Identify each bond between the component atoms as sigma bonds (single bonds), one sigma bond and one pi bond (double bonds), or one sigma bond and two pi bonds (triple bonds)
Answers
In general, there are three types of bonds: sigma bonds (single bonds), one sigma bond and one pi bond (double bonds), and one sigma bond and two pi bonds (triple bonds).
Sigma bonds are the simplest type of covalent bond, formed by the direct overlap of atomic orbitals between two component atoms. These bonds result in a strong, stable connection and are typically found in single bonds.
In double bonds, there is one sigma bond and one pi bond between the component atoms. The sigma bond is formed as mentioned earlier, while the pi bond results from the sideways overlap of p orbitals, creating a bond above and below the sigma bond plane.
This combination of bonds leads to a shorter and stronger connection between the atoms compared to a single bond.
Lastly, in triple bonds, there is one sigma bond and two pi bonds between the component atoms.
The sigma bond is formed in the same manner as single and double bonds, while the two pi bonds occur when two sets of p orbitals overlap perpendicularly to each other, with one set above and below, and the other set in front and behind the sigma bond plane.
This configuration leads to an even shorter and stronger bond compared to double bonds.
To identify the bond types between component atoms, you will need to examine the molecular structure and electron sharing between the atoms involved. Count the number of shared electron pairs to determine if it's a single (sigma), double (sigma and pi), or triple bond (sigma and two pi bonds).
To know more about bonds, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/17405470#
#SPJ11
Related Questions
if a gas is 16 times as heavy as hydrogen which will diffuse faster and by what ratio
Answers
Answer:
1. Hydrogen will diffuse faster.
2. The ratio of diffusion of hydrogen gas to that of the unknown gas is 4 : 1
Explanation:
Let the rate of diffusion of hydrogen gas, H2 be R1
Let the molar mass of H2 be M1
Let the rate of diffusion of the unknown gas be R2.
Let the molar mass of the unknown gas be M2.
Molar mass of H2 (M1) = 2x1 =2g/mol
Molar mass of unknown gas (M2) = 16 times that of H2
= 16 x 2 = 32g/mol
1. Determination of the gas that will diffuse faster. This is illustrated below:
R1/R2 = √(M2/M1)
R1/R2 = √(32/2)
R1/R2 = √16
R1/R2 = 4
Cross multiply
R1 = 4R2
From the above calculations, we can see that the rate of diffusion H2 (R1) is four times the rate of diffusion of the unknown gas (R2).
Therefore, hydrogen will diffuse faster.
2. Again, from the calculations made above, the ratio of diffusion of hydrogen (R1) to that of the unknown gas (R2) is given by;
R1/R2 = 4
Therefore, the ratio of diffusion of hydrogen (R1) to that of the unknown gas (R2) is:
4 : 1
A chemistry student weighs outof phosphoric acid, a triprotic acid, into avolumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid withsolution.
Calculate the volume ofsolution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point. Round your answer tosignificant digits.
Answers
To calculate the volume of solution needed to reach the equivalence point, we need to know the concentration of the phosphoric acid solution in the volumetric flask. Let's assume that the student weighed out 0.1 moles of phosphoric acid and dissolved it in a 250 mL volumetric flask, resulting in a concentration of 0.4 M (0.1 moles / 0.25 L).
Since phosphoric acid is a triprotic acid, it can donate up to three protons (H+ ions) in a reaction. To fully titrate the acid, we need to add three equivalents of a solution that can accept these protons. Let's assume the solution used for titration is sodium hydroxide (NaOH), which can accept one proton per molecule.
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction between phosphoric acid and sodium hydroxide is:
H3PO4 + 3 NaOH → Na3PO4 + 3 H2O
From the equation, we can see that for every mole of phosphoric acid, we need three moles of NaOH to reach the equivalence point.
