how is a trihalomethane molecule different from a methane molecule
Answers
A trihalomethane molecule is different from a methane molecule in terms of the presence of halogen atoms.
The carbon atom in a methane molecule (CH4) is joined to four hydrogen atoms to form the compound. It is a straightforward hydrocarbon and doesn't have any halogen atoms in it.
A trihalomethane molecule, on the other hand, is a halogenated form of methane.
It is similar to methane in that it has one carbon atom connected to three hydrogen atoms, but it additionally has three halogen atoms (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine) coupled to the carbon atom.
Iodoform (CHI3), bromoform (CHBr3), and chloroform (CHCl3) are a few examples of trihalomethanes.
Trihalomethanes differ from methane molecules in the chemical characteristics and reactivities introduced by the addition of halogen atoms. Polarity, boiling point, and solubility are impacted by it.
To learn more about halogen, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/31220722
#SPJ11
Related Questions
help me with my bell work

Answers
Answer:
1) It gets slower the farther out they are.
2) The farther out you are from the sun the less gravitational pull you have, which makes it go slower as it orbits.
3) Gravity ;) :)
Explanation:
Hope this helps! Plz mark as brainliest! :)
1.) The four inner planets have slower orbits and the four outer planets have faster orbits.
2.) The closer a planet is to the Sun, the stronger the Sun's gravitational pull on it, and the faster the planet moves.
3.) Gravity
In a laboratory setting, concentrations for solutions are measured in molarity, which is the number of moles per liter (mol/L). Concentrations are often converted to more common units on the labels of household products. For a particular brand of bleach, the concentration of sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) is reported on the bottle as 7.25% by mass. The following information can thus be used to calculate the molarity of NaClO in the bleach:
• 1L of bleach has a mass of 1,100 grams.
• 7.25% of the mass of bleach is NaClO.
• 1 mol of NaClO has a mass of 74.44 grams.
What is the molarity (mol/L) of NaClO in the bleach?
Answers
The molarity of NaClO in the bleach is 0.101 M (mol/L).
Molarity (M) is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
It is calculated by dividing the number of moles of solute by the volume of the solution in liters.
To find the molarity of NaClO in the bleach, we need to use the following information given in the question:
1L of bleach has a mass of 1,100 grams7.25% of the mass of bleach is NaClO1 mol of NaClO has a mass of 74.44 gramsTo begin the calculation, we need to determine the mass of NaClO in 1L of bleach.
To do this, we can use the fact that 7.25% of the mass of bleach is NaClO:Mass of NaClO in 1L of bleach = 0.0725 x 1,100 g = 79.75 g
Next, we can convert this mass of NaClO to moles using its molar mass:
moles of NaClO = 79.75 g / 74.44 g/mol = 1.07 mol.
Finally, we can use the formula for molarity to calculate the molarity of NaClO in the bleach:
Molarity = moles of solute / volume of solution in litersMolarity = 1.07 mol / 10 L = 0.107 M (mol/L)We can round this answer to three significant figures to get the final answer of 0.101 M (mol/L).
For more such questions on molarity
https://brainly.com/question/17138838
#SPJ8
In a particular experiment, a 4. 00 g sample of CaO is reacted with excess water and 2. 14 g of Ca(OH)2 is recovered. What is the percent yield in this experiment
Answers
\textbf{Question:}
In a particular experiment, a 4.00 g sample of CaO is reacted with excess water, and 2.14 g of Ca(OH)2 is recovered. What is the percent yield in this experiment?
\textbf{Answer:}
The Percent yield in this experiment is 40.5%.
What is the percent yield?
In chemistry, the percentage yield is used to compare a reaction's actual outcome to the maximum anticipated outcome.
The actual yield and the theoretical yield must be compared in order to calculate the percent yield.
Given: \ce{CaO}mass equals 4.00 g
\ce{Ca(OH)2}
recovered mass (actual yield): 2.14 g
The reaction's chemical equation is balanced as follows:
\ce{Ca(OH)2(s)} is created when \ce{CaO(s)} and water combine.
