

Answers
Answer:
C
Explanation: Freedmens Bureau provided resources for southerners and newly freed slaves
How many hours must be traveled by car for each hour of rock climbing to make the
risks of fatality by car equal to the risk of fatality by rock climbing? (FAR for car
travelling is 52 and FAR for rock climbing is 3400).
Answers
The number of hours that must be travelled by car to make the risks of fatality by car equal to the risk of fatality by rock climbing is = 65hours
Calculation of risk of fatalities (FAR)The FAR of car = 52
This means for every one hour there is risk of 52 people dying by car accident.
The FAR of rock climbing = 3400
This means that for every one hour there is risk of 3400 dying by car accident.
If FAR for 1 hour = 52
X hours = 3400
Make X the subject of formula,
X hours = 3400/52
= 65 hours approximately
Therefore, the number of hours that must be travelled by car to make the risks of fatality by car equal to the risk of fatality by rock climbing is = 65 hours.
Learn more about hours here:
https://brainly.com/question/1739912
#SPJ1
what event caused the leaning tower of pisa to lean
Answers
The leaning tower of pisa is leaning due to several factors over the years, including poor foundation design and soft soil.
The Leaning Tower of Pisa is one of the most famous tourist attractions in Italy and has become an iconic symbol of the city of Pisa. It is known for its noticeable tilt, which has fascinated people for centuries.The tower's lean has been attributed to several factors over the years, including poor foundation design and soft soil. However, the primary cause of the leaning of the tower is the foundation soil of the tower.The soil beneath the tower is composed of clay, fine sand, and shells, which are not stable enough to support the tower's weight.
The soil began to settle unevenly under the tower shortly after construction began in 1173, causing one side of the tower's foundation to sink deeper than the other.The tower's engineers tried to correct the lean during the construction process by making the columns on the tower's higher side slightly taller, but this only made the tower lean more. The tower eventually reached a tilt of 5.5 degrees, which is why it is known as the Leaning Tower of Pisa. A series of restoration projects in the late 20th and early 21st centuries have helped stabilize the tower's lean and ensure that it can continue to be enjoyed by tourists for generations to come.
To know more about construction process refer to:
https://brainly.com/question/17739286
#SPJ11
professional engineer engagement record and reference form example
Answers
The Professional Engineer Engagement Record and Reference Form is a document that is used to provide evidence of an engineer's experience and competence.
It typically includes information about their education, work experience, and specific engineering projects they have been involved in. The form serves as a way for the engineer to demonstrate their practical experience and for references to validate their qualifications.
References, who are typically other professional engineers or supervisors, provide their assessment of the candidate's technical abilities, ethical conduct, and overall suitability for professional engineering practice. This document plays a vital role in the licensure process by ensuring that engineers meet the necessary criteria and standards to protect the public and maintain the integrity of the engineering profession.
It provides a comprehensive overview of an engineer's professional journey, serving as a crucial component in the evaluation and approval of their application for professional engineering licensure.
To know more about Professional Engineer visit:
https://brainly.com/question/19819958
#SPJ11
What are 4 different telescopes that are used to see radio waves?
Answers
Answer:
A radio telescope can be divided into 4 functional parts. The four parts are: the reflector dish, the antenna, the amplifier and the receiver/recorder. The large dish that most people associate with a radio telescope is used to focus the radio waves.
Explanation:
Slabs in a slab and beam frame construction can be as thin as 2 inches. The concrete beams must be Closely spaced in order to provide adequate support to the thin slab. True or false?
Answers
The given statement is "False". In slab and beam frame construction, the slabs can indeed be relatively thin, but the concrete beams do not need to be closely spaced to provide support to the thin slab.
In fact, the purpose of the beams in this type of construction is to distribute the load from the slab to the supporting columns or walls.
The beams act as structural members that span between the columns or walls, providing additional support and helping to distribute the load evenly. They are responsible for transferring the loads from the slab to the columns or walls, thus reducing the span of the slab and preventing excessive deflection or sagging.
