Consider the dissolution of PbS in water:PbS(s) + H₂O(l) ⇄ Pb²⁺(aq) + HS⁻(aq) + OH⁻(aq)Adding aqueous NaOH causes more PbS to dissolve. Does this violate Le Châtelier’s principle? Explain.
Answers
No. It indicates the formation of a complex ion between lead and hydroxide in solution
Pb2+(aq) + nOH- → [Pb(OH)n]2-n(aq)
PbS(s) + H2O(l) ⇌ Pb2+(aq) + HS- (aq) + OH- (aq)if we add NaoH solution then the concentration of OH- ions increases and it recombine with HS- and finally form more amount of PbS.This indicates decreses solubility of PbS. When a system is in equilibrium if we change any one of the factor like temperatue, pressure, concentration then equilibrium shifted to either forward or backward to neutralise the factor.What is PBS in water?
Phosphate-buffered saline (abbreviated PBS) is a buffer solution (pH ~ 7.4) commonly used in biological research. It is a water-based salt solution containing disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium chloride and, in some formulations, potassium chloride and potassium dihydrogen phosphate.Learn more about OH- ions
brainly.com/question/17439197
#SPJ4
Related Questions
What is the mass of 5.119 102 molecules of copper sulfate
(CuSO4)?
Answers
Answer:
Mass = 135.66 ×10⁻²¹ g
Explanation:
Given data:
Number of molecules of CuSO₄= 5.119×10²
Mass of CuSO₄= ?
Solution:
The given problem will solve by using Avogadro number.
1 mole contain 6.022×10²³ molecules
5.119×10² molecules ×1 mol / 6.022×10²³ molecules
0.85×10⁻²¹ mol
Mass in grams:
Mass = number of moles × molar mass
Mass = 0.85×10⁻²¹ mol × 159.6 g/mol
Mass = 135.66 ×10⁻²¹ g
How to solve , how many grams of KI are in 25. 0 ml of a 3. 0%(m/v) KI solution
Answers
The grams of the KI are in the 25.0 ml of a 3.0 % m/v of the KI solution is 0.75 g.
The volume of the solution = 25 mL
The mass by volume of KI = 3 % m/v
The potassium iodide solution will contain the 3.0 g of the potassium iodide for the every 100 mL of the solution.
The amount of the KI in grams is as follows :
The mass of the KI in grams = (25 mL× 3 g ) / 100 mL
The mass of the KI in grams = 0.75 g
Thus, the amount of the KI in the grams is 0.75 g in the volume of the 25 mL.
To learn more about KI here
https://brainly.com/question/13684032
#SPJ4
The pH of a weak-acid solution is calculated using systematic treatment; that means writing down same number of independent equations as there are unknown concentrations. Which of the following is NOT an equation that is needed to solve for pH? [H][4] L. K= THA CHA total = [HA] + [A") [H] = [A-] + [OH-] [HA]OH IV. Ky (4) V. K = [H] x [OH)
Answers
The equation that is NOT needed to solve for pH is option V: K = [H] x [OH].
Above equation represents the equilibrium constant for the autoionization of water (Kw) and is not directly relevant for calculating the pH of a weak-acid solution. To solve for the pH of a weak-acid solution using systematic treatment, we typically require equations related to the dissociation of the weak acid and the equilibrium expressions for the acid and its conjugate base. These equations allow us to set up a system of equations equal to the number of unknown concentrations, which can then be solved to determine the pH. Equations I, II, III, and IV are all relevant in the systematic treatment for calculating the pH of a weak-acid solution. They involve the concentration of the weak acid ([HA]), its dissociation into its conjugate base ([A-]) and hydrogen ions ([H]), and the equilibrium constant (Ka) associated with the weak acid dissociation.
To learn more about weak-acid click here: brainly.com/question/29833185
#SPJ11
Correct question to answer : Wine goes bad soon after opening because the ethanol CH3CH2OH dissolved in it reacts with oxygen O2 gas to form water and aqueous acetic acid CH3COOH, the main ingredient in vinegar. Calculate the moles of ethanol needed to produce 0.900mol of acetic acid. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round it to 3 significant digits.Do not answer : Ammonium phosphate ((NH4)3(PO4) is an important ingredient in many solid fertilizers. It can be made by reacting aqueous phosphoric acid with liquid ammonia. Calculate the moles of ammonia needed to produce of ammonium phosphate. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, if necessary, and round it to significant digits.
Answers
• The balanced equation for the reaction is given by:
CH3CH2OH + O2 → CH3COOH+ H2O• From the above reaction we can see that:
1 mole of ethanol (CH3Ch2OH) produces 1 mol of acetic acid(CH3COOH)
so . x mole of ethanol will produce 0.9mol of acetic acid ....(cross multiply)
xmol ethanol * 1mol acetic = 1mol ethamol* 0.9molacetic
∴ xmol ethanol = 1*0.9 /1
= 0.90 mol
• This means that, 0.90 mol of ethanol, is needed to produce 0.9mol acetic acid,.
Why is human waste hazardous when it enters the water system? for London and Ancient Rome?
I will mark as brainliest
Answers
Promiscuous enzymes metabolize many alcohols in the human liver The example molecule used in the Chemistry Tutorial (1-propanol) and its metabolite are not the only molecules that can be oxidized by ADH and ALDH, respectively. In fact, ADH and ALDH are promiscuous enzymes, meaning that they are not specific in catalyzing the oxidation of just one specific alcohol or aldehyde. On the other hand, ADH will not catalyze the oxidation of every alcohol either.
For example, ADH can oxidize all of the following compounds except tert-butanol
- Methanol
- Isopropanol
- Ethylene glycol
- Tert-butanol
What characteristic of the substrate must the active site of ADH recognize? a. a hydrogen atom located on a carbon next to a with an-OH group (vicinal position)
b. atom located on the same carbon as an-OH group (geminal position)
c. an internal - OH group (a secondary alcohol)
d. a terminal -OH group (a primary alcohol)
Answers
The characteristic of the substrate that the active site of ADH must recognize is option A: "hydrogen atom located on a carbon next to a with an-OH group (vicinal position)".
This is because ADH is an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones. In order for this reaction to occur, the substrate must have a hydrogen atom located on a carbon next to an -OH group. This allows the enzyme to recognize the substrate and catalyze the reaction.
Without this characteristic, the enzyme will not be able to recognize the substrate and the reaction will not occur.
ADH specifically recognizes and binds to this particular feature of the substrate through its active site, which has a complementary shape and chemical properties to the substrate. This binding allows the enzyme to position the substrate in a way that facilitates the transfer of a hydrogen ion and a pair of electrons to the coenzyme NAD+ to form NADH, while producing an aldehyde or ketone.
Learn more about ADH https://brainly.com/question/13943468
#SPJ11
The characteristic of the substrate that the active site of ADH must recognize is option A: "hydrogen atom located on a carbon next to a with an-OH group (vicinal position)".
This is because ADH is an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones. In order for this reaction to occur, the substrate must have a hydrogen atom located on a carbon next to an -OH group. This allows the enzyme to recognize the substrate and catalyze the reaction.
Without this characteristic, the enzyme will not be able to recognize the substrate and the reaction will not occur.
ADH specifically recognizes and binds to this particular feature of the substrate through its active site, which has a complementary shape and chemical properties to the substrate. This binding allows the enzyme to position the substrate in a way that facilitates the transfer of a hydrogen ion and a pair of electrons to the coenzyme NAD+ to form NADH, while producing an aldehyde or ketone.
Learn more about ADH
brainly.com/question/13943468
#SPJ4
_CuCl + _H2S -> _Cu2S + _HCl
If 0.20 mols of CuCl react, how many grams of H2S would react?
Answers
The number of grams of hydrogen sulfide that will react if 0.20 moles of CuCl also reacts is 3.4grams.
How to calculate mass using stoichiometry?Stoichiometry is the study and calculation of quantitative (measurable) relationships of the reactants and products in chemical reactions (chemical equations).
According to this question, copper chloride reacts with hydrogen sulphide as follows:
2CuCl + H₂S → Cu₂S + 2HCl
Based on the above equation, 2 moles of CuCl reacts with 1 mole of H₂S.
0.2 moles of CuCl will react with 0.2/2 = 0.1 moles of H₂S.
mass of H₂S = 34g/mol × 0.1 mol = 3.4 grams
Learn more about stoichiometry at: https://brainly.com/question/28780091
#SPJ1
maleic anhydride is an exceptionally reactive dienophile. choose the right answer, which explains why? . It has two electron donating groups. B. It has two electron withdrawing groups. C. None of the above. D. It is sterically hindered. E. It is not sterically hindered.
Answers
Maleic anhydride is an exceptionally reactive dienophile the correct option that explains the reason for it is B. It has two electron withdrawing groups.
Maleic anhydride is an exceptionally reactive dienophile because it has two electron-withdrawing groups. The electron-withdrawing groups in maleic anhydride are the two carbonyl groups, which are highly polarized due to the electronegativity of the oxygen atoms. The electron-withdrawing groups in maleic anhydride make it highly susceptible to attack by electron-rich dienes, which can undergo a Diels-Alder reaction to form a cycloadduct.
In contrast, dienophiles with electron-donating groups are less reactive in Diels-Alder reactions because the electron-donating groups decrease the electrophilicity of the dienophile. Additionally, the reactivity of a dienophile is not usually affected by steric hindrance because the reaction involves the formation of a transition state, rather than the direct collision of molecules. Therefore, options A, D, and E are not correct.
Hence, the correct answer is B. It has two electron-withdrawing groups.
Learn more about Maleic anhydride here:
https://brainly.com/question/14080641
#SPJ4
geologists attempting to locate metallic mineral resources such as copper and iron will first consider the ____ of the rock and how it formed.
Answers
Minerals can be located using geochemical surveys and remote sensors that analyze satellite images. Following that, mining or quarrying is used to remove many minerals.
What do you do to find mineral resources first?Search for Potential Deposits, Locating areas that are likely to contain mineral deposits is one of the first steps in the exploration process. Prospective areas might be close to other known mineralization areas or to active mine sites because mineral deposits frequently form in clusters.Minerals can be located using geochemical surveys and remote sensors that analyze satellite images. Following that, mining or quarrying is used to remove many minerals. Pumping, however, can be used to extract liquid minerals like oil or gas.When choosing which deposit to pursue, some factors include the deposit's location and shape, the rock's strength, the grade of the ore, the costs associated with mining it, and the commodity's current market price.To learn more about minerals refer to:
https://brainly.com/question/15844293
#SPJ4
A box of paperclips contains 2.21x10 24 atoms of aluminum. How many moles are in the box of paperclips? I am starting with the unit _______________ and solving for the unit ________________
Answers
Taking into account the definition of Avogadro's Number, a box of paperclips contains 2.21×10²⁴ atoms of aluminum and 3.67 moles of aluminum.
Definition of Avogadro's NumberAvogadro's number is a number that defines the amount of elements (which can be electrons, atoms, ions, molecules) found in one mole of a substance.
Its value is 6.023×10²³ particles per mole. Avogadro's number applies to any substance.
Amount of moles in the box of paperclipsThen you can apply the following rule of three: if 6.023×10²³ atoms are contained in 1 mole of aluminum, then 2.21×10²⁴ atoms are contained in how many moles of aluminum?
amount of moles of aluminum= (2.21×10²⁴ atoms × 1 mole)÷ 6.023×10²³ atoms
amount of moles of aluminum= 3.67 moles
Finally, 3.67 moles of aluminum are present.
Learn more about Avogadro's Number:
brainly.com/question/11907018
#SPJ1
aerobic cellular respiration requires an adequate supply of
Answers
Answer:
oxygen ?
Explanation:
not sure but I think so
Aerobic cellular respiration requires an adequate supply of oxygen. In the presence of oxygen, the cell completely oxidised the glucose molecule to form ATP.
What is cellular respiration?In cellular respiration, the cell takes glucose and breaks it down to form energy. Cellular respiration is of two types: aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
In aerobic respiration, the cell requires oxygen. Due to the presence of oxygen, the complete oxidation of glucose takes place. Glucose is converted into pyruvic acid and then enters the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain to make ATP.
In the aerobic cellular respiration process, the maximum amount of ATP is derived. In anaerobic respiration, the cell performs respiration without the presence of oxygen. An example is glycolysis.
In this glycolysis process, the complete oxidation of glucose does not take place. In the absence of oxygen from pyruvate, lactic acid and ethanol are produced. This is called fermentation.
Hence, for aerobic cellular respiration, oxygen is required.
To learn more about cellular expression, refer to the following link:
https://brainly.com/question/3928558
#SPJ6
I'm just looking for someone to check my answers on this and correct me if I'm wrong :)This is the question:You have three elements, A, B, and C, with the following electronegativity values:A = 0.9B = 3.0C = 3.5You react the elements to form the substances AB, AC, and BC. Answer the following questions:What type of substance is AB? What types of bonds are present? Explain your answer.What type of substance is AC? What types of bonds are present? Explain your answer.What type of substance is BC? What types of bonds are present? Explain your answer.If any of the substances are ionic compounds, which element is the cation and which is the anion? Explain your answer.And these are my answers:AB is a compound. It'd be an ionic compound because the electronegativity is different in each.AC is a compound. It'd be an ionic compound because the electronegativity is different in each.BC is a compound, but the bond between them is covalent.AB is an ionic compound. A is the cation and B is the anion because the element with lower electronegativity is the cation and the element with the higher electronegativity is the anion.
Answers
Answer:
Explanations:
Given the following electronegativity of three elements as:
Nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen gas to produce ammonia according to the following equation.
N2(g)+3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
What is the mass of ammonia produced from 7.23 x 10−4
moles of the hydrogen reactant, assuming there is sufficient nitrogen to react?
Answers
The mole of ammonia produced from 7.23 x 10⁻⁴ moles of the hydrogen reactant when there is sufficient nitrogen to react is 4.82×10⁻⁴.
What is moles?Moles is a unit which is used to estimate the amount of any substance and it is represented as:
n = W/M , where
W = given mass
M = molar mass
Given chemical reaction is:
N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) → 2NH₃(g)
In the question it is given that sufficient moles of N₂ is present, so the formation of product depends on the moles of H₂. From the stoichiometry of the reaction, it is clear that:
3 moles of H₂ = produce 2 moles of NH₃
7.23×10⁻⁴ moles of H₂ = produce 2/3 × 7.23×10⁻⁴=4.82×10⁻⁴ moles of NH₃
Hence, option (C) is correct i.e. 4.82×10⁻⁴.
To know more about moles
brainly.com/question/1464305
#SPJ1
Given that a for HBrO is 2. 8×10^−9 at 25°C. What is the value of b for BrO− at 25°C?
Answers
If Ka for HBrO is 2. 8×10^−9 at 25°C, then the value of Kb for BrO− at 25°C is 3.5× 10^(-6).
What is base dissociation constant?The base dissociation constant (Kb) is defined as the measurement of the ions which base can dissociate or dissolve in the aqueous solution. The greater the value of base dissociation constant greater will be its basicity an strength.
The dissociation reaction of hydrogen cyanide can be given as
HCN --- (H+) + (CN-)
Given,
The value of Ka for HCN is 2.8× 10^(-9)
The correlation between base dissociation constant and acid dissociation constant is
Kw = Ka × Kb
Kw = 10^(-14)
Substituting values of Ka and Kw,
Kb = 10^(-14) /{2.8×10^(-9) }
= 3.5× 10^(-6)
Thus, we find that if Ka for HBrO is 2. 8×10^−9 at 25°C, then the value of Kb for BrO− at 25°C is 3.5× 10^(-6).
DISCLAIMER: The above question have mistake. The correct question is given as
Question:
Given that Ka for HBrO is 2. 8×10^−9 at 25°C. What is the value of Kb for BrO− at 25°C?
learn more about base dissociation constant:
https://brainly.com/question/9234362
#SPJ4
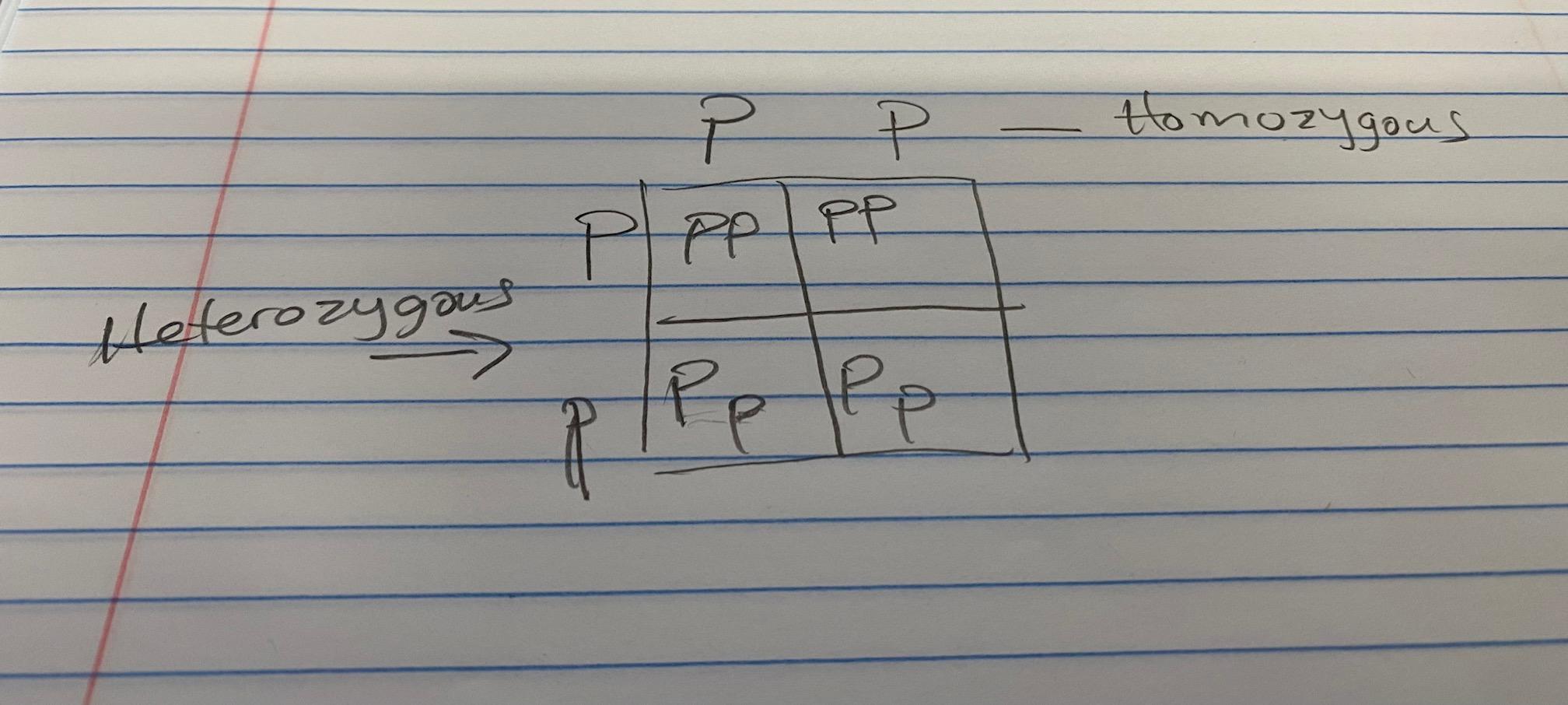
This is the picture btw because it wont let me say all the words.

Answers
Answer:
see image
D is the answer
Explanation:
see image
the box is like a mini multiplication table
8th Grade Checkpoint 1
Which statement accurately describes the atoms of a specific element?
An iridium, Ir, atom contains 77 protons inside the nucleus and 115 neutrons outside the nucleus.
palladium, Pd, atom contains 46 electrons outside the nucleus and 45 neutrons inside the nucle
An antimony, Sb,atom contains 51 protons inside the nucleus and 51 electrons outside the nucleu
A mercury, Hg, atom contains 80 electrons and 80 protons inside the nucleus.
Answers
Answer:
Antimony, Sb, an atom contains 51 protons inside the nucleus and 51 electrons outside the nucleus.
Explanation:
Option “C” is correct because protons exist inside the nucleus and electrons exist outside the nucleus. Moreover, Sb has the number of protons 51 that is found in the nucleus and it has 51 electrons that exist outside the nucleus. However, the nucleus contains protons and neutrons while electrons exist outside of the nucleus. All the given options do not follow such condition therefore, all the statements are incorrect accept option 3rd.
Question 3
Which of the objects described is most likely a galaxy?
A particle of debris in the solar system that does not
orbit any object
o A ball of ice and gas orbiting a star
o A massive system of stars, gas and dust held together
o A body of gas and dust that gives birth to stars
Answers
Answer:
maybe the third option?
The theoretical yield of NaBr from 2.36 mol FeBr3 is 7.08 mol NaBr. What is the percent yield if 6.14 mol NaBr were collected?
Answers
The percent yield for the reaction in this example is 100%, which is equal to the theoretical yield of NaBr from 2.36 mol FeBr3 of 7.08 mol NaBr.
What is NaBr's theoretical yield?The lesser amount, or 13.7 g NaBr, represents the potential yield. 15.45 grams of NaBr can never be produced because after 13.7 grams of NaBr are created, the reaction runs out of NaI and stops generating NaBr product. As the limiting reactant, NaI is well-known.
How is % yield determined?The final answer is expressed in percent by dividing the experimental yield by the theoretical yield and multiplying the result by 100. In general, the percent yield value is less than 100%,
To know more about theoretical yield visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/14966377
#SPJ1
Answer: 87%.
Explanation:
The only sure evidence for chemical reaction is
Answers
A second grade student approaches you and says that she learned that a lunar eclipse is the result of the Earth blocking the sun's rays from reaching the moon, which makes it look like the moon "disappears" from the sky for a night. Explain to her why this is incorrect.
Answers
Answer:
nah she right
Explanation:
Answer:
This is incorrect because a Lunar Eclipse blocks the Sun's rays from reaching EARTH. So for a few seconds, maybe minutes, there is not direct light on earth. So she is incorrect.
Explanation:
I am pretty sure this is right. I hope this helps
Write the rate of reaction in terms of the rate of disappearance of reactant and the rate of formation of the product NO(g) +O3 _NO2(g) + O2(g)
Answers
Answer:
See Explanation
Explanation:
The rate of reaction means the same thing as the speed of a reaction. It refers to how quickly or slowly the reactants disappear or how quickly or slowly the products appear per unit time.
The equation of the reaction is; NO(g) + O3(g)→ NO2(g) + O2(g)
We can write differential equations to show the rate of disappearance of reactants or rate of appearance of products as shown below where the rate of reaction has been denoted as r;
r = -d[NO(g)]/dt = -d[O3(g)]/dt
OR
r = d[NO2(g)]/dt = d[O2(g)]
The negative signs shows that the concentration of reactants decreases with time while the positive sign shows that the concentration of products increases with time.
a possible excited state for the atom has an electron in the orbital. list all possible sets of quantum numbers , , and for this electron
Answers
A possible excited state for the atom has an electron in the orbital. list all possible sets of quantum numbers and for this electron depend on the specific orbital it occupies
For example, if the electron is in a 2p orbital, the possible sets of quantum numbers are n=2, l=1, and ml=-1, 0, or 1. If the electron is in a 3d orbital, the possible sets of quantum numbers are n=3, l=2, and ml=-2, -1, 0, 1, or 2. The set of quantum numbers that fully describes an electron also includes the spin quantum number, ms, which can have a value of +1/2 or -1/2.
So for the excited state with an electron in an orbital, the possible sets of quantum numbers are unique to each orbital and include n, l, ml, and ms. Overall, the specific combination of quantum numbers characterizes each electron and determines its properties and behavior within the atom. So therefore the possible sets of quantum numbers for an electron in an excited state depend on the specific orbital it occupies.
Learn more about quantum numbers at
https://brainly.com/question/14307071?
#SPJ11
what mass of sulfur must be used to produce 13.7 liters of gaseous sulfur dioxide at STP accoring to the following equation?
S8(s)+8Oz(g)->8 So2 (g)
URGENT
Answers
Approximately 17.24 grams of sulfur must be used to produce 13.7 liters of gaseous sulfur dioxide at STP. S8(s)+8Oz(g)->8 So2 (g)
To determine the mass of sulfur required to produce 13.7 liters of gaseous sulfur dioxide at STP, we can use the stoichiometry of the given chemical equation. From the balanced chemical equation, we know that 1 mole of S8 reacts with 8 moles of O2 to produce 8 moles of SO2. We also know that at STP, 1 mole of any gas occupies 22.4 liters of volume. Therefore, we can use the following steps to calculate the mass of sulfur required:
Convert the given volume of SO2 to moles using the ideal gas law:
n = PV/RT = (1 atm x 13.7 L)/(0.08206 L.atm/mol.K x 273 K) = 0.535 mol
Use the stoichiometry of the equation to determine the moles of S8 required:
1 mol S8 : 8 mol SO2
x mol S8 : 0.535 mol SO2
x = 0.067 mol S8
Finally, calculate the mass of S8 required using its molar mass:
mass = n x M = 0.067 mol x 256.5 g/mol = 17.24 g
for more questions on gaseous
https://brainly.com/question/25736513
#SPJ11
Sublimation is snow or ice changing to a gas without melting. What must happen to the molecules for this to happen?
Answers
Answer:Sublimation is the conversion between the solid and the gaseous phases of matter, with no intermediate liquid stage. For those of us interested in the water cycle, sublimation is most often used to describe the process of snow and ice changing into water vapor in the air without first melting into water.
Explanation:
I am struggling big time with this whole worksheet. Could somebody please help me? Thanks

Answers
Answer:
1.) Answer: of atoms (molecules)÷ avogadro no. Since one mole is defined as 6.022 x 10^23, and there are two hydrogen per molecule, that would mean that there are exactly 12.044 x 10^23 molecules of hydrogen in one mole of water.
2.)How many moles are in 8.30 X 1023 molecules of H2O? 1.38 moles H2O
3.)1 mol of water contains 6.022 × 1023 H2O molecules Therefore 0.500 mol contains 0.500 × (6.022 × 1023) = 3.01 × 1023 H2O molecules.
4.)6.02x1023 atoms
5.) 9.03x1023 atoms Hg 9.03x1024 atoms Hg 903 atoms of Hg
6.)6.022×1023
7.)1.51x1023 atoms Rb
8.)0.048 moles
9.)2.04
10.)How many moles are in 5.25 X 1025 atoms of Au? 87.2 moles Au
Explanation:
name gaseous element in period 2 group 16?
Answers
Answer:
mark me as a brainlist answer
Explanation:
Oxygen
2. If a student drops a 2.3 g piece of magnesium into a flask of hydrochloric acid, this reaction occurs: Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2
How many liters of hydrogen can be produced at a pressure of 2 atm and a temperature of 298 K?
Answers
1.2 L of hydrogen can be produced at a pressure of 2 atm and a temperature of 298 K.
What is an ideal gas equation?The ideal gas law (PV = nRT) relates the macroscopic properties of ideal gases. An ideal gas is a gas in which the particles (a) do not attract or repel one another and (b) take up no space (have no volume).
Step 1: Write the balanced equation
Mg + 2 HCl ⇒ MgCl₂ + H₂
Step 2: Calculate the moles corresponding to 2.3 g of Mg
The molar mass of Mg is 24.31 g/mol.
2.3 g × 1 mol ÷24.31 g = 0.095 mol
Step 3: Calculate the moles of H₂ produced
0.095 mol Mg × 1 mol H₂ ÷ 1 mol Mg = 0.095 mol H₂
Step 4: Calculate the volume occupied by the hydrogen
We will use the ideal gas equation.
P × V = n × R × T
V = n × R × T÷P
V = 0.095 mol × (0.0821 atm.L/mol.K) × 298 K÷2 atm
V = 1.2 L
Learn more about the ideal gas here:
https://brainly.com/question/27691721
#SPJ1
When a mycelium infiltrates an unexploited source of dead organic matter, what are most likely to appear within the food source soon thereafter?.
Answers
Fungal digestive enzymes are most likely to appear within the food source soon thereafter. Mycelium has a porous structure made up of tubular filaments known as hypha.
Every single mycelium fiber is made up of an array of slender cells that are separated by cross walls, known as septum, and are all enclosed within the same cell wall. Tiny holes in the septum allow nutrients, water, and other small molecules, as well as mycelium fiber, to move quickly from cell to cell. Mycorrhizae are symbiotic relationships that fungi and plants form. Fungi colonize the root system of a host plant, increasing water and nutrient absorption, while the plant provides carbohydrates formed by photosynthesis to the fungus.
Learn more about mycelium here-
https://brainly.com/question/28299182
#SPJ4
Answer:
Explanation:
Fungal haustoria are most likely to appear in the food source shortly after a mycelium invades an untapped source of dead organic matter.
What do fungal haustoria do?
A specialized fungal hypha that breaks through the wall of a plant cell and expands inside of it creates a haustorium.
The haustorium is encircled by an extrahaustorial membrane, a thickened version of the plant cell plasma membrane, rather than being situated inside the cytoplasm of the plant cell.
Are haustoria produced by fungi?
All significant divisions of fungi create haustoria.
There are various types of haustoria.
Generally, the fungus increases the surface area in contact with the host plasma membrane upon penetration and releases enzymes that disintegrate the cell walls, allowing for a greater potential transfer of organic carbon from the host to the fungus.
What kind of structure is a haustoria?
Haustoria are incredibly diverse plant parasite structures.
Haustoria are visible on exposed roots in root parasites.
At the location of contact between the parasite and the host, they manifest as swollen tissue.
In dodders, haustoria are structures that connect the host and parasite and have the appearance of pegs or suction cups.
To learn more about fungual haustoria visit:
https://brainly.com/question/15171673
#SPJ4
Calculate the mass of crystals expected when a saturated solution of potassium chloride is cooled from 75
degreess Celsius to 55 degrees Celsius
Answers
The solubility of potassium chloride decreases, leading to the formation of crystals.
The mass of crystals expected to form when a saturated solution of potassium chloride is cooled from 75 degrees Celsius to 55 degrees Celsius can be calculated using the principles of solubility and saturation.
As the temperature of the solution decreases, the solubility of potassium chloride decreases, which means that the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in the solution also decreases. This leads to a situation where the solution becomes supersaturated, meaning that there is more solute in the solution than it can hold at that temperature.
When a solution is supersaturated, any slight disturbance can cause the excess solute to crystallize out of the solution. This can be achieved by introducing a seed crystal or simply by cooling the solution.
The mass of crystals that will form depends on the amount of excess solute in the solution and the rate at which it crystallizes. Factors such as the surface area of the container and the rate of cooling can also affect the crystal formation.
Therefore, without knowing the initial conditions such as the volume of the solution or the amount of potassium chloride initially dissolved, it is impossible to accurately predict the mass of crystals expected to form. However, it can be concluded that as the temperature of the solution decreases, the solubility of potassium chloride decreases, leading to the formation of crystals.
To know more about potassium chloride, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/22528097
#SPJ1
The Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG) has the composition of 60% Propane (C 3
H 8
) and 40% Butane (C 4
H 10
) by volume: (a) Find the wet volumetric and gravimetric analysis of the products of combustion when the equivalence ratio (Φ)=1.0. (b) What is the stoichiometric air to fuel ratio for the LPG.
Answers
The balanced combustion reaction for propane can be represented as:
C₃H₈ + (5/2)O₂ → 3CO₂ + 4H₂O
And the balanced combustion reaction for butane can be represented as:
C₄H₁₀ + (6.5)O₂ → 4CO₂ + 5H₂O
Since LPG is composed of 60% propane and 40% butane by volume, we can calculate the wet volumetric and gravimetric analysis based on these proportions.
Wet volumetric analysis:
For the wet volumetric analysis, we consider the volume of the products of combustion relative to the volume of the LPG consumed.
Propane (C₃H₈):
The stoichiometric coefficient of propane in the combustion reaction is 3. Therefore, for every mole of propane burned, we will have 3 moles of CO₂ and 4 moles of H₂O formed.
Butane (C₄H₁₀):
The stoichiometric coefficient of butane in the combustion reaction is 4. Therefore, for every mole of butane burned, we will have 4 moles of CO₂ and 5 moles of H₂O formed.
Considering the initial composition of 60% propane and 40% butane by volume, we can calculate the volumetric composition of the products of combustion:
Volumetric composition of CO₂:
(0.6 * 3) + (0.4 * 4) = 3.6
Volumetric composition of H₂O:
(0.6 * 4) + (0.4 * 5) = 4.6
Therefore, the wet volumetric analysis of the products of combustion is 3.6 parts CO₂ to 4.6 parts H₂O.
Wet gravimetric analysis:
For the wet gravimetric analysis, we consider the mass of the products of combustion relative to the mass of the LPG consumed.
Using the molar masses of the compounds involved in the combustion reaction:
Molar mass of CO₂ = 44 g/mol
Molar mass of H₂O = 18 g/mol
Gravimetric composition of CO₂:
(0.6 * 3 * 44 g/mol) + (0.4 * 4 * 44 g/mol) = 158.4 g
Gravimetric composition of H₂O:
(0.6 * 4 * 18 g/mol) + (0.4 * 5 * 18 g/mol) = 74.4 g
Therefore, the wet gravimetric analysis of the products of combustion is 158.4 grams CO₂ to 74.4 grams H₂O.
(b) The stoichiometric air to fuel ratio for LPG can be determined based on the balanced combustion equations for propane and butane.
For propane (C₃H₈):
C₃H₈ + (5/2)O₂ → 3CO₂ + 4H₂O
The stoichiometric coefficient for propane is 1, which means we need 5/2 moles of O₂ for every mole of propane.
For butane (C₄H₁₀):
C₄H₁₀ + (6.5)O₂ → 4CO₂ + 5H₂O