The stoichiometric ratio of \ce{CaO}to \ce{Ca(OH)2} is 1:1, as can be shown from the equation. It follows that 1 mole of \ce{CaO} interacts to become 1 mole of \ce{Ca(OH)2}.
We first compute the amount of moles of \ce{CaO} to be used in the theoretical yield calculation:
Moles of \ce{CaO} = \(\frac{{\text{{Mass of \ce{CaO}}}}}{{\text{{Molar mass of \ce{CaO}}}}}\)
\ce{CaO}'s molecular weight is 40.08 \, \text{g/mol}.
Moles of CaO = \(\frac{{4.00 \, \text{{g}}}}{{40.08 \, \text{{g/mol}}}}\)
Next, we determine the theoretical yield of \ce{Ca(OH)2} in grams:
Theoretical yield = Moles of CaO \times \text{{Molar mass of \ce{Ca(OH)2}}}
The molar mass of \ce{Ca(OH)2} is 74.09 \, \text{g/mol}.
Theoretical yield = Moles of CaO \times 74.09 \, \text{{g/mol}}
Finally, we can calculate the percent yield:
Percent yield = \(\frac{{\text{{Actual yield}}}}{{\text{{Theoretical yield}}}} \times 100\%\)
Percent yield = \(\frac{{2.14 \, \text{{g}}}}{{(\text{{Moles of CaO}}) \times 74.09 \, \text{{g/mol}}}}\) \times 100\%
Hence, the percent yield in this experiment is approximately 40.46\%.
---
To know more about percent yield from the given link:
https://brainly.com/question/2451706
#SPJ4
Explain what happens to the temperature of an ice cube as it melts.
Answers
Answer:
the temperature of the ice cube makes it gets warmer
The atomic mass of iron is 55.85, and oxygen is 16.0. What is the mass of 6.02 × 1023 molecules of Fe2O3?
Answers
Answer:159.7grams
Explanation:
(55.85)2+(16)3
159.7grams
Answer:
The correct answer for plato/edmentum is C (159.7g)
Iron has a density of 7.87 g/cm3. If 52.4 g of iron is added to 75.0 mL of water in a graduated cylinder, to what volume reading will the water level in the cylinder rise?
Answers
Answer: 81.7 ml
Explanation:
1 cm^3 = 1 ml
Divide the total mass by it's density to find it's volume:
(52.4g/7.87g/ml) = 6.658 ml
Add to 75.0 ml to arrive at a final volume of 81.7 ml
The mass number is used to calculate the number of___________ in one atom of an element. In order to calculate the number of neutrons you must subtract the ______________________ from the________
Answers
Answer:
Neutrons, Atomic Number, Atomic Mass
Explanation:
The Atomic mass is used to calculate the number of Neutrons in an atom.
Every atom is composed of Protons and Neutrons forming a tight compact nucleus orbited by electrons. The Atomic number of an element tells how many Protons the nucleus has. This is important because it determines how many electrons the atom has and consequently, its chemical properties. The Atomic mass (rounded to the nearest whole number) is the sum of the Protons and Neutrons in the elements nucleus, since their masses are nearly identical (Neutrons have one electron worth more mass than Protons). You subtract an element's Atomic number from its Atomic mass and you get the number of neutrons the element has in the nuclei of its atoms.