The spacing of the beams in a slab and beam frame construction depends on various factors, including the design requirements, load considerations, and engineering calculations. The beams are typically spaced at predetermined intervals based on structural design considerations rather than the thickness of the slab alone.
Therefore, the statement that the concrete beams must be closely spaced in order to provide adequate support to the thin slab is false. The spacing of the beams is determined based on structural engineering principles and considerations, taking into account the anticipated loads and design requirements.
Thus, the correct option is "False".
Learn more about concrete beams:
https://brainly.com/question/27909048
#SPJ11
(a) What is the distinction between hypoeutectoid and hypereutectoid steels? (b) In a hypoeutectoid steel, both eutectoid and proeutectoid ferrite exist. Explain the difference between them. What will be the carbon concentration in each? (c) In bullet format compare and contrast the expected mechanical behavior of hypoeutectoid and hypereutectoid steels in terms of: (i) Yield strength (ii) Ductility (iii) Hardness (iv) Tensile strength (d) If you want to choose an alloy to make a knife or ax blade would you recommend a hypoeutectoid steel alloy or a hypereutectoid steel alloy? Explain your recommendation in 1-3 bullet points. (e) If you wanted a steel that was easy to machine to make a die to press powders or stamp a softer metal, would you choose a hypoeutectoid steel alloy or a hypereutectoid steel alloy? Explain your choice in 1-3 bullets.
Answers
Answer:
See explanation below
Explanation:
Hypo-eutectoid steel has less than 0,8% of C in its composition.
It is composed by pearlite and α-ferrite, whereas Hyper-eutectoid steel has between 0.8% and 2% of C, composed by pearlite and cementite.
Ferrite has a higher tensile strength than cementite but cementite is harder.
Considering that hypoeutectoid steel contains ferrite at grain boundaries and pearlite inside grains whereas hypereutectoid steel contains a higher amount of cementite, the following properties are obtainable:
Hypo-eutectoid steel has higher yield strength than Hyper-eutectoid steel
Hypo-eutectoid steel is more ductile than Hyper-eutectoid steel
Hyper-eutectoid steel is harder than Hyper-eutectoid steel
Hypo-eutectoid steel has more tensile strength than Hyper-eutectoid steel.
When making a knife or axe blade, I would choose Hyper-eutectoid steel alloy because
1. It is harder
2. It has low cost
3. It is lighter
When making a die to press powders or stamp a softer metals, I will choose hypo-eutectoid steel alloy because
1. It is ductile
2. It has high tensile strength
3. It is durable
Answer:
(a)
Steels having carbon within 0.02% – 0.8% which consist of ferrite and pearlite are known as hypoeutectoid steel.
Steels having greater than 0.8% carbon but less than 2.0% are known as hypereutectoid steel.
(b)
The proeutectoid ferrite formed at a range of temperatures from austenite in the austenite+ferrite region above 726°C. The eutectoid ferrite formed during the eutectoid transformation as it cools below 726°C. It is a part of the pearlite microconstiutents . Note that both hypereutectoid and hypoeutectoid steels have proeutectoid phases, while in eutectoid steel, no proeutectoid phase is present.
Proeutectoid signifies is a phase that forms (on cooling) before the eutectoid austenite decomposes. It has a parallel with primary solids in that it is the first phase to crystallize out of the austenite phase. If the steel is hypoeutectoid it will produce proeutectoid ferrite and if it is hypereutectoid it will produce proeutectoid cementite. The carbon concentration for both ferrites is 0.022 wt% C.
(c)
(i) Yield strength: The hypoeutectoid steel have good yield strength and hypereutectoid steels have little higher yield strengh.
(ii) Ductility: The hypoeutectoid steel is more ductile and the ductility has decreased by a factor of three for the eutectoid alloy. In hypereutectoid alloys the additional, brittle cementite on the pearlite grain boundaries further decreases the ductility of the alloy. The proeutectoid cementite restricts plastic deformation to the ferrite lamellae in the pearlite.
(iii) Hardness: hypoeutectoid steels are softer and hypereutectoid steel contains low strength cementite at grain boundary region which makes it harder than hypoeutectoids.