Therefore, the number of moles of NaOH needed to titrate the 0.1 moles of phosphoric acid is:
0.1 moles H3PO4 x 3 moles NaOH / 1 mole H3PO4 = 0.3 moles NaOH
To calculate the volume of 0.3 M NaOH solution needed to provide 0.3 moles of NaOH, we can use the formula:
moles = concentration x volume
Rearranging the formula, we get:
volume = moles / concentration
Plugging in the values, we get:
volume = 0.3 moles / 0.3 M = 1 L
Therefore, the chemistry student will need to add 1 liter (or 1000 mL) of 0.3 M NaOH solution to the phosphoric acid solution in the volumetric flask to reach the equivalence point.
https://brainly.com/question/1434653
#SPJ11
List the metals and non metals in CBr4
Answers
Answer:
Metals: Carbon,
Non-mental: bromine
Astronomers studying the planet of Acer have detected igneous rock under its surface. One astronomer makes a claim that some of the material that this igneous rock formed from used to be in sedimentary rock on the surface of Acer. If the scientist is correct, how could sedimentary rock have become igneous rock?
Answers
If the astronomer's claim is correct and igneous rock was formed from material that was originally in sedimentary rock on the surface of Acer, then the process that likely occurred is called "igneous intrusion."
What is Igneous intrusion?Igneous intrusion happens when molten rock, known as magma, is forced into layers of sedimentary rock, which is formed from the accumulation of sediments like sand, mud, or organic matter. As the magma intrudes into the sedimentary rock, it heats up the surrounding rocks and causes them to partially melt and recrystallize. Over time, as the magma cools and solidifies, it forms igneous rock.
The process of igneous intrusion can also cause the sedimentary rock layers to fold or deform, creating features like faults, folds, and uplifts. These changes in the sedimentary rock can be used by geologists to understand the history and geology of a particular region.
Learn more about igneous rock here: https://brainly.com/question/20538428
#SPJ1
Blonde hair is a dominant trait. (True or flase)
Answers
Answer:
False
Explanation:
Answer:
false
Explanation:
Which of the following is the correct sequence for the discovery of subatomic particles? a Electrons> Protons > Neutrons b Protons> Electrons> Neutrons C Electrons> Neutrons > Protons d Neutrons> Electrons > Protons
Answers
Answer:
It is A
Explanation:
Who is known for being the first to prove the earth is a sphere and not fat galileo
Answers
how many liters of hydrogen can be produced from the reaction of 80.0 g of ch4 and 16.3 g of water? what is the limiting reagent?
Answers
The reaction of 80.0 g of CH4 and 16.3 g of H2O produces 58.3 litres of H2 gas, with H2O serving as the limiting reagent.
To determine the limiting reagent and the amount of hydrogen gas produced, we need to write and balance the chemical equation for the reaction between methane (CH4) and water (H2O):
CH4 + H2O → CO + 3H2
From the balanced equation, we see that 1 mole of CH4 reacts with 1 mole of H2O to produce 3 moles of H2. Therefore, we need to first calculate the number of moles of each reactant provided:
moles of CH4 = 80.0 g / 16.04 g/mol = 4.98 mol
moles of H2O = 16.3 g / 18.02 g/mol = 0.905 mol
Next, we need to determine the limiting reagent by comparing the number of moles of each reactant to the stoichiometric ratio in the balanced equation. The reactant that produces fewer moles of H2 is the limiting reagent:From the balanced equation, 1 mole of CH4 produces 3 moles of H2, while 1 mole of H2O produces only 1 mole of H2. Therefore, H2O is the limiting reagent because it produces only 0.905 mol of H2, while CH4 would produce 14.94 mol of H2 (3 × 4.98 mol) if it were fully consumed.
Now, we can calculate the amount of H2 produced from the reaction with the limiting reagent, H2O:
moles of H2 = 0.905 mol H2O × 3 mol H2 / 1 mol H2O = 2.715 mol H2
Finally, we can convert the moles of H2 to liters of H2 at standard temperature and pressure (STP) using the ideal gas law:
V = nRT/P = (2.715 mol)(0.08206 L·atm/mol·K)(273.15 K) / (1 atm) = 58.3 L
Therefore, 58.3 liters of H2 gas can be produced from the reaction of 80.0 g of CH4 and 16.3 g of H2O, and H2O is the limiting reagent.
