A uniformly charged disk has radius 2.50 cm and carries a total
charge of 5.0×10−12 C
A-
Find the magnitude of the electric field on the xx-axis at xx =
20.0 cmcm
Express your answer in newtons per
Answers
A uniformly charged disk has radius 2.50 cm and carries a total charge of 5.0×10−12 C .The magnitude of the electric field on the xx-axis at xx = 20.0 cm is approximately 1.44×10³ N/C.
To calculate the magnitude of the electric field on the xx-axis at xx = 20.0 cm, we can use the formula for the electric field created by a uniformly charged disk. The electric field at a point on the xx-axis due to a uniformly charged disk is given by:
E = (σ / (2ε₀)) * (1 - (z / \(\sqrt{(z^2+ R^2)}\)))
Where:
E is the electric field magnitude,
σ is the surface charge density of the disk,
ε₀ is the permittivity of free space,
z is the distance from the center of the disk to the point on the xx-axis,
R is the radius of the disk.
Given:
σ = 5.0×10⁻¹² C/A,
R = 2.50 cm = 0.025 m,
z = 20.0 cm = 0.20 m.
First, we need to calculate the surface charge density σ. The formula for surface charge density is:
σ = Q / A
Where Q is the total charge of the disk and A is the area of the disk. The area of the disk can be calculated using the formula:
A = πR²
Substituting the given values, we have:
A = π(0.025 m)² = π(6.25×10⁻⁴) m² ≈ 1.96×10⁻³ m²
Now, we can calculate the surface charge density:
σ = (5.0×10⁻¹² C) / (1.96×10⁻³ m²) ≈ 2.55×10⁻⁹ C/m²
Next, we can calculate the electric field magnitude using the formula mentioned earlier:
E = (σ / (2ε₀)) * (1 - (z / \(\sqrt{(z^2+ R^2)}\)))
Substituting the given values, we have:
E = ((2.55×10⁻⁹ C/m²) / (2 * 8.85×10⁻¹² C²/(N·m²))) * (1 - (0.20 m / (\(\sqrt{(0.20 m)^2 + (0.025 m)^2)}\)
E = (2.55×10⁻⁹ / (2 * 8.85×10⁻¹²)) * (1 - (0.20 / \(\sqrt{(0.04 + 0.000625)}\)))
E = (2.55×10⁻⁹ / (2 * 8.85×10⁻¹²)) * (1 - (0.20 / \(\sqrt{(0.040625)}\)))
E = (2.55×10⁻⁹ / (2 * 8.85×10⁻¹²)) * (1 - (0.20 / 0.2016))
E ≈ (2.55×10⁻⁹ / 1.77×10⁻¹²) * (1 - 0.9911)
E ≈ 1.44×10³ N/C
For more such information on: magnitude
https://brainly.com/question/30337362
#SPJ8
Related Questions
Two blocks are arranged at the ends of a massless cord over a frictionless massless pulley as
shown in the figure. Assume the system starts
from rest. When the masses have moved a distance of 0.317 m, their speed is 1.33 m/s.
The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s
2
What is the coefficient of friction between
m2 and the table?
What is the magnitude of the tension in the
cord?
Answer in units of N.

Answers
Answer:
The coefficient of friction between m₂ and the table is approximately 0.2703
The magnitude of the tension in cable is 28.737 N
Explanation:
The given parameters are;
The mass of the block on the table, m₂ = 5.8 kg
The mass of the hanging block, m₁ = 4.5 kg
The distance in which the block has moved = 0.317 m
The speed after the block moves = 1.33 m/s
The acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s²
The coefficient of friction between m₂ and the table = μ
The acceleration, a, of the blocks is given from the formula of speed, v, of a body at a given distance, s, from rest as follows;
v² = 2 × a × s
Where;
v = 1.33 m/s
s = 0.317 m
Substituting the values gives;
1.33² = 2 × a × 0.317
a = 1.33²/(2 × 0.317) ≈ 2.79
The acceleration, a ≈ 2.79 m/s²
Therefore, we have the force acting on the system given as follows;
Weight of m₁ - Frictional force of m₂ = (m₁ + m₂) × a
4.5 × 9.8 - 5.8 × 9.8 × μ = (4.5 + 5.8) × 2.79
4.5 × 9.8 - 5.8 × 9.8 × μ = 28.737 N
(4.5 × 9.8)N - 28.737 N = 5.8 × 9.8 × μ
44.1 N - 28.737 N =56.84 N × μ
15.363 N = 56.84 N × μ
μ = 15.363 N/(56.84 N) ≈ 0.2703
The coefficient of friction between m₂ and the table = μ ≈ 0.2703
The coefficient of friction between m₂ and the table ≈ 0.2703
The magnitude of the tension in cable = (m₁ + m₂) × a = 28.737 N.
The magnitude of the tension in cable = 28.737 N
What physical quantity is represented by the slope of a potential energy versus velocity graph
Answers
The slope of the line in the velocity versus time plot is equal to the acceleration of the object.
What is velocity?Velocity refers to the directional velocity of a moving object as an indicator of the rate of change of position observed from a particular frame of reference and measured by a particular time standard.Velocity defines the direction of movement of a body or object. Velocity is primarily a scalar quantity. Velocity is basically a vector quantity. Rate of change of distance. Velocity is the Rate of change of displacement.Velocity is a vector representation of the displacement an object or particle experiences with respect to time. The standard unit for velocity magnitude (also called velocity) is meters per second (m/s). Alternatively, centimeters per second (cm/s) can be used to express velocity magnitude.To learn more about velocity from the given link :
https://brainly.com/question/18084516
#SPJ1
How much force is needed to keep the bowling ball moving towards the pins once it has
left the man's hand?
Please help me!
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
The amount of force needed needs to be greater than all the forces acting in the opposite direction that the bowling ball was thrown. This includes air resistance, floor friction, gravity, and any other force involved. As long as the force acting on the bowling ball that is causing it to go in the direction of the pins is slightly greater than the opposite acting forces then it will continue in that direction. Since no values are provided we cannot calculate the actual precise value of force needed.
What would be the final velocity, in m/s, if a disk of the same mass and radius as the hoop rolled down the hill?.
Answers
The final velocity will be \(\rm V= \sqrt{\frac{4gh}{3} }\ m/sec\). Speed is a scalar quantity. It is a time-based component. Its unit is m/sec.
What is velocity?The change of distance with respect to time is defined as speed.
From the law of conservation of energy:
\(\rm KE_i + PE_i = KE_f+PE_f \\\\ 0+mgh = \frac{1}{2} mV^2 +\frac{1}{2} I\omega^2\)
The moment of inertia of the disc;
\(\rm I= mr^2\)
It can also be found as;
\(\rm I = \frac{V}{r} \\\\\)
Put the obtained values;
\(mgh = \frac{1}{2} mv^2+\frac{1}{2} mv^2=mv^2\\\\ mgh = mv^2 \\\\ v=\sqrt{gh}\)
if a disk of the same mass and radius as the hoop rolled down the hill;
\(mgh= \frac{1}{2} M+\frac{mr^2}{2r^2} V^2 \\\\ gh = \frac{3}{4} V^2 \\\\ V= \sqrt{\frac{4gh}{3} }\ m/sec\)
Hence the final velocity will be \(\rm V= \sqrt{\frac{4gh}{3} }\ m/sec\).
To learn more about the velocity refer to the link;
https://brainly.com/question/862972
#SPJ1
BRAINLIEST! I NEED HELP ASAP!
The ratio of xi to xo for a certain mirror is 2.5. Which is true of an image produced by this mirror?
It is 2.5 times larger and virtual.
It is 2.5 times larger and real.
It is 2.5 times smaller and virtual.
It is 2.5 times larger and real.
Answers
The true of an image produced by this mirror will be 2.5 times smaller and virtual. Option C is correct.
What is the image?When light beams from an object reflect off a mirror, they intersect with the picture of that thing called an image. Real and virtual images are the two sorts of images.
The ratio of xi to xo for a certain mirror is 2.5;
\(\rm \frac{x_i}{x_0} =2.5 \\\ x_i=2.5 x_0\)
Where,
\(\rm x_0\) is the true of an image produced by this mirror.
The true of an image produced by this mirror will be 2.5 times smaller and virtual.
Hence,option C is correct.
To learn more about the image refer to the link;
https://brainly.com/question/25029470
#SPJ1
calculate the number of kilojoules to warm 125 g of iron from 23.5 to 78.0 degrees celsius.
Answers
The amount of energy required to warm 125 g of iron from 23.5 to 78.0 degrees Celsius is approximately 192.7 kilojoules.
To calculate the amount of energy required to warm a substance, we can use the formula:
Q = m * c * ΔT
where Q represents the energy (in joules), m is the mass of the substance (in grams), c is the specific heat capacity of the substance (in joules/gram·degree Celsius), and ΔT is the change in temperature (in degrees Celsius).
The specific heat capacity of iron is typically around 0.45 joules/gram·degree Celsius. Converting the mass of iron to kilograms (125 g = 0.125 kg) and the temperature change to Kelvin (ΔT = 78.0 - 23.5 = 54.5 °C = 54.5 K), we can plug the values into the formula:
Q = 0.125 kg * 0.45 J/g°C * 54.5 K = 3.04125 joules
Converting joules to kilojoules (1 kilojoule = 1000 joules), we get:
\(Q = \frac{3.04125 joules }{ 1000}\\ Q= 0.00304 kilojoules\)
Therefore, the amount of energy required to warm 125 g of iron from 23.5 to 78.0 degrees Celsius is approximately 0.00304 kilojoules or approximately 192.7 kilojoules when rounded to three significant figures.
Learn more about specific heat capacity Refer: https://brainly.com/question/29766819
#SPJ11
If Argon's melting point is -309 degrees then what is its freezing point?
Answers
The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which the substance changes its phase from solid to liquid.
The freezing point is the temperature at which the substance changes its phase from liquid to solid.
The melting point of a substance is the same as the freezing point. That is when the temperature of the substance in the liquid form is increased continuously, the temperature at which the substance turns into a solid is equal to the temperature at which the substance will turn into liquid from solid if the temperature is decreased continuously, from a higher temperature.
A hailstone propelled by turbulent convection within a cloud reaches an elevation within a cloud where the air temperature is -16.9 degrees C; if this location is 4111 meters above the base of the cloud and the surface dew point temperature is 12 degrees C, what is the relative humidity at the surface?
Answers
The relative humidity at the surface is 63.55%. Relative Humidity (RH) refers to the measure of the degree of water vapor present in the atmosphere as compared to the maximum amount of water vapor required for saturation at that temperature.
In order to determine the relative humidity at the surface of the given problem, we will first need to determine the saturation vapor pressure at
-16.9°C.1.
Using the Tetens formula, we get;
es = \(6.11 × 10 ^ ((7.5T)/(T + 237.3))\)
Here,
T = -\(16.9°Ces = 6.11 × 10 ^ ((7.5(-16.9))/( -16.9 + 237.3))= 1.07 kPa2\).
Using the Clausius-Clapeyron relation, we get;
e = \(es × e^[-L/R (1/T - 1/T0)]\)
Here, L is the latent heat of vaporization of
water = \(2.45 × 10 ^ 6 J/kg\)
R is the specific gas constant for water
vapor = 461.5 J/kg K.1/T
is the Kelvin temperature at which es occurs,
i.e. (-16.9 + 273) = 256 K.1/T0
is the Kelvin temperature of the surface dew point temperature,
i.e. \((12 + 273) = 285 K.e = 1.07 kPa × e^[-(2.45 × 10 ^ 6 / 461.5)(1/256 - 1/285)]= 0.68 kPa3.\)
The relative humidity at the surface is given by;
RH = (e/es) × 100RH = (0.68/1.07) × 100= 63.55%
Therefore, the relative humidity at the surface of the given problem is 63.55%.
For more question humidity
https://brainly.com/question/17889594
#SPJ8
an infinitely long circular cylinder carries a uniform magnetization m parallel to its axis. find the magnetic field (due to m) inside and outside the cylinder.
Answers
Ampere's law used to find bound current density. Symmetry considered. Magnetic field outside cylinder = µ₀M/2 + µ₀Mr²/2R³.
To find the magnetic field due to the uniform magnetization M inside and outside an infinitely long circular cylinder, follow these steps:
1: Apply Ampere's law
Ampere's law states that the integral of the magnetic field B around a closed loop is equal to the product of the permeability of free space (µ₀) and the current enclosed by the loop.
2: Determine the bound current density
For a uniformly magnetized cylinder, the bound current density Jb can be found by taking the cross product of M and the normal vector n to the surface: \(Jb = M × n\).
3: Consider the symmetry of the problem
Since the cylinder is infinitely long and uniformly magnetized along its axis, the magnetic field will be cylindrically symmetric. This means that the magnetic field will only have an azimuthal component (B_phi), and it will not depend on the azimuthal angle (phi).
4: Calculate the magnetic field inside the cylinder
Inside the cylinder, there is no bound current enclosed by the Amperian loop, so the magnetic field B_inside is zero.
5: Calculate the magnetic field outside the cylinder
Outside the cylinder, the bound current enclosed by the Amperian loop is given by the product of the magnetization M and the cylinder's cross-sectional area (A = πR², where R is the cylinder's radius).
Thus, the magnetic field B_outside can be calculated using Ampere's law:
\(B_{outside} * 2πr = µ₀ * M * πR²,\)
where r is the distance from the cylinder's axis.
Step 6: Solve for the magnetic field outside the cylinder
\(B_{outside}= (µ₀ * M * R²) / (2 * r),\)
where R is the cylinder's radius and r is the distance from the cylinder's axis.
In conclusion, the magnetic field due to the uniform magnetization M inside the infinitely long circular cylinder is zero (B_inside = 0), and the magnetic field outside the cylinder is given by \(B_{outside} = (µ₀ * M * R²) / (2 * r).\).
Read about magnetic field under uniform magnetization: https://brainly.com/question/26257705
#SPJ11
Define the following:
Variable
Data
Control
Technology
Hypothesis
Physical Science
Experiments
Answers
Answer:
Variable- not consistent or having a fixed pattern; liable to change
Data- facts and statistics collected together for reference or analysis
Control- a group or individual used as a standard of comparison for checking the results of a survey or experiment
Technology- the application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes, especially in industry
Hypothesis- a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation
Physical Science- the sciences concerned with the study of inanimate natural objects, including physics, chemistry, astronomy, and related subjects
Experiments- a scientific procedure to make a discovery, test a hypothesis, or demonstrate a known fact
Explanation:
9. A speedboat engine exerts 90000 W of power in moving the boat through the water. The velocity of the boat is 1P = 5 m/s. What force does the engine apply to do this?
P = F x V
Answers
Answer:
it g hope it helps you out
If two runners cover the same distance in different amounts of time, how do there speeds compare
Answers
Calculate the potential difference across a 25-Ohm. resistor if a 0.3-A current is flowing through it.
Answers
Answer:
I=0.3 A
R=25 Ohm
V=?
V=IR
0.3X25=7.5
Answer:
7.5 V
Explanation:
current × resistance = voltage
A reaction has a standard free‑energy change of −12.50 kJ mol−1(−2.988 kcal mol−1). Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction at 25 °C.
Keeq=
Answers
The equilibrium constant (Keeq) for a reaction at 25 °C can be calculated using the equation Keeq = e^(−ΔG°/RT)
How can the equilibrium constant (Keeq) be calculated from the standard free-energy change (ΔG°)?The equilibrium constant (Keeq) for a chemical reaction can be calculated using the equation Keeq = e^(−ΔG°/RT), where ΔG° represents the standard free-energy change, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
In this case, the given standard free-energy change is −12.50 kJ mol−1 (−2.988 kcal mol−1). To calculate the equilibrium constant at 25 °C, we need to convert the temperature to Kelvin by adding 273.15 (25 °C + 273.15 = 298.15 K). Then, we substitute the values into the equation to find the equilibrium constant.
Keeq = e^(−12.50 kJ mol−1 / (8.314 J K−1 mol−1 × 298.15 K))
By evaluating the expression, we can determine the equilibrium constant (Keeq) for the given reaction at 25 °C.
The relationship between standard free-energy change and equilibrium constant in chemical reactions to understand the thermodynamic aspects of chemical equilibria
Learn more about equilibrium
brainly.com/question/30694482
#SPJ11
How can the strength of an electromagnet be increased?
Answers
Answer:
You can make an electromagnet stronger by doing these things: wrapping the coil around a piece of iron (such as an iron nail) adding more turns to the coil. increasing the current flowing through the coil.
Explanation:
how do you balance
___Ca + __O2 → ___CaO
Answers
Answer:
2Ca+ O2 ------> 2CaO
mark me as brainiest
How do conditions in the wild differ from conditions in captivity?
Answers
The wild offers more natural structures and temperatures that keep animals adapted to their surroundings. However, in captivity animals tend to differ from their wild counterparts. For one thing, the wild cultivates an animal's hunting skills but, when or if they are releasing into the wild, they do not know what to do whereas they have been sheltered their entire life. They don't know how to find natural structures to keep warm in, what places are safe or even survival strategies. The conditions in the wild teach an animal to survive while the conditions from man-made structures just give them an easy survival.
Hope this helps and have a nice day.
-R3TR0 Z3R0
How many significant figures below?
3.7 x 10^-3 L
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D.4
E. 0
Answers
Answer:C.3
Explanation:
a milling machine processes a part with t0=15 mins and sigma0=3mins. the mean time to failure 750 mins and the mean time to repair is 200 muns. the coefficient of varuation for the repair time is 1.2. the product of the milling machine is feeding the downstream turning machine. the turning maching had the same t0 and sigma0, but the mean time to failure and mean time to replair are 110 muns and 38 muns. (cv=1.2).Assuming the arrival to the milling machine is 1.2 parts/hrwith an arrival Cv =1. find the cycle time of the entire line.
Answers
The cycle time of the entire line is 30.00528 minutes per part.
To calculate the cycle time of the entire line, we need to consider the processing times, failures, and repairs of both the milling machine and the turning machine.
For the milling machine:
Mean processing time (t0) = 15 mins
Standard deviation of processing time (sigma0) = 3 mins
Mean time to failure (MTTF) = 750 mins
Mean time to repair (MTTR) = 200 mins
For the turning machine:
Mean processing time (t0) = 15 mins
Standard deviation of processing time (sigma0) = 3 mins
Mean time to failure (MTTF) = 110 mins
Mean time to repair (MTTR) = 38 mins
We also know that the arrival rate to the milling machine is 1.2 parts/hr, with a coefficient of variation (CV) of 1.
To calculate the cycle time, we can use the following formula:
Cycle time = Processing time + Failure time + Repair time
Processing time:
The processing time is the sum of the mean processing times of the milling machine and the turning machine:
Processing time = t0 (milling machine) + t0 (turning machine) = 15 mins + 15 mins = 30 mins
Failure time:
The failure time is the inverse of the MTTF, considering the arrival rate:
Failure time = 1 / (MTTF * Arrival rate) = 1 / (750 mins * (1.2 parts/60 mins)) = 0.00111 parts/min
Repair time:
The repair time is the inverse of the MTTR, considering the coefficient of variation (CV):
Repair time = 1 / (MTTR * CV) = 1 / (200 mins * 1.2) = 0.00417 parts/min
Cycle time:
Cycle time = Processing time + Failure time + Repair time = 30 mins + 0.00111 parts/min + 0.00417 parts/min
to know more about Cycle time, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/31215630
#SPJ11
a sled is given a push across a horizontal surface. the sled has a mass m, the push gives it an initial speed of 3.50 m/s, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled and the surface is 0.135. (a) use energy considerations to find the distance (in m) the sled moves before it stops. m (b) what if? determine the stopping distance (in m) for the sled if its initial speed is doubled to 7.00 m/s.
Answers
stopping distance = 4.52m
stopping distance when speed is doubled = 18.09m
The stopping distance of a sled depends on several factors, including its initial speed, the surface on which it is sliding,
kinetic friction and the resistance provided by the sled's runners or skis.
The stopping distance of the sled can be found using the formula:
stopping distance = (initial speed^2)/(2*coefficient of kinetic friction*acceleration due to gravity)
(a) Plugging in the given values, we get:
stopping distance = (3.50^2)/(2*0.135*9.81) = 4.52 m
Therefore, the sled moves 4.52 meters before it comes to a complete stop.
(b) If the initial speed is doubled to 7.00 m/s, the stopping distance can be calculated as:
stopping distance = (7.00^2)/(2*0.135*9.81) = 18.09 m
Therefore, the stopping distance for the sled would be 18.09 meters if its initial speed is doubled.
This shows that the stopping distance increases significantly as the initial speed increases.
To learn more about Kinetic friction, visit: https://brainly.com/question/30886698
#SPJ11
A solenoid that is 105 cm long has a radius of 2.83 cm and a winding of 1090 turns; it carries a current of 4.40 A. Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field inside the solenoid.
Answers
The magnetic field inside the solenoid has a magnitude of 5.74*10^-3 T. A 105 cm long solenoid with 1090 turns of winding and a 2.83 cm radius.
The greatest size and direction of an object are referred to as its magnitude. Both vector and scalar values use magnitude as a common factor. We know that scalar quantities are those that have magnitude and nothing else by definition. An electric charge, an electric current, and magnetic materials are all affected magnetically by a magnetic field, which is a vector field. Is called as magnetic field.
Given: length l = 1,05 m,
radius r = 2,83*10-2 m,
number of revolutions N = 1090,
current I = 4,
B = 4*3.14*10^-7*1090*4.4/1.05
B = 5.74*10^-3 T is the magnetic field inside the solenoid.
Learn more about magnetic field here
https://brainly.com/question/23096032
#SPJ4
consider the 6 stages listed below for the lives of a human being and a star. describe what a 1 solar mass star does in each stage of its existence:
Answers
Note that this is a trick question. It is true that the mass of a star affects its life cycle but all stars must go through the stages listed below. Note that the larger the solar mass of a star, the shorter its life cycle. Hence, in each of the stages given here is what will occur:
Prenatal Stage
Birth Stage
The star is able to sustain itself by making its own energy by nuclear fusionAdolescence/Adulthood
The nuclear fusion continues and maintains equilibriumNote that 90% of the stars life is in the main sequenceMiddle age
The sun is in middle age, in the middle of main sequence cycleIt reaches it's prime of lifeOld age
Nuclear fusion of hydrogen to helium ends in the core and the star goes into another fusion stage of helium to carbonIt then swells into a red giant.Death
All fusion processes stop as the outer part of the star is lost Turns in to a planetary nebula and the hot, inert core begins to cool offWhat is the Solar Mass of a Star?
The solar mass is a unit of mass used to measure the masses of objects in the solar system, including stars. It is defined as the mass of the Sun, which is approximately 1.989 x 10³⁰ kilograms, or about 333,000 times the mass of the Earth.
Hence, since the earth's sun is 1.989 x 1010³⁰ kilograms, a star described as having 1 solar mass is simply a star equivalent of the Earth's sun.
Note however that the solar mass is often used as a standard unit of mass for comparing the masses of objects in the universe, such as planets, asteroids, and stars.
Learn more about solar mass:
https://brainly.com/question/28043778
#SPJ1
Full Question:
Compare the following stages in the lives of a human being and a star: prenatal, birth, adolescence/ adulthood, middle age, old age, and death. What does a star with a solar mass of 1 solar mass do in each of these stages?
The main reason a person weighs less at the equator than at the poles involves theA) spin of the Earth.B) influence of the Sun, Moon, and all the planets.C) law of action and reaction
Answers
The main reason a person weighs less at the equator than at the poles is due to the Earth's rotation, which causes a centrifugal force at the equator due to law of planet motion.
This centrifugal force is caused by the Earth's rotation around its axis, which is faster at the equator than at the poles. As a result, objects at the equator are moving faster and experience a weaker gravitational pull towards the Earth's center compared to objects at the poles due to law of planet motion.
The difference in gravitational force between the equator and the poles is relatively small, around 0.5%, but it is still measurable. The gravitational force at the poles is stronger because the Earth's rotation is slower there, so there is less centrifugal force pushing objects away from the Earth's center.
The influence of the Sun, Moon, and planets on a person's weight is much smaller than the effect of the Earth's rotation. These celestial bodies do have an effect on the Earth's gravitational field, but their impact is relatively minor compared to the Earth's rotation.
Learn more about planet here:
https://brainly.com/question/13851553
#SPJ4
A horse pulls a wagon with a force of 200 N for a distance of 80 m. How much work
does the horse do?
Answers
Answer:
w=f×s
w = 16000 J, hope this helps
An object with a mass of 20 kg has a net force of 80 N acting on it. What is the acceleration of the object?
Answers
Answer:
the answer is 4m/ s²
hope this helps love!! <3
Through the process of blank
, old, dense crust is pushed toward a deep-ocean blank
. There, it sinks under lighter crust. It returns to molten rock, becoming part of the
again.
Answers
Answer:
Subduction, Trench, Mantle
Explanation:
Answer: subduction, trench, and mantle
Explanation:

This doesn’t make sense, there is no angle so I can’t use Fnet=mgcos(theta) and can’t find acceleration in a=mgsin(theta).
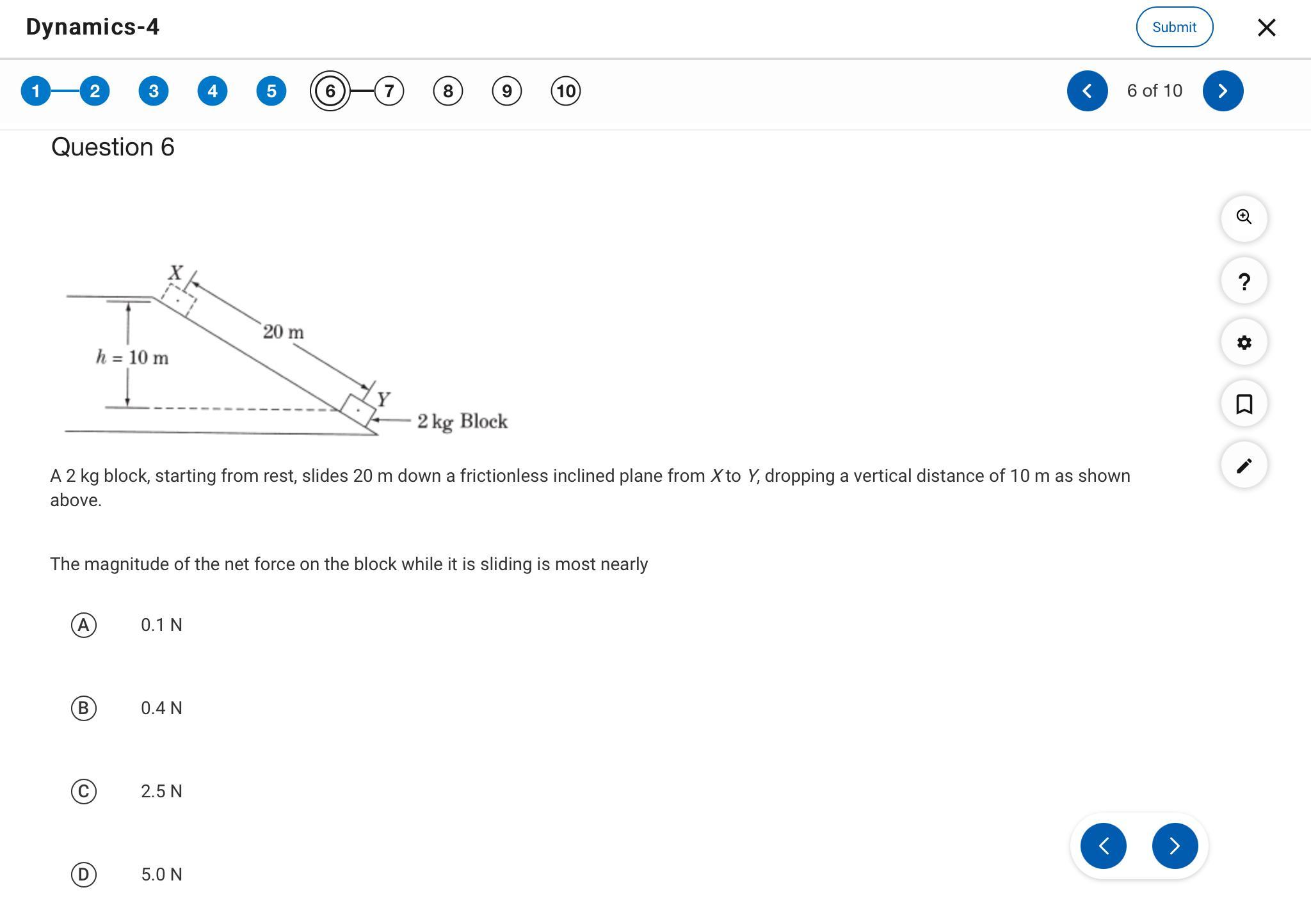
Answers
The magnitude of the net force on the block while it is sliding is 9.8 N.
What is the angle of inclination of the plane?
The angle of inclination of the plane is calculated by applying the principle of trigonometry ratio.
Considering the vertical height (10 m) and length of the incline (20 m);
sin θ = 10 m / 20 m
sin θ = 1/2
sin θ = 0.5
θ = arc sin(0.5)
θ = 30⁰
The magnitude of the net force on the block while it is sliding is calculated as follows;
F(║) = F(net) = mg sinθ
where;
m is mass of the blockg is acceleration due to gravityF(║) implies parallel force, since there is no friction on the inclineF(net) = (2 x 9.8) x sin(30)
F(net) = 9.8 N
Thus, the net force on the block is the parallel component of the weight of the block.
Learn more about net force here: https://brainly.com/question/14361879
#SPJ1
A girl, standing 150m in front of a tall building, fires a shot using a starting pistol. A boy, standing
350 m from the girl
, hears two bangs 1s apart.
June 200
my
PATI
gid
boy
47
150 m
350 m
From this information, what is the speed of sound in air?
A 300 m/s
B 350 m/s
D 650 m/s
C 500 m/s
Answers
Answer:
I believe 650 or C
Explanation:
plz mark brainnlyist :)
2. A ball with a mass of 5. 0 g is moving at a speed of 2. 0 m/s. Would doubling the mass or doubling the speed have a greater effect on the kinetic energy of the ball? Explain.
Answers
Answer:
yes
Explanation:
Answer:Doubling the mass or doubling the speed will have a greater effect on the kinetic energy of the ball. Because doubling the mass would have a greater effect on the kinetic energy of the ball because you are dividing the mass by velocity.
Explanation:
7. Our state of mind affects how we observe our surroundings. What
mental state is the best for observing?
I
a) happy
c) nervous
b) relaxed d) excited