(iv) Tensile strength: Grain boundary regions of hypereutectoid steel are high energy regions prone to cracking because of cementite in the grain boundaries, its tensile strength decreases drastically even though pearlite is present. Hypoeutectoid steel contains ferrite at grain boundaries and pearlite inside grains, so grain boundaries being the high energy state region, it has a higher tensile strength.
(d)
I would recommend hypereutectoid steel alloy to make a knife or ax blade
1- Hardness is required at the surface of the blades.
2- Ductility is not needed for such application.
3- Due to constant impact, the material will not easily yield to stress.
(e)
I would choose a hypoeutectoid steel alloy to make a steel that was easy to machine.
1- hypoeutectoid steel alloys have high machinability, hence better productivity
2- It will be used on softer metals, hence its fitness for the application
3- Certain amount of ductility is required which hypoeutectoid steel alloys possess.
Explanation:
See all together above
A refrigeration system was checked for leaks. The system temperature and surroundings were 75°F when the system was charged with nitrogen to 100 psig. The temperature then dropped to 50°F. What should the pressure be if no nitrogen has escaped?
A) 9 psig
B) 94 psig
C) 100 psig
D) 90 psig
Answers
The temperature and pressure of an ideal gas are directly proportional
The pressure of the system should be in the range B) 94 psig
The given refrigerator parameters are;
The temperature of the system and the surrounding, T₁ = 75 °F = 237.0389 K
The pressure to which the system was charged with nitrogen, P₁ = 100 psig
The temperature to which the system dropped, T₂ = 50 °F = 283.15 K
The required parameter;
The pressure, P₂, of the system at 50°F
Method:
The relationship between pressure and temperature is given by Gay-Lussac's law as follows;
At constant volume, the pressure of a given mass of gas is directly proportional to its temperature in Kelvin
Mathematically, we have;
\(\dfrac{P_1}{T_1} = \mathbf{\dfrac{P_2}{T_2}}\)
Plugging in the values of the variables gives;
\(\mathbf{\dfrac{100 \ psig}{297.0389}} = \dfrac{P_2}{283.15}\)
Therefore;
\(P_2 = \mathbf{283.15 \, ^{\circ}F \times \dfrac{100 \ psig}{297.0389\ ^{\circ}F} \approx 95.3 \, ^{\circ}F}\)
The closest option to the above pressure is option B) 94 psig
Learn more about Gay-Lussac's law here;
https://brainly.com/question/16302261

What observation can you notice in transferring heat by changing the intermediate section
material with a different cross-sectional area?
Answers
The observation that will be noticed in transferring heat by changing the intermediate cross sectional area is that;
An increase in the intermediate cross sectional area would lead to an increase in the rate of heat transfer and vice versa.
According to fourier's equation for heat conduction, the rate of heat transfer is given by the equation;dQ/dt = kA(dT/dx)
Where;
dQ/dt is rate of heat transfer
k is thermal conductivity of the medium
A is cross sectional area
dT/dx is the rate of change of the temperature per unit length
Now, from the above equation, we can see that the rate of heat transfer is directly proportional to the cross sectional area of the material through which the heat is being conducted. This means that the wider the cross sectional area, the more the surface particles required to conduct heat and definitely the higher the rate of heat transfer.Read more at; https://brainly.com/question/13051858
Examine the pressure-measuring device shown in the figure below. (a) What is the gauge pressure reading in psi at point A? (b) What is the pressure difference between point A and B? (c) Which is higher, pressure at point A or at point B? (d) What is the absolute pressure in psi at point D? State any assumptions you made
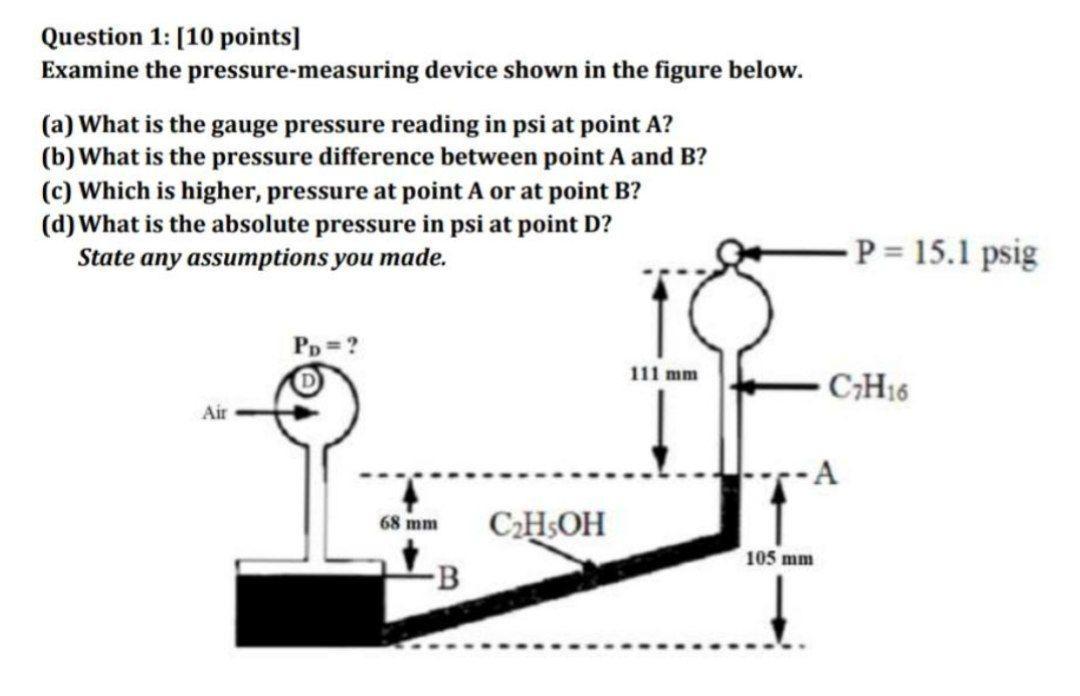
Answers
Answer: 45
Explanation:just cuase I need to
Water at 20 C and 500 kPa flows in a 50mm diameter horizontal commercial steel pipe at a velocity of 6 m/s. The pipe then goes through a contraction to 25mm diameter. What is the maximum pressure that the water in the smaller pipe can have
Answers
The maximum pressure that the water in the smaller pipe can have is 362.5 kPa.
We have given:
Water temperature (T1) = 20°C
Water pressure (P1) = 500 kPa
Diameter of pipe (D1) = 50mm
The velocity of water (V1) = 6 m/s
Diameter of pipe (D2) = 25mm Using Bernoulli’s equation, we can relate the pressure in the larger diameter pipe to the pressure in the smaller diameter pipe as:
(1/2)*ρ*V1² + P1 + ρ*g*h1 = (1/2)*ρ*V2² + P2 + ρ*g*h2, where h1 = h2; z1 = z2; ρ = Density of fluid and g = acceleration due to gravity.
Where P2 is the pressure in the smaller diameter pipe.
Hence, (1/2)*ρ*V1² + P1 = (1/2)*ρ*V2² + P2 ∴ P2 = P1 + (1/2)*ρ*(V1² - V2²)
The continuity equation states that the mass flow rate is constant across the two sections of the pipe. It can be written as A1*V1 = A2*V2, where A1 and A2 are the cross-sectional areas of the larger diameter pipe and the smaller diameter pipe, respectively.
Rearranging this equation to get V2:V2 = (A1 / A2) * V1V2 = (π/4) * D₁² * V1 / ((π/4) * D₂²)V2 = D₁² * V1 / D₂²∴ V2 = (50mm)² * 6 m/s / (25mm)² = 288 m/s
Plugging this value in the above expression for P2: P2 = 500 kPa + (1/2) * 1000 kg/m³ * (6 m/s)² * [1 - (25/50)²]P2 = 362.5 kPa
Therefore, the maximum pressure that the water in the smaller pipe can have is 362.5 kPa.
Learn more about Bernoulli's equation:
https://brainly.com/question/15396422
#SPJ11
Technician A says that tailor-rolled parts may be used for collision energy managements.
Technician B says that tailor-welded parts are aluminum and steel parts joined together. Who is right?
A Only
B only
Both A and B
Neither A nor B
Answers
Select the correct text in the passage.
Identify which of the following sentences describes the working of a piezoelectric gauge.
Answers
Answer:
The gauge converts the charge into a measurable electrical signal.
Explanation:
trust me
draw the diagram of synchronous modulo-3 counter flip flop
Answers
A synchronous modulo-3 counter is a type of digital circuit that can count up to three before resetting back to zero.
How to explain the moduloIt is called "synchronous" because all of its flip-flops change state at the same time, based on a clock signal.
A modulo-3 counter has three states: 0, 1, and 2. It uses two flip-flops, with their outputs connected in a specific way to produce the counting sequence.
The circuit works as follows:
Initially, both flip-flops are reset to 0.
When the clock input goes from 0 to 1, the first flip-flop (Q1) changes state based on its previous state and the value of the second flip-flop (Q0).
Learn more about modulo on
https://brainly.com/question/30636701
#SPJ1

Be-16 a garbage dumping placard must be prominently posted on boats longer than what size?
Answers
Answer:
26 feet and longer boats that have garbage dumping placard must be prominently posted and the boats which are 40 feet and longer must have the written waste management plan.
Eigth people work in an office.they are paid hourly rates of £12 £15 £15 £14 £13 £14 £13 £13
Answers
Answer:
What about it?
Explanation:
A venture tube is used to measure the flow rate of a liquid in a pipe (liquid density is 800 kg/m3). The pipe has a diameter of 10 cm and the smallest diameter of the venture has a diameter of 4 cm. A manometer with a manometer fluid of mercury (specific weight of 133 kN/m3) is used to calculate the flow rate which is connected to the venture section such that one leg is far upstream and the second leg is at the minimum diameter of the venture tube. If the flow rate is 0.05 m3/s determine the elevation change in the manometer fluid.
a. 14.6 m
b. 9.28 m
c. 4.64 m
d. 2.32 m
Answers
Answer:
\(\triangle h=4.935m\)
Explanation:
From the question we are told that:
Liquid density \(\rho=800\)
Diameter of pipe \(d=4cm \approx 0.004m\)
Diameter of venture \(d=10cm \approx 0.010m\)
Specific weight of mercury P_mg \(133 kN/m^3\)
Flow rate \(r=0.05 m^3/s\)
Area A:
\(A_1=\frac{\pi}{4}0.1^2\\A_1=0.00785m^2\\A_2=\frac{\pi}{4}0.04^2\\A_2=0.001256m^2\\\)
Generally the Bernoulli's equation is mathematically given by
\(\frac{P_1}{\rho_1g}+\frac{V_1^2}{2g}=\frac{P_2}{\rho g}+\frac{V_2^2}{2g}\\\)
Where
\(V_1=\frac{r}{A_1} \\\\ &V_1=\frac{r}{A_2}\)
Therefore
\(P_1-P_2=\frac{Pr^2}{2}(\frac{A_1^2-A_2^2}{A_1^2A_2^2})\)
Generally the equation for pressure difference b/w manometer fluid is given as
\(P_1-P_2=(p_mg-pg)\triangle h\)
Therefore
\((p_mg-pg)\triangle h=\frac{Pr^2}{2}(\frac{A_1^2-A_2^2}{A_1^2A_2^2})\)
\(\triangle h=\frac{\frac{Pr^2}{2}(\frac{A_1^2-A_2^2}{A_1^2A_2^2})}{(p_mg-pg)}\)
\(\triangle h=\frac{\frac{(800)(0.05)^2}{2}(\frac{(0.1)^2-(0.4)^2}{(0.1)^2(0.04)^2})}{(1.33*10^3-800*9.81)}\)
\(\triangle h=4.935m\)
Therefore elevation change is mathematically given by
\(\triangle h=4.935m\)
does advanced auto parts install engine air filter
Answers
Answer:
You have to do it yourself.
Explanation:
A) Describe factor substitution with respect to building heights. Be sure to explain at least two reasons why office buildings (with extra benefits from proximity) tend to "build up" rather than build out. B) A key assumption for being able to model building heights is that building a taller building increases the cost per square foot (the second floor is more expensive to construct than the first floor, ect.) What sort of strange result would we predict if this was not the case? ("Building up" got cheaper per floor with each floor constructed)?
Answers
A) Factor substitution: replacing factors of production for desired outcomes, like building taller or expanding horizontally in limited urban land.
B) Cheaper per floor: no height limit incentive, leading to excessively tall structures and inefficient resource allocation.
A) Factor substitution refers to the decision-making process where factors of production, such as land and capital, are substituted for one another to achieve a desired outcome. In the context of building heights, it relates to the trade-off between constructing taller buildings (building up) versus expanding horizontally (building out).
One reason office buildings tend to "build up" is the limited availability of land in urban areas. Cities often have limited space for new construction, leading to higher land costs. By constructing taller buildings, developers can maximize the utilization of limited land resources and accommodate more office space within a smaller footprint.
Another reason is the benefit of proximity. In urban environments, being close to other businesses, amenities, transportation, and potential clients is advantageous. Building up allows office buildings to take advantage of centralized locations and create a concentration of economic activity. This proximity can lead to increased collaboration, networking opportunities, and accessibility, which are beneficial for businesses.
B) If the assumption that building a taller building increases the cost per square foot were not valid and instead "building up" became cheaper per floor with each floor constructed, a strange result would be observed. In such a scenario, there would be no economic incentive to limit the height of buildings. Developers would have a strong incentive to keep building higher and higher, as each additional floor would cost less per square foot compared to the previous ones.
This could lead to extremely tall buildings with a large number of floors, possibly surpassing the practical and engineering limits. The skyline of cities would be dominated by excessively tall structures, even if there was no corresponding increase in demand or economic justification. The lack of increasing costs per floor would disrupt the typical cost-benefit trade-off associated with building heights and result in an inefficient allocation of resources.
Learn more about urban development here: brainly.com/question/20063741
#SPJ11
when the national advisory committee for aeronautics (naca) measured the lift and drag on airfoil models in the 1930s and 1940s in their specially designed airfoil wind tunnel at the langley aeronautical laboratory, they made wings that spanned the entire test section, with the wing tips butted against the two sidewalls of the tunnel. this was done to ensure that the flow over each airfoil section of the wing was essentially two-dimensional (no wing-tip effects). such an arrangement prevented measuring the lift and drag with a force balance. instead, using a pitot tube, the naca obtained the drag by measuring the velocity distribution behind the wing in a plane perpendicular to the plane of the wing, i.e., the pitot tube, located a fixed distance downstream of the wing, traversed the height from the top to the bottom of the test section. using a control volume approach, derive a formula for the drag per unit span on the model as a function of the integral of the measured velocity distribution. for simplicity, assume incompressible flow.
Answers
The drag per unit span on the model can be calculated using a control volume approach as follows:
Drag per unit span = 1/2 * ρ * ∫VdzWhere ρ is the density of the fluid, V is the velocity of the fluid, and z is the distance from the top of the test section to the bottom. The integral can be calculated by summing up the velocity of the fluid at each point from the top to the bottom of the test section. This can be expressed as:
∫Vdz = ΣVzWhere Vz is the velocity of the fluid at each point in the test section.
Learn more about The National aeronautics advisory committee:
https://brainly.com/question/28800764
#SPJ4
Assume:
A = 1101 0011 1111 0110
B = 0110 1101 1101 1110
Write the series of operations necessary to pack A into B (and store the result in C), where the 8 lowest order bits of B are stored in the 8 highest order bits of C, and the 8 highest order bits of A are stored in the 8 lowest order bits of C.
Answers
To pack A into B and store the result in C, the following operations can be performed.
What is the explanation for the above response? Perform a logical shift right on A by 8 bits, which will result in 0000 0000 1101 0011.Perform a logical shift left on B by 8 bits, which will result in 1011 0110 1101 1110.Perform a logical OR operation between the results of step 1 and step 2, which will result in 1011 0110 1111 1110.Perform a logical shift left on A by 8 bits, which will result in 0000 0000 0000 0000.Perform a logical shift right on B by 8 bits, which will result in 0000 0000 0110 1101.Perform a logical OR operation between the results of step 4 and step 5, which will result in 0000 0000 0110 1101.Perform a logical OR operation between the results of step 3 and step 6, which will result in C = 1011 0110 1111 1110 0000 0000 0110 1101.Learn more about operations at:
https://brainly.com/question/9697567
#SPJ1
The system ________ can communicate with each other and adjust system operation to match the heat load and operating conditions.
Answers
The system automatically can communicate with each other and adjust system operation to match the heat load and operating conditions.
What is system operation?
System operation is the process of managing, controlling, and monitoring the operations of a computer system or network. It encompasses the planning and implementation of system operations, including the coordination of hardware, software, and communication components. System operation includes activities such as system configuration, system monitoring, performance tuning, system backup, system recovery, and system maintenance. System operation ensures that the system or network is secure, reliable, and available to users. It also involves troubleshooting and responding to incidents, analyzing system performance, and identifying areas for improvement. System operation is critical to the success of any organization, as it ensures the availability, reliability, and security of the system or network.
To learn more about system operation
https://brainly.com/question/29990235
#SPJ4
A pointer is spun on a fair wheel of chance having its periphery labeled Trom 0 to 100. (a) Whhat is the sample space for this experiment? (b)What is the probability that the pointer will stop between 20 and 35? (c) What is the probability that the wheel will stop on 58?
Answers
Answer:
A pointer is spun on a fair wheel of chance having its periphery labeled Trom 0 to 100. (a) Whhat is the sample space for this experiment? (b)What is the probability that the pointer will stop between 20 and 35? (c) What is the probability that the wheel will stop on 58?
Explanation:
thats all you said
Answer:
hii my name is RAGHAV what is your name
Explanation:
this question is which chapter
Assuming the non-pressurized boiling point of a 50-50 mix of coolant is 6°C higher than the boiling
point of water (100°C), and every one psi increase in pressure will raise the cooling system boiling
point by 17 °C. Calculate the coding system boiling point if a 15 psi pressure cap is used. How will
the value change if a 12 psi cap is used instead. If pure water is used rather than a 50-50 mix, then
how is the boiling point changed? What about the freezing point?
Answers
Answer:
To calculate the coolant boiling point with a 15 psi pressure cap, we need to consider the base boiling point of water, the increase in boiling point due to the 50-50 mix of coolant, and the increase in boiling point per psi of pressure.
Base Boiling Point of Water: 100°C
Increase in Boiling Point due to Coolant Mix: 6°C
Increase in Boiling Point per psi: 17°C
Calculation for a 15 psi pressure cap:
Base Boiling Point + Increase due to Coolant + (Pressure Increase × Increase per psi)
= 100°C + 6°C + (15 psi × 17°C/psi)
= 100°C + 6°C + 255°C
= 361°C
Therefore, with a 15 psi pressure cap, the cooling system boiling point would be 361°C.
Now let's calculate the boiling point with a 12 psi pressure cap:
Base Boiling Point + Increase due to Coolant + (Pressure Increase × Increase per psi)
= 100°C + 6°C + (12 psi × 17°C/psi)
= 100°C + 6°C + 204°C
= 310°C
With a 12 psi pressure cap, the cooling system boiling point would be 310°C.
If pure water is used instead of a 50-50 mix of coolant, the boiling point would remain at 100°C since there would be no additional increase in boiling point due to the coolant mix.
As for the freezing point, the presence of the coolant mix or the pressure cap does not directly affect the freezing point of water. The freezing point of water is generally 0°C, regardless of the coolant mix or pressure conditions.
Explanation: