Answers
Answer:
2.0 g Na
Explanation:
Stoichiometry.
8.4g sodium hydrogen citrate x (1 mol sodium hydrogen citrate / 192 g sodium hydrogen citrate) x (2 mol Na/1 mol sodium hydrogen citrate) x (23g Na/1 mol Na)
^write it out it makes more sense that way
Related Questions
this woman is riding a bicycle down a hill at a constant speed and in a straight line.
Which change will increase the speed of the bicycle?
A. Added forces of 30 N up the hill and 20 N down the hill
B. Added forces of 30 N up the hill and 30 N down the hill
C. An added force of 20 N down the hill
D. An added force of 20 N to the side of the hill

Answers
Answer:
what is your zoom email
teĺlllll
What is the mass percentage of calcium in calcium carbonate CaSO4?
Answers
- A company in the plastics-making industry is currently using an additive in their
manufacturing process. This additive, when combined with any common plastic resin,
renders an end-product that can be metabolized into inert biomass by the
communities of microorganisms commonly found almost everywhere on Earth.
Which of the following is an environmental benefit of the end-product produced in this
plastic-making process?
Answers
try and find a better answer or ask ur teacher please
Calculate the volume in mL of 0.589 M NaOH needed to neutralize 52.1 mL of 0.821 M HCl in a titration.
Answers
Answer:
72.6 mL
Explanation:
A quick way to solve this titration problem when you have a monoprotic acid is to use the Dilution equation, M1V1=M2V2.
.589(x)=.821(52.1)
X=72.6 mL
Determine the average rate of change of B from t=0 s to t=402 s.
A ---> 2B
Time: Concentrations of A:
0 0.710
201 0.430
402 0.150
Answers
the average rate of change of B from t=0 s to t=402 s. A ---> 2B with
Time: Concentrations of A: 0 0.710, 201 0.430, 402 0.150 is 0.07%
To determine the average rate of change of B from t=0 s to t=402 s, we need to find the change in concentration of B (delta B) and divide it by the change in time (delta t). From t=0 s to t=201 s, the concentration of A changes from 0.710 to 0.430. Since the reaction is A ---> 2B, we can assume that the concentration of B doubles the concentration of A. So, the concentration of B changes from 0.710/2 = 0.355 to 0.430/2 = 0.215.The change in concentration of B is 0.215 - 0.355 = -0.140
From t=201 s to t=402 s, the concentration of A changes from 0.430 to 0.150. Using the same assumption, the concentration of B changes from 0.215 to 0.150/2 = 0.075. The change in concentration of B is 0.075 - 0.215 = -0.140 The total change in concentration of B is the sum of the two changes, which is -0.140 + (-0.140) = -0.280. The total change in time is 402s - 0s = 402sTherefore, the average rate of change of B is -0.280 / 402s = -0.000696, or -0.07% (two significant figures)
learn more about rate of change here:
https://brainly.com/question/29518179
#SPJ4
A hit-and-run accident has left a pedestrian injured. The investigators have used eyewitness testimony and motor vehicle records to narrow down the list of suspects. When one of these suspects is interviewed, he is asked if they would find any blood on his car. He says that he hit a deer a few weeks ago, so it is possible that there is blood. How could this statement be tested?
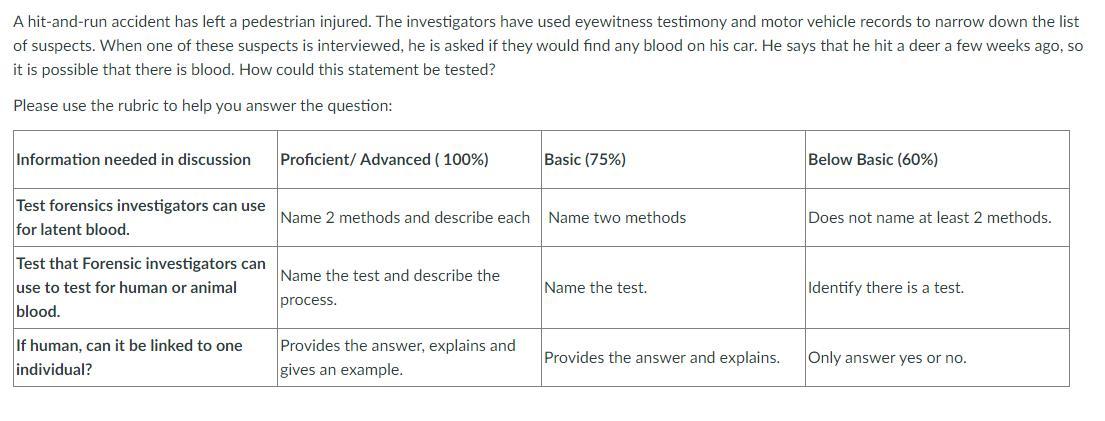
Answers
Test forensic investigators can use to test for human or animal blood will be
required to test the statement.
What is Forensics?These are different tests and techniques used by appropriate body to
investigate a crime in order to know what really happened and who is
responsible.
The test which can be used to differentiate between human and animal
blood is Precipitin Test. This is done by identifying the presence of proteins
that are found only in human blood such as albumin.
Read more about Blood tests here https://brainly.com/question/3731326
What type of bonding does Ir and Hg have?
Answers
Iridium forms metallic bonds, while mercury exhibits a combination of metallic and covalent bonding. These covalent interactions give rise to the low boiling point and weak intermolecular forces in liquid mercury.
Iridium (Ir) and mercury (Hg) exhibit different types of bonding based on their electronic configurations and properties.
Iridium is a transition metal belonging to Group 9 of the periodic table. It has a partially filled d-orbital in its atomic structure, which allows it to form metallic bonds. Metallic bonding occurs when the outer electrons of metal atoms are delocalized and form a "sea" of electrons that are free to move throughout the crystal lattice. This results in the characteristic properties of metals, such as high electrical and thermal conductivity, malleability, and ductility. Iridium forms metallic bonds with other iridium atoms, contributing to its solid, dense, and lustrous nature.
Mercury, on the other hand, is a unique element. It is a transition metal, but it exhibits characteristics of both metallic and covalent bonding. At room temperature, mercury exists as a liquid, which is highly unusual for a metal. This is because mercury atoms have a weak interatomic interaction, known as metallic bonding, similar to other metals. However, due to the presence of unpaired electrons in its 6s orbital, mercury can also form weak covalent bonds. These covalent interactions give rise to the low boiling point and weak intermolecular forces in liquid mercury.
In summary, iridium forms metallic bonds, while mercury exhibits a combination of metallic and covalent bonding.
For more question on bonds
https://brainly.com/question/29794367
#SPJ8
What does the strong nuclear force do?
Answers
Answer:
The strong force binds quarks together in clusters to make more-familiar subatomic particles, such as protons and neutrons. It also holds together the atomic nucleus and underlies interactions between all particles containing quarks. The strong force originates in a property known as colour.
Explanation:
A car hits a bug with a force of 100N. With how much force does the bug hit the car?
(A). 10 N
(B). 100 N
(C). 1000 N
Answers
Answer:
B
Explanation:
actin and reaction force are equal Newton 3 law
Predict the chemical shifts for the signals in the proton NMR spectrum of each of the following compounds.

Answers
The proximity of unsaturated groups (C=C, C=O, aromatic) and electronegative atoms (O, N, halogen) has an impact on the proton NMR chemical shift. Electronegative groups shift to the left (down field; ppm rise).
What does NMR spectroscopy's chemical shift entail?The chemical shift in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy refers to the atomic nucleus' resonant frequency in relation to a standard in a magnetic field. The location and quantity of chemical changes frequently serve as diagnostic indicators of molecular structure.
You take into account the chemically non-equivalent proton(s) one at a time while making chemical shift predictions. Find the origin of each proton or proton pair that is not chemically comparable. Whether the proton(s) is/are linked to a methyl, methene, or methine determines the beginning point.
learn more about nuclear magnetic resonance
https://brainly.com/question/21024524
#SPJ1
HN5O3+Mg reaccion de sustitucion sencilla
Responder por favor lo necesito rapido
Answers
The balanced equation of the reaction could be written as; \(HN_{5} O_{3} + Mg ------ > MgO + HNO_{3}\)
What is a reaction?We know that in chemistry, the term reaction has to do with the combination of two or more species to give a product. Now the process of the reaction would alter the chemical composition of the reactants as we move on the way to get the ne substances called the products. There would be a breaking down of the bonds that holds the reactant molecules together and then there is a recombination of the atoms in a different way so as to obtain the products of the reaction. This is how a chemical reaction takes place in a given system.
In this case we have the oxidation of the compound called \(HN_{5} O_{3}\). In this case, the compound is actually being oxidized as we can see from the process that would be shown in the reaction equation accurately.
Learn more about reaction equation:https://brainly.com/question/3588292
#SPJ1
What is the name of Bel on the periodic table
Answers
Answer:
Nobelium or Beryllium
What is the de Broglie wavelength of an electron traveling at 1.02×105m/s?
Answers
Answer:
1.82 x 10^-12 m.
Explanation:
The de Broglie wavelength of an electron traveling at 1.02 x 10^5 m/s is 1.82 x 10^-12 m.
The de Broglie wavelength of a particle is a measure of the particle's wave-like behavior, and it is given by the following equation:
λ = h / mv
where λ is the de Broglie wavelength, h is the Planck constant, m is the mass of the particle, and v is the velocity of the particle.
In the case of an electron traveling at 1.02 x 10^5 m/s, the de Broglie wavelength is given by the following calculation:
λ = 6.62 x 10^-34 J * s / (9.11 x 10^-31 kg * 1.02 x 10^5 m/s)
This simplifies to:
λ = 1.82 x 10^-12 m
Therefore, the de Broglie wavelength of an electron traveling at 1.02 x 10^5 m/s is 1.82 x 10^-12 m.
A nonmetal in the third period that should have chemical properties similar to oxygen.
Answers
Answer:
Sulfur
Explanation:
A non-metal in the third period that should have chemical properties similar to oxygen is sulfur.
This is because elements in the same group/family have similar chemical properties.
Chemical properties is predicated on the number of valence electrons within an atom. The number of valence electrons is the number of outermost shell electrons within an atom. Elements combines with one another using these valence shell electrons. Since sulfur is in the third period and the same vertical group as oxygen, they have similar chemical properties.What do scientist use to form a hypothesis
Answers
Answer:
an if/then statement
Explanation:
How many grams of AuCl3 contain 5.0 x 1023 molecules?
Answers
Answer:
approximately 251.55 grams of AuCl3 would contain 5.0 x 10^23 molecules.
I have included an overview of the topics you MUST include in your presentation.
Topic Outlines:
Biomass (10 points)
1. What does “Biomass” mean? How is Biomass being used today as a substitute for gasoline to run cars, trucks or buses?
2. What are some different ways Biomass is being used to heat homes today?
3. Name and explain 3 advantages/disadvantages in using Biomass compared to using Fossil Fuels or other alternative energies (specifically include environmental issues that can happen).
4. Explain the energy conversions when producing energy with Biomass. (Use the words: Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy).
Geothermal (10 point)
5. Where does geothermal energy come from?
6. How can geothermal energy be used to create electricity?
7. How can geothermal energy be used directly to heat homes and factories?
8. What is a “heat pump”?
9. Name and explain 3 advantages and disadvantages in using geothermal energy compared to using fossil fuels and other alternative energies. (Specifically include environmental issues that can happen).
Hydroelectric (10 points)
10. What is a good definition of hydroelectric power?
11. How does “moving water” get turned into electrical energy? Explain each part of the dam from the moving water to production of electricity.
12. Name and explain 3 advantages/disadvantages of getting electricity from hydroelectric power and how it compares to using fossil fuels or alternative energies. (specifically include environmental issues that can happen
13. Find one example in the U.S. that uses hydroelectric power to create electricity?
Hydrogen (10 points)
14. What does using hydrogen as a fuel source mean? How is it combined to create an energy source?
15. Explain where hydrogen is found. What are sources of hydrogen found on Earth?
16. Name and explain 3 advantages/disadvantages of using hydrogen as a fuel source and how it compares to using fossil fuels and other alternative energies (specifically include environmental issues that can happen.
17. What is a fuel cell? How does it work? (include diagram)
Solar Power (10 points)
18. What is a good definition of solar energy?
19. How does a solar cell make electricity? What is it made of?
20. Name and explain 3 advantages/disadvantages about solar energy to heat or produce electricity compared to using fossil fuels or other alternatives (specifically include environmental issues that can happen.
21. Find an example of solar energy being used in the U.S.?
Wind Energy (10 points)
22. Where does wind energy come from? What is a good definition of wind energy?
23. How does wind energy get turned into electrical energy?
24. Name and explain 3 advantages/disadvantages of getting electricity from wind energy compared to using fossil fuels or other alternative energies (specifically include environmental issues that can happen.
25. Find an example in the U.S. that uses wind energy to create electricity?
Answers
Answer:
Introduction: (5 points)
Before diving into each topic, it's important to understand why alternative energies are important. Fossil fuels are limited resources that produce harmful emissions and contribute to climate change. Therefore, we must turn to alternative energies to reduce our reliance on these resources and mitigate their negative impacts on the environment. In this presentation, we will discuss five alternative energies: Biomass, Geothermal, Hydroelectric, Hydrogen, Solar Power, and Wind Energy.
Biomass: (10 points)
1.
Biomass refers to organic matter, such as wood, crops, and waste, that can be converted into energy. Biomass can be used as a substitute for gasoline to run cars, trucks or buses.
2.
Biomass can be used to heat homes through wood stoves, pellet stoves, and biomass boilers.
3.
Advantages of biomass include its renewability, availability, and its ability to reduce waste. However, it can also lead to deforestation, land-use change, and pollution.
4.
Biomass energy production involves converting potential energy (stored in biomass) into kinetic energy (in the form of steam), which is then used to generate electricity.
Geothermal:
5.
Geothermal energy comes from the heat within the Earth's crust.
6.
Geothermal energy can be used to create electricity through steam turbines.
7.
Geothermal energy can be used directly to heat homes and factories through geothermal heat pumps.
8.
A heat pump is a device that transfers heat from a colder area to a hotter area.
9.
Advantages of geothermal energy include its reliability, low emissions, and its ability to provide heating and cooling. However, it can also lead to land subsidence, water pollution, and seismic activity.
Hydroelectric:
10.
Hydroelectric power is electricity generated from the movement of water.
11.
Moving water turns a turbine, which spins a generator to produce electricity. The dam is used to regulate the flow of water and to control the amount of electricity generated.
12.
Advantages of hydroelectric power include its renewability, efficiency, and ability to provide flood control. However, it can also lead to the displacement of communities, harm aquatic life, and reduce downstream water availability.
13.
The Hoover Dam in Nevada is an example of a hydroelectric power plant.
Hydrogen:
14.
Using hydrogen as a fuel source involves combining it with oxygen to produce energy in the form of electricity and water vapor.
15.
Hydrogen is found in water, fossil fuels, and organic matter.
16.
Advantages of using hydrogen as a fuel source include its renewability, abundance, and its ability to reduce emissions. However, it can also be expensive to produce, transport, and store.
17.
A fuel cell is an electrochemical device that converts hydrogen and oxygen into electricity. It works by passing hydrogen through an anode, where it is oxidized, producing electrons and protons. The electrons flow through a circuit to produce electricity, while the protons pass through a membrane to the cathode, where they combine with oxygen to form water.
Solar Power:
18.
Solar energy is energy from the sun that can be converted into electricity.
19.
A solar cell is made of a semiconductor material, such as silicon, that absorbs photons from the sun and generates electrons. These electrons flow through a circuit to produce electricity.
20.
Advantages of solar energy include its renewability, low emissions, and its ability to reduce dependence on fossil fuels. However, it can also be expensive to install, dependent on weather conditions, and can lead to land-use change.
21.
The Topaz Solar Farm in California is an example of solar energy being used in the U.S.
Wind Energy
22.
Wind energy is a type of renewable energy that comes from the wind. Wind energy is generated by the movement of air across the earth's surface caused by differences in temperature and pressure. Wind turbines are used to convert wind energy into electrical energy.
23.
Wind energy is converted into electrical energy by wind turbines. The turbines are equipped with blades that capture the wind and spin a rotor. The rotor turns a shaft, which drives a generator that produces electricity.
24.
Advantages of wind energy include:
Wind energy is a renewable source of energy that does not emit harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases.Wind turbines can be installed on a small or large scale, making it suitable for both individual and industrial use.Wind energy can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to a more sustainable energy mix.Disadvantages of wind energy include:
Wind turbines can be noisy and may cause visual pollution.Wind energy production is intermittent, meaning that wind turbines do not produce electricity when the wind is not blowing.Wind turbines can be dangerous to birds and bats.25.
Alta Wind Energy Center in California is an example of a wind energy project in the US. It is one of the largest wind farms in the world, with a total capacity of 1,548 MW.

You have 6.0 g of C2H6 and 20.0 g of O2 for a combustion reaction. If you actuallyproduce 3.80 g of CO2 , What is the percent yield?
Answers
Answer:
The percent yield is 24.2%.
Explanation:
1st) It is necessary to balance the chemical reaction:
\(2C_2H_6+7O_2\rightarrow4CO_2+6H_2O\)2nd) From the balanced reaction, we know that 2 moles of C2H6 react with 7 moles of O2 to produce 4 moles of CO2. With the molar mass of C2H6 (30g/mol), O2 (32g/mol) and CO2 (44g/mol), we can convert the moles to grams:
- C2H6 conversion:
\(2moles*\frac{30g}{1mole}=60g\)- O2 conversion:
\(7moles*\frac{32g}{1mole}=224g\)-CO2 conversion:
\(4moles*\frac{44g}{1mole}=176g\)Now we know that 60g of C2H6 react with 224g of O2 to produce 176g of CO2.
3rd) From the given values of C2H6 (6.0g) and O2 (20.0g), it is necessary to find out which one is the limiting reactant and which one is the excess reactant:
\(\begin{gathered} 60gC_2H_6-224gO_2 \\ 6.0gC_2H_6-x=\frac{6.0gC_2H_6*224gO_2}{60gC_2H_6} \\ x=22.4gO_2 \end{gathered}\)We can see that the 6.0g of C2H6 will need 22.4g of O2 to react, but we only have 20.0g of O2, so O2 is the limiting reactant and C2H6 will be the excess reactant.
4th) Now, using the limiting reactant, we have to calculate the grams of CO2 that should be produced from the stoichiometry of the reaction (this is the Theoretical yield):
\(\begin{gathered} 224gO_2-176gCO_2 \\ 20.0gO_2-x=\frac{20.0gO_2*176gCO_2}{224gO_2} \\ x=15.7gCO_2 \end{gathered}\)5th) Finally, we can calculate the Percent yield of the reaction, by using the Theoretical yield (15.7g) and the Actual yield (3.80g):
\(\begin{gathered} PercentYield=\frac{ActualYield}{TheoreticalYield}*100\% \\ PercentY\imaginaryI eld=\frac{3.80g}{15.7g}*100\operatorname{\%} \\ PercentY\mathrm{i}eld=24.2\% \end{gathered}\)So, the percent yield is 24.2%.
2.59 Using the periodic table to guide you, predict the chemical formula and name of the compound formed by the following elements: (a) Ga and F, (b) Li and H, (c) Al and I, (d) K and S.
Answers
Answer:
(a) GaF3, gallium(III) fluoride
(b) LiH, lithium hydride
(c) AlI3, aluminum(III) iodide
(d) K2S, potassium sulfide
What is ostwald process?? Give the first catalytic reaction of this process. .
Don't spam
Answers
Answer: Smelling salts and oxygen are introduced into a metal catalyst-containing tube (platinum). Typically warmed to get the reaction started. The alkali is then oxidized to produce nitric oxide.
Answer:
The Ostwald process is a chemical process used for making nitric acid. Wilhelm Ostwald developed the process, and he patented it in 1902. The Ostwald process is a mainstay of the modern chemical industry, and it provides the main raw material for the most common type of fertilizer production
Explanation:
The first stage of the Ostwald process involves the catalytic oxidation of ammonia into nitric oxide, using platinum as the catalyst. The nitric oxide is then transferred to a different oxidizing tower, where it is oxidized into nitrogen dioxide
2 H + 3 H -----> 2 He + 1 n
1 1 4 0
Explain in 1-2 sentences: Is the above equation an example of fission or fusion? How do you know? Give at least 2 reasons why.
Answers
The given reaction is an example of nuclear fusion.
This is because two lighter hydrogen atoms fuse to give a heavier helium atom. There is also an increase in the atomic number of the product.
What are nuclear fission and nuclear fusion reactions?Nuclear fission reactions are reactions in which the nucleus of large atoms are split into nucleus of two or more smaller atoms.
For example, uranium atoms split into krypton and barium.
Nuclear fusion reactions involve the nucleus of two or more smaller atoms combining to give an atom of a larger nucleus.
For example, hydrogen atoms fuse to give a helium atom.
Learn more about nuclear fusion and fission at: https://brainly.com/question/14019172
#SPJ1
Calculate the pH of a 0.005 M NaOH (PLS)
Answers
To calculate the pH of a solution of NaOH (sodium hydroxide), we need to consider that NaOH is a strong base that dissociates completely in water, producing hydroxide ions (OH⁻).
Given:
Concentration of NaOH = 0.005 M
Since NaOH dissociates into one hydroxide ion (OH⁻) per molecule, we can determine the concentration of hydroxide ions in the solution, which will allow us to calculate the pOH. Then, we can convert the pOH to pH using the relationship: pH + pOH = 14.
1. Calculate the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻):
The concentration of OH⁻ ions will be the same as the concentration of NaOH since NaOH dissociates completely.
Concentration of OH⁻ = 0.005 M
2. Calculate the pOH:
pOH = -log[OH⁻]
pOH = -log(0.005)
Using logarithm properties, we can determine the pOH value:
pOH = -log(0.005)
pOH = -(-2.301)
pOH = 2.301
3. Calculate the pH:
pH = 14 - pOH
pH = 14 - 2.301
pH ≈ 11.699
Therefore, the pH of a 0.005 M NaOH solution is approximately 11.699.
The pH of a 0.005 M concentration of NaOH ( sodium hydroxide ) solution is approximately 11.70.
What is the pH of the sodium hydroxide?The pH of a solution is defined as the logarithm of the reciprocal of the hydrogen ion concentration [H+] of the given solution.
From the formula;
pH = -log[ H⁺ ]
pOH = -log[ OH⁻ ]
pH + pOH = 14
Given that; the concentration of solution (molarity) ( OH⁻ ) is 0.005 M.
First, we determine the pOH.
pOH = -log[ OH⁻ ]
Plug in ( OH⁻ ) = 0.005
pOH = -log[ 0.005 ]
pOH = 2.30
Now, plug pOH = 2.30 into the above formula and solve for the pH:
pH + pOH = 14
pH + 2.30 = 14
Subtract 2.30 from both sides:
pH + 2.30 - 2.30 = 14 - 2.30
pH = 14 - 2.30
pH = 11.7
Therefore, the pH of the solution is 11.7.
Learn more about pH & pOH here: brainly.com/question/17144456
#SPJ1
How many water molecules are found within the crystalline structure of one hydrate molecule?
What is the molecular formula of the hydrate?
Attached my worksheets to it and the questions


Answers
a. The Mass of water driven off = 0.15 g
b. Moles of anhydrate = 0.00257 moles
c. Moles of water driven off is 0.00833 moles
d. There are 3 moles of water within the crystalline structure of one molecule of the hydrated salt.
e. The molecular formula of the hydrated salt will be X.3H₂O
What is the mass of water driven off from the hydrated salt?a. The mass of water driven off from the hydrated salt is:
Mass of water driven off = 0.5 g - 0.35 g
Mass of water driven off = 0.15 g
b. Molecular mass of salt = 136 g/mol
moles of anhydrate = 0.35/136
Moles of anhydrate = 0.00257 moles
c. Moles of water driven off = mass/molar mass
molar mass of water = 18 g/mol
Moles of water driven off = 0.15/18
Moles of water driven off = 0.00833 moles
d. Moles of water within the crystalline structure of one molecule of the hydrated salt is determined by converting to whole number mole ratio by dividing with the smallest ratio,
Salt to water ratio = 0.00257 /0.00257 : 0.00833/0.00257
Salt to water ratio = 1 : 3
Therefore, there are 3 moles of water within the crystalline structure of one molecule of the hydrated salt.
e. Assuming the anhydrous salt is X, the molecular formula of the hydrated salt will be X.3H₂O
Learn more about hydrated salts at: https://brainly.com/question/14447094
#SPJ1
2HCl(aq) + Ba(OH)2(aq) → BaCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l) ΔH = –118 kJ Calculate the heat when 250.0 mL of 0.500 M HCl is mixed 500.0 mL of 0.500 M Ba(OH)2. Assuming that the temperature of both solutions was initially 25.0 oC and that the final mixture has mass of 750.0 g and a specific heat capacity of 4.18 J oC–1g–1, calculate the final temperature (in oC) of the mixture.
Answers
Answer:
Heat = 7375J
Final temperature of the mixture = 27.35°C
Explanation:
In the reaction:
2HCl(aq) + Ba(OH)₂(aq) → BaCl₂(aq) + 2H₂O(l) ΔH = –118 kJ
When 2 moles of HCl reacts with excess of Ba(OH)₂ there are released 118kJ.
In the reaction, moles of HCl and Ba(OH)₂ that reacts are:
Moles HCl = 0.250L ₓ (0.500 moles / L) = 0.125 moles HCl
Moles Ba(OH)₂ = 0.500L ₓ (0.500 moles / L) = 0.250 moles Ba(OH)₂
For a complete reaction of 0.125 moles of HCl you need:
0.125 mol HCl ₓ (1 mole Ba(OH)₂ / 2 moles HCl) = 0.0625 moles Ba(OH)₂
As you have 0.250 moles of Ba(OH)₂, this reactant is in excess
2 moles of HCl that react release 118kJ, 0.125 moles of HCl release:
0.125 moles HCl ₓ (118kJ / 2 moles) = 7.375kJ =
7375JThe heat released can be obtained with the formula:
Q = C×m×ΔT
Where Q is heat, C specific heat of the solution, m its mass and ΔT change in temperature.
Replacing:
Q = C×m×ΔT
7375J = 4.18J/g°C×750.0g×ΔT
2.35°C = ΔT
As ΔT = Final T - Initial T:
2.35°C = Final T - 25.0°C
27.35°C = Final temperature of the mixture
What was one idea Dalton taught about atoms?
Answers
Explanation:
All atoms of one type were identical in mass and properties.
A constant electric current deposited 365 mg of Ag in 216 minutes from an aqueous Silver trioxonitrate (v). What is the Current?
Answers
The electric current is 0.025 A
Electric current refers back to the go with the flow of energy in an electronic circuit and to the amount of strength flowing through a circuit. it's far measured in amperes (A). the bigger the cost in amperes, the more energy is flowing within the circuit.
Ag+ + e¯ →Ag
1F deposits 107.87 g/mol (molecular mass) of silver
1F = 96500 C
Let, 107.87 g/mol needed = 96500 C
Number of coulombs required to deposit 0.3650 g of silver =(96500/107.87) 0.3650
Q = 326.5 C
According to Faraday’s law, Q = I x t
I = 326.5 C / (216 x 60 s) = 0.025 A
Learn more about electric current here:-https://brainly.com/question/2984202
#SPJ9
Solar and wind energy are both intermittent resources that cannot be relied upon for a constant stream of energy production. Explain why developing better ways to store energy is an important part of making these energy sources more practical to use.
Answers
By removing the need to build additional transmission lines and equipment, energy storage may reduce costs for utilities and their customers.
By removing the need to build additional transmission lines and equipment, energy storage may reduce costs for utilities and their customers. Energy storage's inherent ability to offer backup power in the event of grid failure is a feature that both residential consumers and commercial owners find highly desirable.
To know more about energy, here:
https://brainly.com/question/1932868
#SPJ1
PLEASE ANSWER THROUGHLY FOR BRAINLEST ASAP

Answers
Observation statements: When the mass of the sun is larger, Earth moves around the sun at a slower pace.
When the mass of the sun is smaller, Earth moves around the sun at a faster pace.
When Earth is closer to the sun, its orbit becomes faster.
When Earth is farther from the sun, its orbit becomes slower.
Hypothesis:
The gravitational force between two objects depends on their masses and the distance between them, as described by the law of universal gravitation. Therefore, if we change the mass of the sun or the distance between Earth and the sun, we should observe changes in the speed and shape of Earth's orbit around the sun.
Results:
Our observations confirm our hypothesis. When we increased the mass of the sun, we noticed that Earth's orbit around the sun became slower.
How to explain the informationConversely, when we decreased the mass of the sun, Earth's orbit became faster. This is consistent with the idea that larger masses exert a stronger gravitational force, which in turn affects the speed and shape of Earth's orbit.
Similarly, when we moved Earth closer to the sun, we observed that its orbit became faster, while moving it farther away from the sun resulted in a slower orbit. This is because the gravitational force between Earth and the sun is stronger when they are closer together, and weaker when they are farther apart. Therefore, the speed and shape of Earth's orbit are influenced by both the mass of the sun and the distance between Earth and the sun.
Overall, our observations suggest that the laws of universal gravitation played a crucial role in the formation and evolution of the Solar System, as they determine the dynamics of planetary motion and the stability of planetary orbits.
Learn more about observations on
https://brainly.com/question/2419635
#SPJ1
A chemist must dilute 93.1 mL of 7.79 of uM aqueous mercury (I) chloride solution until the concentration falls to 3.00 uM. She’ll do this by adding distilled water to the solution until it reaches a certain final volume. Calculate the final volume in liters.
Answers
Taking into account the definition of dilution, if chemist must dilute 93.1 mL of 7.79 of uM aqueous mercury (I) chloride solution until the concentration falls to 3.00 uM, the final volume is 0.24175 L.
Definition of dilutionDilution is a procedure by which the concentration of a solution is lowered, usually with the addition of a diluent.
In a dilution the amount of solute does not change, but as more solvent is added, the concentration of the solute decreases, as the volume of the solution increases.
A dilution is mathematically expressed as:
Ci×Vi = Cf×Vf
where
Ci: initial concentrationVi: initial volumeCf: final concentrationVf: final volumeFinal volumeIn this case, you know:
Ci= 7.79 uMVi= 93.1 mLCf= 3 uMVf= ?Replacing in the definition of dilution:
7.79 uM× 93.1 mL= 3 uM× Vf
Solving:
(7.79 uM× 93.1 mL)÷ 3 uM= Vf
241.75 mL= 0.24175 L = Vf (being 1000 mL= 1 L)
In summary, the final volume is 0.24175 L.
Learn more about dilution:
brainly.com/question/6692004
#SPJ1
A chemist needs to determine the concentration of a sulfuric acid solution by titration with a standard sodium hydroxide solution. He has a 0.1071 M standard sodium hydroxide solution. He takes a 25.00 mL sample of the original acid solution and dilutes it to 250.0 mL. Then, he takes a 10.00 mL sample of the dilute acid solution and titrates it with the standard solution. The endpoint was reached after the addition of 12.69 mL of the standard solution. What is the concentration of the original sulfuric acid solution?
Answers
Answer:
The way the chemist works is through the chemistry of astronomical events in the atmosphere of delocalisation which causes a significant impact on Kanye West which ellaborates the terrific police of the UK. And thats why me and Jennifer Lopez share the same hair band.