To learn more about limiting reagent:
https://brainly.com/question/11848702
#SPJ11
A 125 cm3 soap bubble is formed outside, where the temperature is 10.0°C. It drifts through an open door, expands and pops in a house. If the maximum volume of the bubble could be 140 cm3, what is the temperature inside the house? (In C°)
Answers
In this question, we have a situation where a gas is in constant pressure but changing its volume and temperature, and the best way to solve a situation like this, is through the Charles's gas law formula, which shows the relationship between volume and temperature when the pressure is constant. The formula is:
V1/T1 = V2/T2
We have:
V1 = 125 cm3, or 0.125 Liters
T1 = 10.0°C, or 283 K
V2 = 140 cm3, or 0.140 Liters
T2 = ?
Now we add these values into the formula:
0.125/283 = 0.140/T2
0.000442 = 0.140/T2
T2 = 0.140/0.000442
T2 = 317 K, or 44°C
What type of energy results from the burning of wood or gasoline?
electric
nuclear
chemical
Answers
Answer:Electric
Explanation: Its right.
Chemical energy results from the burning of wood or gasoline. Therefore, option (C) is correct.
What is chemical energy?Chemical energy is described as the energy which is stored in the chemical bonds formed in the chemical compounds. It is liberated during the chemical reaction and produces heat as a side-product which is known as an exothermic reaction.
Examples of chemical energy are biomass, natural gas, batteries, petroleum, and coal. When chemical energy is released from a compound, it is transformed into a completely new substance.
While burning wood or fuel, the chemical energy in the wood or gasoline is liberated as heat because of the chemical reaction of oxygen in the air and wood. This kind of chemical reaction is known as a combustion reaction. Combustion reaction converts the chemical energy stored in the wood into light energy and heat.
Therefore, in the burning of wood or gasoline, chemical energy is emitted.
Learn more about chemical energy, here:
https://brainly.com/question/1371184
#SPJ2
Water has a large number of unique properties that make it essential for our survival. Many of these properties can not exist without the others. Explain how the properties of cohesion, adhesion, capillary action, and polarity contribute to the ability of a plant to take in water through it's roots
Answers
The properties of cohesion, adhesion, capillary action, and polarity are important properties of water. These properties enable water to travel up the plant stem against gravity, leading to the plant being able to absorb water through its roots.
Water is a vital component of plant life. It is a source of nutrients and helps plants to carry out photosynthesis. Cohesion, adhesion, capillary action, and polarity are unique properties of water that are important in this process.Cohesion refers to the ability of water molecules to stick together. This is important because when water molecules stick together, they create a surface tension that helps water to maintain its shape.
This surface tension enables water to be drawn up the plant stem.Adhesion refers to the ability of water molecules to stick to other surfaces. This is important because when water sticks to the sides of the plant stem, it helps to hold the water in place, allowing the plant to absorb water through its roots.Capillary action refers to the ability of water to move through small spaces.
To know more about properties visit:
https://brainly.com/question/30983146
#SPJ11
Label the energy diagram (9 bins) for the conversion of (CH3 CH2)3 CBr to (CH3CH2)3 COH.
Answers
The energy diagram of the reaction is shown in the image attached to this answer.
What is the energy diagram?We know that in a reaction, we are dealing with the conversion of the reactants to products. In this case, there is the breakage of the bonds in the reactants and a recombination of the atoms of the reactants as they are now able to form the products.
We know that the topmost position of the energy diagram shows us the activated complex. This is the highest energy specie whose existence is transient on the way of the conversion of the reactants to the products.
The difference between the energy of the reactants and the energy of the activated complex is what we call the activation energy of the reaction which must be supplied in order for the reaction to proceed.
Learn more about reaction profile:https://brainly.com/question/29254971
#SPJ1

2 h
v=/
3
m=500g
d = ?
Answers
in general, which characteristics are necessary for a location to be suitable for chemical storage? select one or more: warm dark dry poorly-ventilated cool
Answers
Warm, dark, and poorly-ventilated locations are generally not suitable for chemical storage. it can be stored in cool places most of the time.
In general, a location suitable for chemical storage should be:
Cool: Many chemicals are temperature-sensitive and can degrade or react with other substances if exposed to high temperatures.
Dry: Moisture can cause some chemicals to react or degrade, and can also increase the risk of fire or explosion if electrical equipment is present.
Well-ventilated: Proper ventilation is important to ensure that fumes or vapors generated by the chemicals are safely dispersed.