clerice midter
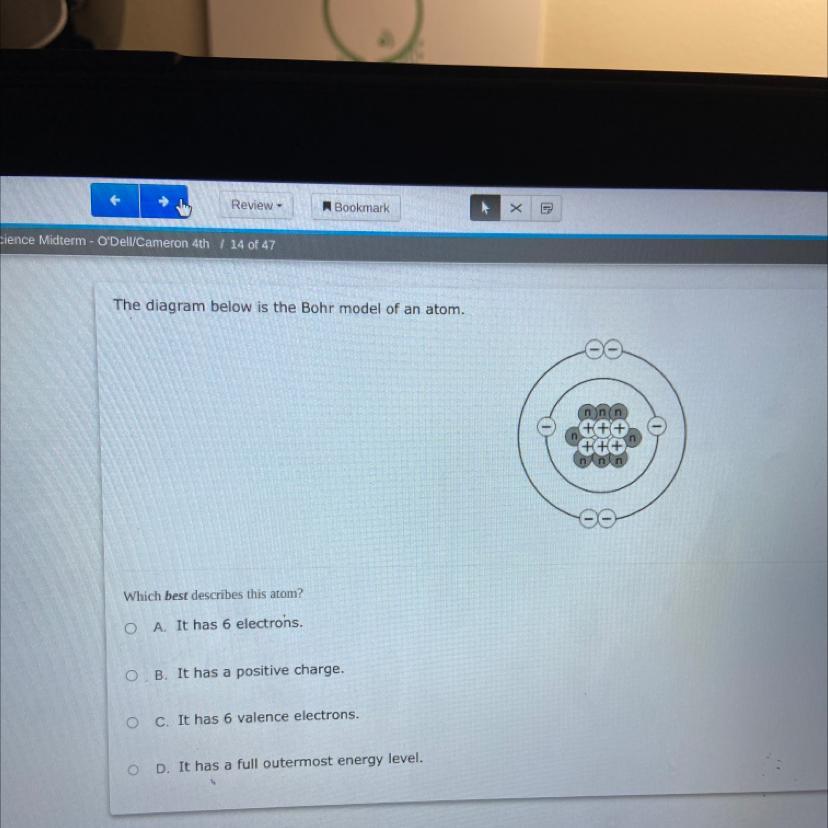
The diagram below is the Bohr model of an atom.
Which best describes this atom?
OA. It has 6 electrons.
OB. It has a positive charge.
O c. It has 6 valence electrons.
OD.
has a full outermost energy level.
Answers
The correct option is (A) - This Bohr Model of atom describes that there are a total of 6 electrons in the given figure.
What is Bohr Model of atom?The electrons are positioned in circular orbitals at particular distances from the central nucleus in the Bohr model of the atom. These orbits create electron shells or energy levels, which allow us to see how many electrons are present in each shell. The number and the letter "n" are used to identify these energy levels. The first energy level nearest to the nucleus, for instance, is represented by the 1n shell. Normally, an electron resides in the shell with the lowest energy, which is the one closest to the nucleus. A photon of light's energy can raise it to a higher energy shell, but this is an unstable position, and the electron quickly returns to the ground state.
Learn more about atom here:
https://brainly.com/question/30898688
#SPJ1
If 14 moles of Oxygen burn how many moles of water are created? *
2C2H6
+
702
4CO2 + 6 H2O
A) 12 mol H20
B) 3.5 mol H20
C) 3 mol H20
D) 42 mol H20
Answers
Answer:
A) 12 mol H2O.
Explanation:
Hello,
In this case, for the given reaction:
\(2C_2H_6+7O_2\rightarrow 4CO_2 + 6 H_2O\)
We notice that oxygen is in a 7:6 molar relationship with water, for that reason, the resulting moles of water turn out:
\(n_{H_2O}=14molO_2*\frac{6molH_2O}{7molO_2} \\\\n_{H_2O}=12molH_2O\)
Thus, the answer is A) 12 mol H2O.
Best regards.
What volume is occupied by 500 g of fluorine gas at 5.00 at a pressure of 735 torr?
Answers
500 g of fluorine gas at 5.00 atm and 735 torr occupies a volume of approximately 4.97 liters.
To solve this problem, we can use the Ideal Gas Law, which states:
PV = nRT
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature.
To find the volume of fluorine gas, we need to rearrange the Ideal Gas Law equation to solve for V:
V = (nRT)/P
We are given the pressure (P = 735 torr), the mass (m = 500 g), and the temperature (T = 5.00 atm). However, we need to find the number of moles of fluorine gas in order to use the Ideal Gas Law.
We can use the molar mass of fluorine (F2) to convert from grams to moles:
molar mass of F2 = 2 x 19.00 g/mol = 38.00 g/mol
moles of F2 = mass/molar mass = 500 g/38.00 g/mol = 13.16 mol
Now we can plug in the values into the Ideal Gas Law equation:
V = (nRT)/P = (13.16 mol x 0.0821 L·atm/mol·K x 278.15 K)/735 torr
V = 4.97 L
Learn more about volume at
https://brainly.com/question/11406830
#SPJ4
if 24.0% of a sample of radioisotope decays in 8.73 s, what is the half-life of this isotope (in seconds)?
Answers
If, a 24.0% of a sample of radioisotope decays in 8.73 s. Then, the half-life of this isotope will be -22.07 s.
To determine the half-life of the radioisotope, we can use the decay constant (λ), which is related to the half-life (T) through the following equation;
λ = ln(2) / T
where; λ = decay constant
T = half-life
Given; Decay percentage = 24.0%
Time = 8.73 s
First, we need to calculate the decay constant (λ) using the decay percentage;
Decay constant (λ) = -ln(1 - (decay percentage / 100)) / Time
λ = -ln(1 - (24.0 / 100)) / 8.73 s
Next, we can calculate the half-life (T) using the decay constant.
T = ln(2) / λ
T = ln(2) / (-ln(1 - (24.0 / 100)) / 8.73 s)
Simplifying further;
T ≈ ln(2) × 8.73 s / ln(1 - 0.24)
T ≈ 0.693 × 8.73 s / ln(0.76)
T ≈ 6.04989 s / (-0.27443)
T ≈ -22.07 s
Therefore, the half-life will be -22.07 s.
To know more about half-life here
https://brainly.com/question/24710827
#SPJ4
if 6 moles of a a compound produce 84 J of energy, what is the h reaction in j/mol
Answers
The enthalpy of the reaction is 14 J/mol.
The enthalpy of a reaction (ΔH) is the amount of energy transferred between a system and its surroundings during a chemical reaction at constant pressure, measured in joules per mole (J/mol). This value is important because it can tell us whether a reaction is exothermic or endothermic, as well as give us information about the strength of chemical bonds within the reactants and products.To calculate the enthalpy of a reaction, we need to know the amount of energy released or absorbed (Q) and the number of moles of the compound involved in the reaction (n). We can use the equation:
ΔH = Q/n
Given that 6 moles of a compound produce 84 J of energy, we can calculate the enthalpy of the reaction as follows:
ΔH = Q/n
ΔH = 84 J / 6 mol
ΔH = 14 J/mol
This means that for every mole of the compound involved in the reaction, 14 J of energy is transferred between the system and the surroundings. Since the value is positive, we can conclude that the reaction is endothermic, meaning that it requires an input of energy to occur.It is worth noting that the enthalpy of a reaction can depend on a number of factors, such as temperature, pressure, and the specific conditions under which the reaction occurs. As such, it is important to take these factors into account when calculating or predicting enthalpy values.
for such more questions on enthalpy
https://brainly.com/question/14047927
#SPJ8
Give reason:
Why Phosphorous is stored under water.
Answers
Answer:
Phosphorus ( white) us highly reactive and ignites at about 30°C when exposed to moist air
What is the mass of 0.45 mol of ammonium sulfate, (NH4)2SO4?
Answers
Answer:
59.46 g
Explanation:
To answer this question, the molecular weight of ammonium sulfate must be computed. To accomplish this, the weights of the individual elements must be noted.
N=14.01\(\frac{g}{mol}\)
H=1.01\(\frac{g}{mol}\)
S=32.07\(\frac{g}{mol}\)
O=16.00\(\frac{g}{mol}\)
To compute the molecular weight:
\(2[14.01\frac{g}{mol}+4(1.01\frac{g}{mol})]+32.07\frac{g}{mol}+4(16.00\frac{g}{mol})=132.14\frac{g}{mol}\)
To calculate the mass:
\(0.45 mol(\frac{132.14g}{1mol})=59.463g\)
What is the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 8.60 g of a solid with a
molar mass of 21.50 g/mol in 280.0 mL of solution.
Answers
Answer:
1.43 M
Explanation:
We'll begin by calculating the number of mole of the solid. This can be obtained as follow:
Mass of solid = 8.60 g
Molar mass of solid = 21.50 g/mol
Mole of solid =?
Mole = mass / molar mass
Mole of solid = 8.60 / 21.50
Mole of solid = 0.4 mole
Next, we shall convert 280 mL to litre (L). This can be obtained as follow:
1000 mL = 1 L
Therefore,
280 mL = 280 mL × 1 L / 1000 mL
280 mL = 0.28 L
Thus, 280 mL is equivalent to 0.28 L.
Finally, we shall determine the molarity of the solution. This can be obtained as illustrated below:
Mole of solid = 0.4 mole
Volume = 0.28 L
Molarity =?
Molarity = mole / Volume
Molarity = 0.4 / 0.28
Molarity = 1.43 M
Thus, the molarity of the solution is 1.43 M.
4. Why does ammonia, NH3, behave as a base when it reacts with an acid?
A It accepts a neutron and becomes NH3+.
B It accepts a proton and becomes NH4+.
OC It donates a proton and becomes NH2
Answers
B is the answer ,ammonium accepts a proton and becomes ammonium ion
What is formed when two liquids are combined but do not mix?
Answers
Answer:immiscible
Explanation:
When two liquids combine to form a new liquid, we call the liquids “miscible.” When two liquids do not mix together and instead form layers, we call them “immiscible.” The chemical properties of the liquids will determine if they will mix or not.
Determine the partial pressure and number of moles of each gas in a 16.75L vessel at 30 degree C containing a mixture of xenon and neon gases only. The total pressure in the vessel is 7.10 atm, and the mole fraction of xenon is 0.721.
What is the partial pressure of xenon?
What is the partial pressure of neon?
What is the number of moles of xenon?
What is the number of moles of neon?
Answers
First, we will calculate the number of moles of mixture of Xenon and Neon gases.Number of moles of mixture of Xenon and Neon gases:
Let x be the mole fraction of Neon.
Therefore, (1 - x) is the mole fraction of Xenon
.Mole fraction of Neon + Mole fraction of Xenon = 1x + (1 - x) = 1x = 1 - (1 -
x = 0 + x
x = 0.279
Mole fraction of Neon = 0.279
Mole fraction of Xenon = 0.721
Number of moles of gas = (Total Pressure * Volume)/(Gas Constant * Temperature)
Number of moles of Xenon = (7.10 atm * 16.75L * 0.721)/(0.08206 * (273 + 30))
Number of moles of Xenon = 8.44 moles
Number of moles of Neon = (7.10 atm * 16.75L * 0.279)/(0.08206 * (273 + 30))
Number of moles of Neon = 3.29 moles
Now, we can calculate the partial pressure of Xenon and Neon.
Partial pressure of Xenon:
Partial Pressure of Xenon = Mole fraction of Xenon * Total Pressure
Partial Pressure of Xenon = 0.721 * 7.10 atm
Partial Pressure of Xenon = 5.12 atm
Partial pressure of Neon
Partial Pressure of Neon = Mole fraction of Neon * Total Pressure
Partial Pressure of Neon = 0.279 * 7.10 atm
Partial Pressure of Neon = 1.98 atm
Learn more about atoms at
https://brainly.com/question/33049833
#SPJ11
A highly persistent chlorinated solvent decays in contaminated soil through a first order reaction where the rate constant is 1.74x10–3 /day. Plot the decay of the solvent for 10 years, and determine the time it takes for 80% decay if the initial spill created a contaminant concentration of 1,200 μg/kg of soil.
Answers
It will take approximately 398.44 days or 1.09 years for the solvent to decay by 80%.
Initial concentration of the solvent, c0 = 1200 μg/kg
Rate constant of the solvent, k = 1.74 x 10-3 /day
Using the first-order rate equation, the concentration of the solvent after time t can be calculated as shown below:
Ct = c0 e-kt
Where Ct is the concentration of the solvent at time t.
So, the concentration of the solvent after 10 years can be calculated as Ct = c0 e-kt
Where t = 10 years= 3650 days
Ct = 1200 e-(1.74 × 10-3/day × 3650 days)
= 1200 e-6.351
= 1200 × 0.0019
= 2.28 μg/kg of soil
The time it takes for 80% decay can be calculated as follows:
Ct/C0 = e-kt
Where C0 is the initial concentration of the solvent.
C0 = 1200 μg/kg, Ct = 0.8C0 = 0.8 × 1200 = 960 μg/kg
Thus, e-kt = Ct/C0 = 960/1200 = 0.8t = -ln(0.8)/k= -ln(0.8)/1.74 x 10-3 /day= 398.44 days
Therefore, it will take approximately 398.44 days or 1.09 years for the solvent to decay by 80%.
To know more about first-order rate equation visit:
https://brainly.com/question/20630467
#SPJ11
Four gases were combined in a gas cylinder with these partial pressures: 3.5 atm N2, 2.8 atm O2, 0.25 atm Ar, and 0.15 atm He.
What is the mole fraction of N2 in the mixture?
atm
Answers
The mole fraction of \(N_2\)in the mixture is approximately 0.522.
To determine the mole fraction of \(N_2\) in the mixture, we need to calculate the total pressure and the partial pressure of \(N_2\).
Given partial pressures:
P(\(N_2\)) = 3.5 atm
P(\(O_2\)) = 2.8 atm
P(Ar) = 0.25 atm
P(He) = 0.15 atm
To calculate the mole fraction, we need to consider the total pressure of the mixture, which is the sum of the partial pressures of all the gases.
Total pressure (P_total) = P(\(N_2\)) + P(\(O_2\)) + P(Ar) + P(He)
P_total = 3.5 atm + 2.8 atm + 0.25 atm + 0.15 atm
P_total = 6.7 atm
Now, we can calculate the mole fraction of \(N_2\)(X(\(N_2\))) using the formula:
X(\(N_2\)) = P(\(N_2\)) / P_total
X(\(N_2\)) = 3.5 atm / 6.7 atm
X(\(N_2\)) ≈ 0.522 (rounded to three decimal places)
Therefore, the mole fraction of \(N_2\)in the mixture is approximately 0.522.
Mole fraction represents the fraction of the total number of moles that is contributed by a particular component. In this case, the mole fraction of \(N_2\)tells us that \(N_2\)contributes about 52.2% to the total moles of the gases in the mixture.
For more such questions on mole fraction visit:
https://brainly.com/question/14783710
#SPJ8
Which is more likely to appear, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide or diatomic oxygen
Answers
Diatomic oxygen (O₂) is more likely to appear than carbon dioxide (CO₂) or carbon monoxide (CO).
This is because diatomic oxygen is a highly abundant molecule in Earth's atmosphere, making up about 21% of the air we breathe. In contrast, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide are present in much lower concentrations, with carbon dioxide making up only about 0.04% of the atmosphere and carbon monoxide being present in trace amounts.
Additionally, diatomic oxygen is involved in many important biological and chemical processes, such as respiration and combustion, which further increases its likelihood of appearing. Carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide, on the other hand, are mostly produced as byproducts of certain chemical reactions or as a result of human activities such as burning fossil fuels or deforestation.
To know more about the Carbon monoxide, here
https://brainly.com/question/22530423
#SPJ4
How does a balanced chemical equation help me predict my product amount?
Answers
The coefficients in front of each reactant and product allow us to predict how much reactants are required to form a given amount of products.
What is chemical equation?Reactants are converted to products and the process is symbolized by a chemical equation. For example (Fe) and (S) combine to form iron sulfide Fe(s) + S(s) → FeS(s) The plus sign indicates that iron reacts with sulfur.
Therefore, chemical equation is a mathematical expression of the chemical reaction which represents the product formation from the reactants. In an equation the reactants are written on the left-hand side and the products are written on the right-hand side demonstrated by one-headed.
Learn more about chemical equation: brainly.com/question/25769000
#SPJ1
“True or False”
Solubility refers to the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a certain temperature.
Answers
Answer:
true
Explanation:
what mass of calcium carbonate (in grams) can be dissolved by 4.1 g of hcl ? ( hint : begin by writing a balanced equation for the reaction between hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate.)
Answers
Mass of calcium carbonate (in grams) can be dissolved by 4.1 g of Hcl is 5.62g.
What is balanced equation?A balanced equation is one for a chemical reaction in which the overall charge and the number of atoms for each component are the same for both the reactants and the products. In other words, the mass and charge of both sides of the reaction are equal.
The reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid can be expressed through the chemical reaction,
CaCO₃ + 2HCl --> CaCl₂ + H₂O + CO₂
Hydrochloric acid has a molecular weight of 36.45 g/mol compared to calcium carbonate's molecular weight of 100 g/mol. According to the equation above, 72.9 g of hydrochloric acid may dissolve 100 g of calcium carbonate.
x = (4.1 g HCl)(100 g CaCO3 / 72.9 HCl)
x = 5.62 g.
To know more about balanced equation visit:
https://brainly.com/question/7181548
#SPJ4
An electron in an atom of hydrogen goes from energy level 6 to energy level 2. What is the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation emitted?
Answers
Answer:
410 nm
Explanation:
when an electron falls from ni=6 to nf=2 , a photon of wavelength 410 nm is emitted.
When an electron falls then the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation emitted is = 410 nm.
What is electromagnetic wavelength?
When The Electromagnetic wavelength directs to the measured distance between the trough or crest of each adjacent wave generated by the electromagnetic disturbance.
When the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is comparable to the de Broglie wavelength of its quantum (photon).
Now we are Showing that the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is comparable to the de Broglie wavelength of its quantum (photon).
Therefore, when an electron falls from ni=6 to nf=2, a photon of wavelength 410 nm is emitted.
Find more information about Electromagnetic wavelength here:
https://brainly.com/question/17212121
If you react 59.54 g of S and 78 g of HNO3, how many grams of NO2 can you
theoretically produce?
S + 6 HNO3 + H2SO4 + 6 NO2 + 2 H2O
Answers
Answer:
56.94759 grams of NO2
Explanation:
Stoichiometric Equation:
1 S + 6 HNO3 → 1 H2SO4 + 6 NO2 + 2 H2O.
This is so you can create ratios between each compound in the reaction, and identify the limiting and excess reactants to determine exactly how much can be produced?
The coefficients or molecular quantity of each compound in the balanced equation represents the amount of moles.
To figure out how much can be produced, you have to convert 59.54 g of S into moles of S and 78 g of HNO3 into moles of HNO3.
A reference such as a periodic table can be very helpful as it has the atomic mass of each element which is the mass with respect to 1 mol of that element.
The lock-and-key model and the induced-fit model are two models of enzyme action explaining both the specificity and the catalytic activity of enzymes. Following are several statements concerning enzyme and substrate interaction. Indicate whether each statement is part of the lock-and-key model, the induced-fit model, or is common to both models. Note: If you answer any part of this question incorrectly, a single red X will appear indicating that one or more of the phrases are sorted incorrectly.
Answers
The statement, which solely follows the lock and key model is that the active site of the enzyme possesses a rigid composition complementary to that of a substrate.
The substrate serves as the key and the enzyme serves as the lock in the lock and key model. This model demonstrates that the substrate has a specific form that only allows it to fit in the enzyme and prevents the binding of any other substrate. According to the induced fit model, when an enzyme's active site interacts with the proper substrate, the enzyme modifies its configuration to conform to the structure of the molecule.
The statement which follows the induced fit model is that the conformation of the enzyme changes when it combines with the substrate so that the active site fits with the substrate.
Both models imply the statements that the substrate and enzyme interact noncovalently and that the binding of the substrate to the active site of the enzyme results in an enzyme-substrate complex.
For more questions like Enzyme click the link below:
https://brainly.com/question/7197043
#SPJ4

Darlene is a dancer with ankle pain and a considerable amount of swelling. She
MOST LIKELY has what muscle disorder?
Answers
Strain is a tear in a muscle as a result of excessive use that results in a minimal bleeding inside the muscle, pain and swelling
How many grams of copper nitrate can be produced from 0.78 grams of silver nitrate and excess copper?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
This link will take you to a work sheet that I think might help.
helppppppppppppppppppppppp

Answers
ITS CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC