Answers
Answer:
The fringe spacing on a distant diffraction screen will increase.
Explanation:
Blue light has a shorter wavelength than red light, so, changing from blue to red light is basically increasing the wavelength of the light involved in the experiment.
In the double slit experiment, the fringe spacing on a diffraction screen is calculated from the equation below
ω = zλ/d
where ω is the fringe spacing
z is the distance of the slit to the screen
λ is the wavelength of the light used
d is separation or distance between the slits
From the equation, one can see that if other parameters are held constant, increasing the wavelength will lead to an increase in the spacing between the fringes, and hence, changing the light from blue to red light will increase the fringe spacing.
Related Questions
What did Kelper discover?
Answers
not sure if this is what you want but hope this helps!!

which of the following is an example of a physical change of matter
Answers
An example of a physical change of matter is (c) Melting ice.
Explanation: Melting ice is an example of a physical change of matter. When ice melts, it undergoes a change in state from a solid to a liquid, but its chemical composition remains the same. The water molecules in ice rearrange themselves to form liquid water, but no new substances are formed. This change can be reversed by cooling the liquid water to below its freezing point, causing it to solidify back into ice. Physical changes do not involve a change in the chemical identity of the substance, only a change in its physical properties, such as shape, size, or state.
In contrast, options a) Burning wood, b) Digesting food, and d) Rusting iron involve chemical changes. Burning wood involves a chemical reaction where wood reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water vapor, and ash. Digesting food involves the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones through chemical reactions in the body. Rusting iron is a chemical reaction where iron reacts with oxygen and moisture in the air to form iron oxide.
for more such questions on matter
https://brainly.com/question/3998772
#SPJ11
Note: The complete question is:
Which of the following is an example of a physical change of matter?
a) Burning wood
b) Digesting food
c) Melting ice
d) Rusting iron
the ratio of force between two charges in vacuum to that the force between two same charges when a medium is placed between them
Answers
The ratio of the force between two charges in a vacuum to the force between two charges when a medium is placed between them is called relative permittivity
What should you know about relative permittivity?Relative permittivity has another term dielectric constant. The dielectric constant measures how well a material can store electrical energy in an electric field. Its equation is ε = ε₀ / εᵣ
ε₀ is the vacuum permittivity, and εᵣ is the relative permittivity or dielectric constant of the medium.
The dielectric constant is different depending on the material.
Find more exercises on relative permittivity;
https://brainly.com/question/30258261
#SPJ1
A long straight wire carrying a current of 3A flowing in a direction parallel to the unit vector 1 (i+j+ k) is placed in a √√3 --↑ this is the a magnetic field of (0.75i + 0.4k)T. What is the magnetic force per unit length of the wire? A. (0.69i-0.61j - 1.3k )N/m.. B. (0.39i-0.4j-2.3 k )N/m C.(0.49i-0.51j - 1.37k )N/m D. (0.59-0.71j-0.13k )N/m
Answers
The magnetic force per unit length of the wire is (C) (0.49i - 0.51j - 1.37k) N/m.
To calculate the magnetic force per unit length of the wire, we can use the formula:
F = I * (L x B),
where F is the force, I is the current, L is the length vector of the wire, and B is the magnetic field.
Given:
Current, I = 3A
Length vector, L = √√3 * (i + j + k)
Magnetic field, B = 0.75i + 0.4k
Let's calculate the cross product of L and B:
L x B = | i j k |
|√√3 √√3 √√3|
|0.75 0 0.4|
To evaluate this cross product, we calculate the determinants:
(i) component: (√√3 * 0 - √√3 * 0.4) = -0.4√√3
(j) component: (-√√3 * 0.75 - √√3 * 0) = -0.75√√3
(k) component: (√√3 * 0.75 - √√3 * 0) = 0.75√√3
Now, multiply the cross product by the current:
F = 3A * (-0.4√√3i - 0.75√√3j + 0.75√√3k)
Simplifying this expression gives:
F = (-1.2√√3i - 2.25√√3j + 2.25√√3k) N
Therefore, the magnetic force per unit length of the wire is approximately (-1.2√√3i - 2.25√√3j + 2.25√√3k) N/m.
Comparing the given answer options, the closest match is C. (0.49i - 0.51j - 1.37k) N/m.
for more such questions on force
https://brainly.com/question/12785175
#SPJ11
What is the “time constant” for a capacitor, and why is it important?
Answers
We know that in a RC circuit the voltage in the capacitor when is charging is given by:
\(V_C(t)=V_0(1-e^{-\frac{t}{RC}})\)when this is happening the voltage in the resistor is given by:
\(V_R(t)=V_0e^{-\frac{t}{RC}}\)In both equations V0 denotes the voltage given by the source, R is the resistance of the resistor and C is the capacitance of the capacitor.
We notice that in both expressions the product RC appear, this product is what we call the time constant of the capacitor; and it is important since it determines the time intervals in which the voltage, charges and currents chage in a RC circuit. This means that while the capacitor is charging or discharging the variables mentioned will always have the time constant in their expressions.
Julianna walks 10 meters East, 15 meters South and 20 meters North. What is her resultant displacement?
Answers
Julianna's resultant displacement when she walks 10 meters East, and 15 meters South and 20 meters North is 11.18m North-East.
What is displacement?displacement can be defined as distance in a specified direction.
To calculate the resultant displacement of the Julianna, we use the formula below.
Formula:
R = √[D²+(d-d')²]............ Equation 1Where:
R = Julianna's resultant displacementD = Julianna's First displacementd' =Julianna's Second displacementd = Julianna's Third displacementFrom the question,
Given:
D = 10 m Eastd = 20 m Northd' = 15 m SouthSubstitute these values into equation 1
R = √[10²+(20-15)²]R = √(100+5²)R = √125R = 11.18 m North-EastHence, Julianna's resultant displacement is 11.18 m North-East.
Learn more about displacement here: https://brainly.com/question/28370322
#SPJ1
Researchers studying the possible effects of “heading” a soccer ball--hitting it with the head--use a force plate to measure the interaction force between a ball and a hard surface. (Figure 1) shows smoothed data of the force when a 430 g
soccer ball is fired horizontally at the force plate with a speed of 15 m/s
With what speed does the ball rebound from the plate?

Answers
The speed of the ball rebounding from the plate is approximately 13.2 m/s.
According to the graph, the greatest force exerted by the football on the force plate during impact is around 1900 N. The ball comes to a halt on the force plate before rebounding.
The kinetic energy of the ball before impact equals the kinetic energy of the ball after the rebound, according to the law of conservation of energy.
The speed of the ball rebounding can be calculated using the formula:
(1/2)mv²= (1/2)mv_0²
where m is the mass of the ball (0.43 kg), v is the speed of the ball rebounding, and v_0 is the initial speed of the ball (15 m/s).
Solving for v, we get:
v = sqrt(v_0² - (2F/m))
where F is the maximum force exerted on the force plate (1900 N).
Plugging in the values, we get:
v = sqrt(15² - (2*1900/0.43)) ≈ 13.2 m/s
Therefore, the speed of the ball rebounding from the plate is approximately 13.2 m/s.
learn more about speed here
https://brainly.com/question/13943409
#SPJ1
Which statement describes a primary difference between an electromagnetic wave and a mechanical wave
Answers
The primary difference is that electromagnetic waves can propagate through a vacuum or empty space, while mechanical waves require a physical medium to transmit energy.
Difference between an Electromagnet and Mechanical WaveA primary difference between an electromagnetic wave and a mechanical wave is the medium through which they propagate.
Electromagnetic waves can propagate through a vacuum or empty space without requiring a material medium. They are generated by the oscillation and interaction of electric and magnetic fields.
Examples of electromagnetic waves include radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. These waves can travel through space, air, or other materials, as they do not rely on physical particles to transmit energy.
On the other hand, mechanical waves require a physical medium to propagate. They are disturbances that travel through a material medium, transferring energy from one location to another. Mechanical waves rely on the interaction and displacement of particles within the medium to transmit energy.
Examples of mechanical waves include sound waves, water waves, seismic waves, and waves on a string. These waves cannot travel through a vacuum as they depend on the physical presence and interaction of particles within the medium.
In summary, the primary difference is that electromagnetic waves can propagate through a vacuum or empty space, while mechanical waves require a physical medium to transmit energy.
Learn more about wave here:
https://brainly.com/question/15663649
#SPJ1
Which of the following is a good analogy for quantization using gravitational energy?A. A rampB. A set of stairsC. An apple falling from a treeD. A swinging pendulum
Answers
We will have that the best analogy will be:
*A set of stairs.
If we know the distance between the steps then using this information and thime using an object of a given mass we can determine the "value" it will have each time it moves one step down or up, thus quantizing the concept.
Which force requires contact?
A.
The force of attraction between two masses
B.
The force exerted by air as an object moves through it
C.
The force produced by interactions between electrically charged objects
D.
The force produced by interactions between magnetic objects
Answers
Answer:
the force produced between magnetic objects
Explanation:
V nx,ny,nz. (x, y, z) = Vnz, (x)Vny, (y)Vnz,(Z),
where are the wave functions that solve the familiar harmonic oscillator in one dimension.
The three integers nx, ny, nz, are independent and each of them can take the any positive
integer value n = 0, 1, ....
(a) Find the spectrum of the spherically symmetric harmonic oscillator. In other words,
find the energies that can be realized in quantum theory.
(b) For the four lowest energies, indicate the quantum numbers (nx, ny, n₂) that give this
energy and note the degeneracy at each level. The degeneracy is the number of distinct
quantum states that have the same energy.
Bonus question: find the degeneracy of an arbitrary energy level..
(c) Another approach to this problem is to exploit radial symmetry. Write the radial
equation for this problem. Also record the boundary conditions for the radial equation.
=
(d) For orbital angular momentum l 0, the radial equation reduces to an eigenvalue
problem that is familiar. Compute the eigenvalues/energies in the l = 0 sector.
Hint: only some solutions are compatible with the applicable boundary conditions.
(e) For other values of l, the radial equation is more difficult to solve. Without doing
explicit work, it reminds us that the degeneracies found in (b) correspond to angular
momentum. At each level, some values of are allowed and for each that appear
there are 2l + 1 values of m.
Use this reasoning to deduce the allowed values of & for the three lowest energies.
Answers
The wave functions that solve the familiar harmonic oscillator in one dimension, then the limit the values of nx, ny, and nz to positive integers only, then there are still infinitely many possible combinations of values, but provide some general observations about the distribution of these values.
(a) The spectrum of the spherically symmetric harmonic oscillator is given by the energy eigenvalues:
E(n) = (n + 3/2)ℏω, where n = nx + ny + nz.
(b) For the four lowest energies:
E(0) = 3/2 ℏω, n = 0, degeneracy = 1
E(1) = 5/2 ℏω, n = 1 (1,0,0), (0,1,0), (0,0,1), degeneracy = 3
E(2) = 7/2 ℏω, n = 2 (2,0,0), (1,1,0), (1,0,1), (0,2,0), (0,1,1), (0,0,2), degeneracy = 6
E(3) = 9/2 ℏω, n = 3 (3,0,0), (2,1,0), (2,0,1), (1,2,0), (1,1,1), (1,0,2), (0,3,0), (0,2,1), (0,1,2), (0,0,3), degeneracy = 10
(c) The radial equation for the spherically symmetric harmonic oscillator is given by:
1/r² (d/dr) (r²(dR/dr)) + (2m/ℏ²) [E - V(r)] R = l(l+1)R
with the boundary conditions:
R(0) < ∞, R(∞) = 0.
(d) For l = 0, the radial equation reduces to:
1/r² (d/dr) (r² (dR/dr)) + (2m/ℏ²) [E - V(r)] R = 0
The eigenvalues for this equation are given by:
E(n) = (n + 3/2)ℏω, where n = 0, 1, 2, ....
(e) For other values of l, the radial equation is more difficult to solve. The allowed values of l for the three lowest energies can be deduced from the fact that for each n, the degeneracy is given by 2l + 1.
Therefore, for the first three energies, the allowed values of l are,
E(0) = 3/2 ℏω, l = 0, degeneracy = 1
E(1) = 5/2 ℏω, l = 0,1, degeneracy = 3
E(2) = 7/2 ℏω, l = 0,1,2, degeneracy = 6
To know more about harmonic oscillator
https://brainly.com/question/16393907
#SPJ4
Jackie studied stresses that affect earth's crust. How is compression of rock different from shearing?.
Answers
"Compression of rock is nothing but squeezing the rock together and shearing is pushing the rock in opposing directions."
It squeezes the boulder as a whole and should cause the pulls to shear. This is because compression causes the weight necessary for rocks to be squeezed. Additionally, the rock's draws shouldn't be spaced apart. It shouldn't be going in opposing ways either.
When rocks are compressed together, they fold, fracture, or even shatter. Compression stress is the most prevalent stress at convergent plate boundaries. There is stress when rocks are being torn apart. Under stress, rocks either lengthen or fragment.
Due to the compression pushing the hanging wall up in relation to the footwall, if the fault arises in a scenario of compression, it will be a reverse fault.
Compressional stresses cause a rock to shorten. A rock elongates or pulls apart as a result of tensional pressures. Shear forces cause rocks to slide past one another.
To know more about rocks:
https://brainly.com/question/419780
#SPJ4
mike took less time to run the 100 meters than mitchell what does this tell us about his speed
Answers
Physical properties can be and Some physical properties of matter such as and are observed using the fives senses.What are the ways to tell if a chemical change has occurred due to a reaction? List and describe them in complete sentences. (Hint: there are five that we read about.
Answers
The ways to tell if a chemical change has occurred due to a reaction include the following below:
Color Change.Production of an odor.Evolution of a gas etc.What is a Chemical change?This is a term which is referred to as the type of reaction which occurs when the substance's composition is changed and also involves the substance combining with another to form a new substance through the process of bond formation etc.
As a result of a new substance being produced during the reaction, there are certain changes in the color and odor due to the new substance being formed.
The evolution of a gas and the presence of precipitate both depicts the formation of a new substance which are therefore the ways to tell if chemical change occurred in the reaction.
Read more about Chemical change here https://brainly.com/question/19794032
#SPJ1
If the 100 g mass is replaced by a 200 g mass, which variables in Tnet = la change, and which
remains constant? Justify your answer.
Answers
The moment of inertia (I) will changes and net torque (Tnet) will also change, while the angular acceleration (a) remains constant.
What is the changed variable in the equation?The formula for net torque acting on an object is given as;
T(net) = Ia
where;
a is the angular accelerationI is the moment of inertiaT(net) is the net torqueThe moment of inertia of an object is given as;
I ∝ MR²
where;
M is the massR is the radius of the objectSo mass, M changes, the moment of inertia (I) changes and net torque will also change, while the angular acceleration remains constant.
Learn more about moment of inertia here: https://brainly.com/question/3406242
#SPJ1
calculate the distance an object moves if 25J of work is done with 3.0N of force
Answers
The distance an object moves if 25J of work is done with 3.0N of force is 8.33 m.
For a given amount of force, F, and a given distance, d, the formula for calculating work done is as follows:
Work done = Force x distance
So, the distance would be,
Work done / force = 25/3 = 8.33 m.
Work is the energy exerted by an object when it applies a force to move another object over some distance.
To learn more about work done,
https://brainly.com/question/31428590
A silver block of silver block of density 10.5 g/cm3 has a volume of 30 cm3. Which of the following is the correct mass of the block
Answers
➝ Density of block = 10.5 g/cm³
➝ Volume of block = 30 cm³
We have to find mass of block\(.\)
➠ Density is defined as mass of substance per unit volume\(.\)
\(\dag\:\boxed{\bf{Density=\dfrac{Mass}{Volume}}}\)
\(:\implies\sf\:Mass=Density\times Volume\)
\(:\implies\sf\:Mass=10.5\times 30\)
\(:\implies\boxed{\boxed{\bf{\red{Mass=315\:g}}}}\)
Mark weighs 375 N and is carrying a full-sized cello as he climbs the stairs to a height of 4 m. It takes him 3 seconds to do this.
How does the amount of work he does change if he were to climb the same flight of stairs again in the same amount of time, but this time without the cello?
A) It depends on the weight of the cello.
B) It remains the same.
C) It increases
D) It decreases.
Answers
Mark's work decreases when he climbs the same flight of stairs again in the same amount of time without the cello.
The correct answer is option D.
The amount of work Mark does depends on the weight of the cello, as well as the distance he climbs and the time it takes. Work is calculated using the formula :
Work = Force × Distance.
In the given scenario, Mark is carrying a full-sized cello while climbing the stairs. The weight of the cello adds to the force he exerts. So, the total force Mark exerts is the weight of the cello plus his own weight (375 N).
When Mark climbs the stairs with the cello, he is doing work against the force of gravity.
The work done is equal to the force exerted multiplied by the distance climbed (375 N + weight of cello) × 4 m.
Now, if Mark were to climb the same flight of stairs again in the same amount of time (3 seconds), but this time without the cello, the amount of work he does would decrease. This is because without the cello, the force exerted would only be Mark's weight (375 N), which is less than the total force exerted with the cello.
Therefore, mark's work decreases.
For more such questions on work visit:
https://brainly.com/question/28356414
#SPJ8
When the liquid is poured through a filter, the remaining salt water is heated until___________
Answers
Answer:
The mixture of insoluble solid and liquid is poured into the filter funnel. 2 of 3 ... When heated, the water evaporates away leaving solid salt crystals behind. ... heat the salt solution
Explanation:
At its peak, a tornado is 65 m in diameter and has 350 km/h winds. What is its frequency in revolutions per second?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
circumference = diameter * \(\pi\)
circumference = 65 * \(\pi\)
circumference = 204.2035225m
350 km/h = 97.222222 m/s
0.4761 revolutions per second
(HURRY 20 MINS)
Which of the following components of a safety plan does a worker usually have to sign before starting work at a new company?
general safety rules
company safety policy
roles and responsibilities
workplace regulations
Answers
Answer:
Roles and responsibilities
Explanation:
Definition of safety plan:
"A Safety Plan is a written document that describes the process for identifying the physical and health hazards that could harm workers, procedures to prevent accidents, and steps to take when accidents occur. Written safety plans can be comprehensive, such as an injury and illness prevention program, or they can be specific to a particular activity, hazard, or piece of equipment. The written safety plan is your blueprint for keeping workers safe."
Alternative definition
"What is an OSHA Safety Plan? An OSHA Safety Plan is a written plan that describes the potential hazards in the workplace, and the company policies, controls, and work practices used to minimize those hazards."
elements of a safety plan:
Basic Safety Plan Elements
Policy or goals statement
List of responsible persons
Hazard identification
Hazard controls and safe practices
Emergency and accident response
Employee training and communication
Recordkeeping
I say roles and responsibilities because it makes sense that if it's your responsibility and possibly something that could be dangerous -- hence a safety plan -- you would have to sign it before working. I hope this helps!
Answer: The correct answer is company safety policy
Explanation: This answer has been confirmed correct.
People who do very detailed work close up, such as jewellers, often can see objects clearly at much closer distance than the normal 25 cm. a. What is the power in D of the eyes of a woman who can see an object clearly at a distance of only 8.5 cm
Answers
This question is incomplete, the complete question is;
People who do very detailed work close up, such as jewelers, often can see objects clearly at much closer distance than the normal 25 cm.
a) What is the power in D of the eyes of a woman who can see an object clearly at a distance of only 8.50 cm? (Assume the lens-to-retina distance is 2.00 cm.)
b) What is the size in mm of an image of a 8.00 mm object, such as lettering inside a ring, held at this distance? (Include the sign of the value in your answer.) __ mm
Answer:
1) the power in D of the eyes of a woman is 61.7647 D
2) the size in mm of an image of a 8.00 mm object is -1.882 mm
Explanation:
Given the data in the question;
a) power in D of the eyes of woman who can see an object clearly at a distance of only 8.5 cm and the lens-to-retina distance is 2.00 cm,
so
u = 8.5 cm = ( 8.5 / 100 )m = 0.085 m
v = 2.00 cm = ( 2 / 100 )m = 0.02 m
Now, we know that power of lens p = 1 / u + 1 / v
so we substitute
p = ( 1 / 0.085 ) + ( 1 / 0.02 )
p = 11.7647 + 50
p = 61.7647 D
Therefore, the power in D of the eyes of a woman is 61.7647 D
b) What is the size in mm of an image of a 8.00 mm object, such as lettering inside a ring, held at this distance? (Include the sign of the value in your answer.)
we know that;
m = -v / u
we substitute
m = -0.02 / 0.085
m = -0.2353
since H₀ = 8.0 mm
H\(_i\) = m × H₀
H\(_i\) = -0.2353 × 8.0
H\(_i\) = -1.882 mm
the size in mm of an image of a 8.00 mm object is -1.882 mm
comparison between copper properties and aluminium properties
Answers
Answer: Aluminum has 61 percent of the conductivity of copper, but has only 30 percent of the weight of copper. That means that a bare wire of aluminum weights half as much as a bare wire of copper that has the same electrical resistance. Aluminum is generally more inexpensive when compared to copper conductors.
Two equal resistors of resistance x ohm each are connected in parallel, and the resultant combination is connected in series with another resistor of resistance x ohm. Calculate the effective resistance of the combination
Answers
The effective resistance of the combination when two resistors are connected in series is 2+x²/x.
The resistance is a quantity that offers obstruction to the current flow and the unit of resistance is the ohm. The resistors are connected in series and parallel. The effective resistance of series connections, R(eff) = R₁+R₂+...+Rₙ. The effective resistance of parallel connections are, 1/R(eff) = 1/R₁+1/R₂+.....+1/Rₙ.
From the given,
the parallel resistance of two-ohm x, the effective resistance,
1/R(eff) = 1/x+1/x = 2/x.
The effective resistance in a series combination of resistors, 2/x, and x are,
R(eff) = R₁+R₂ = 2/x + x = 2+x²/x.
Hence, the effective resistance is 2+x²/x.
To learn more about effective resistance:
https://brainly.com/question/11416040
#SPJ1
An auto, moving too fast on a horizontal stretch of mountain road, slides off the road,
falling into deep snow 43.9 m below the road and 87.7 m beyond the edge of the road. What was the acceleration 10m below the edge of the road?
Answers
Answer:
acceleration = - 9.8 m/s²
Explanation:
From the question, we can deduce that the only force that will be acting on the car is gravity and as such the acceleration during free fall will be equal to the acceleration due to gravity but will be negative since it is towards the ground.
Thus, acceleration = - 9.8 m/s²
which phenomenon supports the particular model of light?
Answers
Answer:
photoelectric effect
Explanation:
The photoelectric effect supports a particle theory of light in that it behaves like an elastic collision (one that conserves mechanical energy) between two particles, the photon of light and the electron of the metal.
A spring stores 68 J of potential energy when it is stretched by 6 cm. What is the spring constant?
Answers
The formula for calculating the elastic potential energy is expressed as
Elastic potential energy = 1/2kx^2
where
k represents the spring constant
x represents the compression or distance by which the spring was stretched.
From the information given,
Elastic potential energy = 68
x = 6 cm
we would convert 6 cm to m. Recall,
100cm = 1 m
6 cm = 6/100 = 0.06 m
By substituting these values into the formula, we have
68 = 1/2 x k x 0.06^2
68 = 0.0018k
k = 68/0.0018
k = 37777.78 N/m
The spring constant is 37777.78 N/m
6.A truck is carrying a steel beam of length 13.0 m on a freeway. An accident causes the beam to be dumped off the truck and slide horizontally along the ground at a speed of 30.0 m/s. The velocity of the center of mass of the beam is northward while the length of the beam maintains an east–west orientation. The vertical component of the Earth's magnetic field at this location has a magnitude of 30.0 T. What is the magnitude of the induced emf between the ends of the beam?
Answers
The magnitude is 13.12 mV.
The steps are attached below.
How do you find the magnitude of an induced emf?The standard SI unit of the magnetic field is the tesla (T). As an end result, we can use these equations and the equation for an induced emf due to changes in magnetic flux, ϵ=−NΔϕΔt ϵ = − N Δ ϕ Δ t, to calculate the importance of a precipitated emf in a solenoid.
The magnitude of the precipitated contemporary depends on the rate of trade of magnetic flux or the fee of reducing the magnetic area strains.
Learn more about the magnitude here: https://brainly.com/question/18109453
#SPJ2

Q1
Q2.
Q3.
Peter measured five samples of ice cubes.
Use the information provided to calculate the unknown volume and density of
each sample of ice cubes. (Note: attach working out for Q1)
Sample Length
Width
Height
A
В
C
D
E
B
C
D
E
1 cm
2 cm
3 cm
2.5 cm
3.5 cm
1.5 cm
1.5 cm
2.5 cm
3 cm
2.5 cm
0.5 cm
2.5 cm
2 cm
2 cm
1.5 cm
Mass
(g)
10
What the weight of each sample of the ice cubes?
Samples Weight( NOTE: 1N= 1 Kgm/s2)
A
15
20
25
30
Volume
(cm³)
0.75 cm)
7.3 cm 2 g/cm³
15 cm
1.3 g/m³
15 cm 1.69/cm³
13.125 2.285 g/cm²
Density
(g/cm³)
13.3 A/cm²
Plot a graph of N (vertical axis) and Kg (Horizontal axis)

Answers
Sample A: Volume = 1.25 cm³, Density = 8 g/cm³, Weight = 98.1 N
Sample B: Volume = 15 cm³, Density = 1 g/cm³, Weight = 147.15 N
Sample C: Volume = 12 cm³, Density = 1.67 g/cm³, Weight = 196.2 N
Sample D: Volume = 5.625 cm³, Density = 4.44 g/cm³, Weight = 245.25 N
Sample E: Volume = 26.25 cm³, Density = 1.14 g/cm³, Weight = 294.3 N
What is density?Density is a measure of how much mass is incorporated in a given volume. It is identified as a substance's mass divided by its volume.
Given measurements:
Sample A: Length = 1 cm, Width = 2.5 cm, Height = 0.5 cm, Mass = 10 g
Volume = 1 cm x 2.5 cm x 0.5 cm = 1.25 cm³
Density = 10 g / 1.25 cm³ = 8 g/cm³
Sample B: Length = 2 cm, Width = 3 cm, Height = 2.5 cm, Mass = 15 g
Volume = 2 cm x 3 cm x 2.5 cm = 15 cm³
Density = 15 g / 15 cm³ = 1 g/cm³
Sample C: Length = 3 cm, Width = 2 cm, Height = 2 cm, Mass = 20 g
Volume = 3 cm x 2 cm x 2 cm = 12 cm³
Density = 20 g / 12 cm³ = 1.67 g/cm³
Sample D: Length = 2.5 cm, Width = 1.5 cm, Height = 1.5 cm, Mass = 25 g
Volume = 2.5 cm x 1.5 cm x 1.5 cm = 5.625 cm³
Density = 25 g / 5.625 cm³ = 4.44 g/cm³
Sample E: Length = 3.5 cm, Width = 2.5 cm, Height = 3 cm, Mass = 30 g
Volume = 3.5 cm x 2.5 cm x 3 cm = 26.25 cm³
Density = 30 g / 26.25 cm³ = 1.14 g/cm³
The weight of each sample can be calculated using the formula:
Weight = Mass x g
where g is the acceleration due to gravity, which is approximately 9.81 m/s² or 9.81 N/kg.
Sample A: Weight = 10 g x 9.81 N/kg = 98.1 N
Sample B: Weight = 15 g x 9.81 N/kg = 147.15 N
Sample C: Weight = 20 g x 9.81 N/kg = 196.2 N
Sample D: Weight = 25 g x 9.81 N/kg = 245.25 N
Sample E: Weight = 30 g x 9.81 N/kg = 294.3 N
To know more about Density, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/29775886
#SPJ1
Refer to the picture!
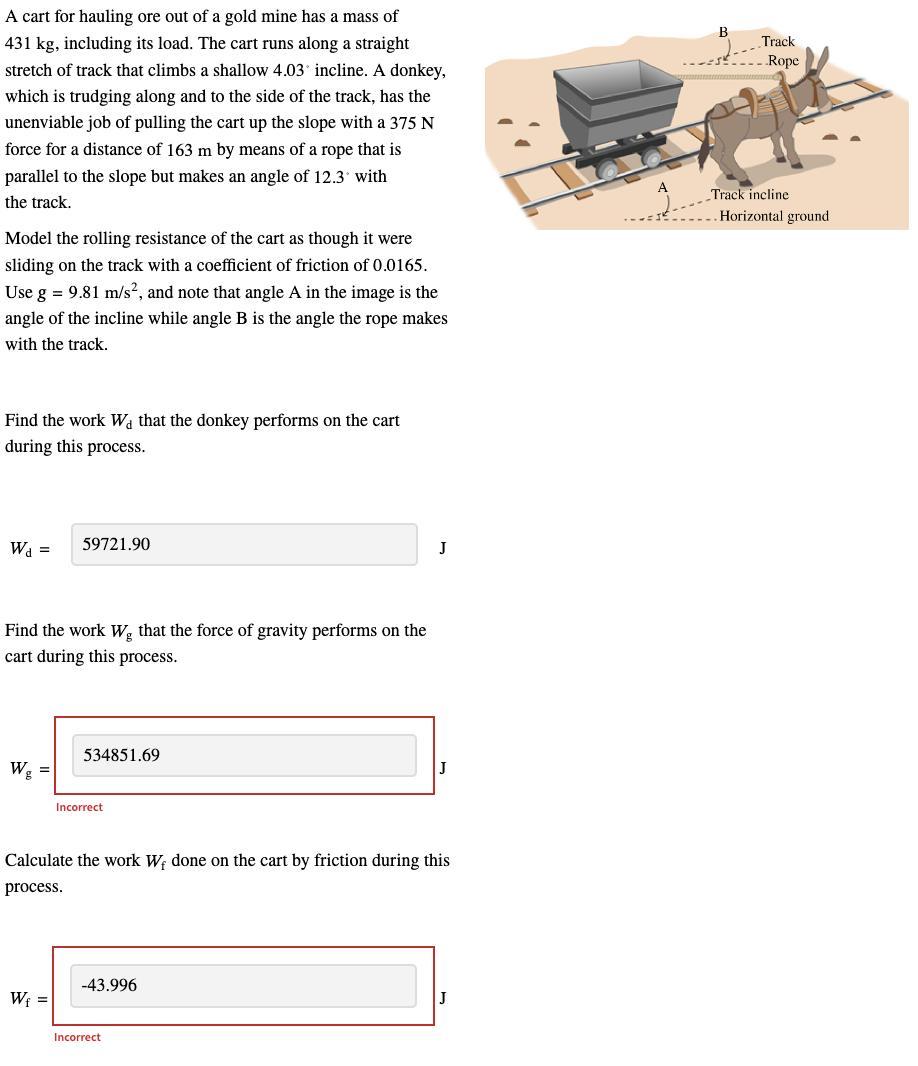
Answers
(a) The work done by the donkey on the cart is 59,721.9 J.
(b) The work done by the force of gravity on the cart is -48,434.87 J.
(c) The work done on the cart by friction during this time is 11,315.12 J.
What is the work done by the donkey on the cart?(a) The work done by the donkey on the cart is calculated as follows;
Wd = Fd cosθ
where;
F is the applied force by the donkeyd is the displacementθ is the angle of inclinationWd = 375 N x 163 m x cos(12.3)
Wd = 59,721.9 J
(b) The work done by the force of gravity on the cart is calculated as;
Wg = Fg x d x cosθ
Where;
Fg is the force of gravityd is the displacementθ is the angle between the force of gravity and displacementθ = 90⁰ + 4.03⁰ = 94.03⁰
Wg = (431 kg x 9.81 m/s²) x 163 m x cos (94.03)
Wg = -48,434.87 J
(c) The work done on the cart by friction during this time is calculated as;
Wf = Ff x d x cosθ
where;
Ff is the force of friction;Ff = μmg cosθ
Ff = 0.0165 x 431 kg x 9.81 x cos (4.03)
Ff = 69.59 N
Wf = 69.59 x 163 x cos (4.03)
Wf = 11,315.12 J
Learn more about work done by gravity here: https://brainly.com/question/15352390
#SPJ1