Away from sources of heat and ignition: Chemicals should be stored away from sources of heat, sparks, and flames, to minimize the risk of fire or explosion.
Learn more about chemical storage here: brainly.com/question/8038400
#SPJ4
Complete question:
in general, which characteristics are necessary for a location to be suitable for chemical storage? select one or more:
A. Warm
B. Dark
C. Dry
D. Poorly-ventilated cool
WHICH LETTER GOES WITH EACH QUESTION
-
The different forms of a gene are each called an __________.
-
Traits are features that are coded for in _________ and can be inherited.
-
___________ developed principles of genetics by experimenting with pea plants.
-
The temperature in which an organism lives is an example of an __________ environmental influence.
-
The law of ___________ states that a parent can pass only one allele for each trait to its offspring.
-
The trait that only appears when both alleles are present is called __________.
-
A sequence of DNA that directs a cell to make a protein is a ________.
-
Millions of __________ have become extinct in the history of the Earth.
A.
allele
B.
segregation
C.
species
D.
gene
E.
recessive
F.
DNA
G.
Mendel
H.
dominant
I.
external
Answers
The answer is dna
Can a larger, cooler object have more TOTAL kinetic energy than a smaller, warmer object?
Answers
Answer:Hotter objects have a higher average kinetic energy and a higher temperature ; cooler objects have a lower average kinetic energy and a lower temperature.
Explanation:
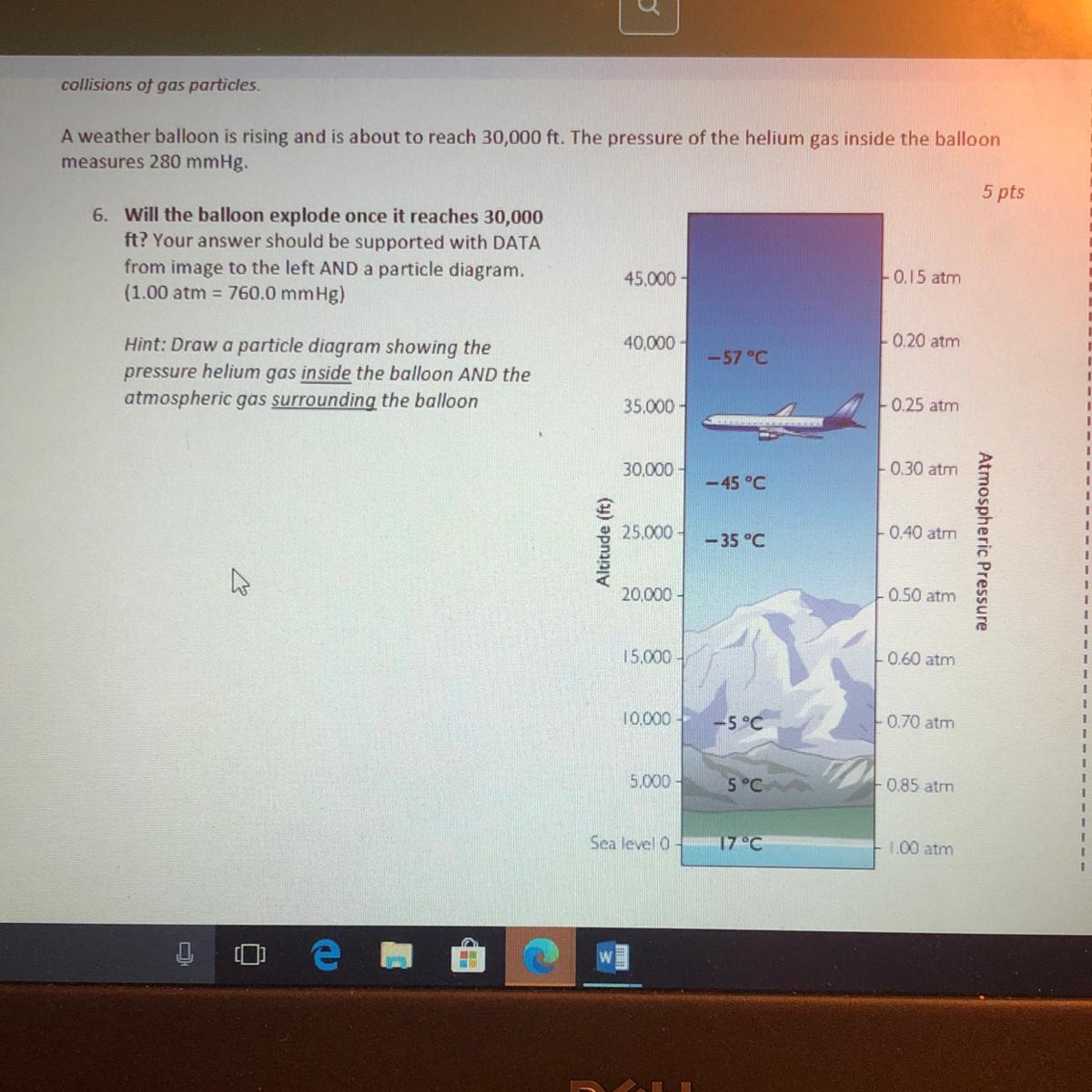
A weather balloon is rising and is about to reach 30,000 ft. The pressure of the helium gas inside the balloon
measures 280 mmHg.
5 pts
6. Will the balloon explode once it reaches 30,000
ft? Your answer should be supported with DATA
from image to the left AND a particle diagram.
45.000
0.15 atm
(1.00 atm = 760.0 mmHg)
40.000
L020 atm
-57°C
Hint: Draw a particle diagram showing the
pressure helium gas inside the balloon AND the
atmospheric gas surrounding the balloon
35.000
025 atm
30.000
0.30 atm
- 45°C
25.000
0.40 atin
Altitude (ft)
- 35 °C
Atmospheric Pressure
20.000
0.50 atm
15.000
0.60 am
10.000
-5°C
070 at
5.000
5°C
0 85 atm
Sea level
17°C
00 am
Answers
Answer:Twice a day, every day of the year, weather balloons are released simultaneously from almost 900 locations worldwide! This includes 92 released by the National Weather Service in the US and its territories. The balloon flights last for around 2 hours, can drift as far as 125 miles away, and rise up to over 100,000 ft.
Explanation:
How many nitrogen atoms are in NH4C2H3O2
Answers
Answer: 1
Explanation:
It says in the formula NH4…
there are no subscripts, or parentheses, associated with it.
Example: Total Hydrogen Atoms = H4 (4 atoms) + H3 (3) atoms = 7
Alternative if it were to say:
N4 = 4 Nitrogen Atoms
(N3Mg)2 = 6 Nitrogen Atoms, 2 Magnesium Atoms
what does zn(hg) hcl do
Answers
Zinc amalgam (Zn(Hg)) with hydrochloric acid (HCl) produces hydrogen gas (H2) and a solution of zinc chloride (ZnCl2) in water (H2O).
When zinc amalgam (Zn(Hg)) is added to hydrochloric acid (HCl), a redox reaction takes place. The HCl donates hydrogen ions (H+) to the Zn(Hg) and forms zinc chloride (ZnCl2) and hydrogen gas (H2) as products. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
Zn(Hg) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
The zinc amalgam acts as a reducing agent and reduces the hydrogen ions (H+) in the hydrochloric acid (HCl) to form hydrogen gas (H2). The hydrogen gas is produced as bubbles, which can be observed during the reaction.
The solution formed is a clear, colorless solution of zinc chloride (ZnCl2) dissolved in water (H2O). This reaction is a common demonstration of the reactivity of metals with acids and the production of hydrogen gas.
Visit here to learn more about Zinc:
brainly.com/question/15678491
#SPJ11
What will happen to the solubility of saturated KHP at room temperature if NaOH is added to the solution? (increase, decrease, or no change)? Explain your reasoning
Answers
The addition of NaOH to a solution of KHP (potassium hydrogen phthalate) will result in a decrease in the solubility of saturated KHP at room temperature.
KHP is a weak acid with the chemical formula C8H5KO4. When KHP dissolves in water, it undergoes a dissociation reaction to form K+ and HPh- ions:
C8H5KO4(s) ⇌ K+(aq) + HPh-(aq)
HPh- is the conjugate base of KHP, and it can further react with water to form H3O+ and PhO-, resulting in a slightly acidic solution:
HPh-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + PhO-(aq)
The solubility of KHP is affected by the presence of other ions in solution, such as Na+ and OH-. When NaOH is added to the solution, it reacts with the H3O+ ions to form water:
NaOH(aq) + H3O+(aq) → Na+(aq) + 2H2O(l)
As a result, the concentration of H3O+ in the solution decreases, which drives the dissociation reaction of KHP to the left, decreasing the solubility of KHP. In addition, the OH- ions can react with the HPh- ions to form water and PhOH (phenol):
HPh-(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l) + PhOH(aq)
This further reduces the concentration of HPh- ions, which also contributes to the decrease in solubility of KHP.
Know more about phenol here: https://brainly.com/question/30650792
#SPJ4
The manhattan project was responsible for the creation of _____. the atomic bomb the hydrogen bomb the first satellite the aswan dam
Answers
Which bomb was created as a part of the manhattan project?
The manhattan project was responsible for the creation of the atomic bomb.
What was the manhattan project?
The first nuclear weapons were created as a result of the Manhattan Project's research and development efforts during World War II. With the help of the United Kingdom and Canada, it was spearheaded by the United States. Major General Leslie Groves of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers oversaw the project from 1942 to 1946. Robert Oppenheimer, a nuclear physicist, served as the lab's director and was responsible for the actual bomb's design, the atomic bomb.
As the Army's first headquarters were located in Manhattan, the project's Army component was given the moniker Manhattan District, gradually replacing the official codename for the entire project, Development of Substitute Materials. The project eventually absorbed Tube Alloys, its previous British counterpart. The Manhattan Project started out small in 1939, but it eventually employed over 130,000 people and cost close to US$2 billion (about $23 billion in 2020). Less than 10% of the cost went toward the design and production of the weapons, with more than 90% going toward the construction of factories and the production of fissile material. More than thirty locations in the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada were used for research and production.
Learn more about the manhattan project here,
https://brainly.com/question/1129537
#SPJ4
Which of the following gives rise to a prominent M - 18 peak in the mass spectrum?
a. hexane.
b. 1-chloropentane.
c. 1 -pentanol.
d. 3-methylpentane.
Answers
1-chloropentane gives rise to a prominent M - 18 peak in the mass spectrum.
In mass spectrometry, a molecule is broken down into fragments and the masses of these fragments are measured. The M-18 peak is a characteristic peak that arises due to the loss of a water molecule (H2O) from the parent molecule. This can happen when a molecule contains a hydroxyl (-OH) group and a hydrogen atom that are adjacent to each other.
To know more about mass spectrum refer here:
https://brainly.com/question/1698571
#SPJ11
Which option is a use of geothermal energy?
Responses
fueling vehicles
capturing solar power
powering hybrid vehicles
generating electricity
Answers
Generating electricity from the given list option is the use of geothermal, therefore the correct option is A .
What is a nuclear power plant ?It is a type of power plant in which the power is generated with the help of a nuclear reactor involving a nuclear which could be either nuclear fission or fusion reaction.
Fueling vehicles, capturing solar power, and powering hybrid vehicles do not use geothermal energy.
Generating electricity from the given list option is the use of geothermal, therefore the correct option is A.
To learn more about Nuclear power plants here, refer to the link ;
brainly.com/question/4246037
#SPJ1
When the kinetic energy of an object changes, there must be some other change in energy at the same time?
Answers
When the kinetic energy of an object changes, the motion of that object also changes at the same time.
The amount of energy that a body posses by virtue of its motion is known as Kinetic energy. Therefore, kinetic energy can only be found in objects which are in motion. The amount of Kinetic energy is calculated as follows:
K = 1 /2 mv²
Where, K represents the kinetic energy, m is the mass of the moving object, and v is the velocity or the speed of the object at which it is moving.
If the kinetic energy of the body increases then the motion of the body also increases and if the kinetic energy decreases then the velocity also decreases.
Learn more about kinetic energy from the link given below.
https://brainly.com/question/16667164
#SPJ1
What is the pH of a 2.20 M solution of the weak acid CH3CO2H, given that the Ka of the acid is 1.76×10−5? The equilibrium expression is:
CH3CO2H(aq)+H2O(l)⇋H3O+(aq)+CH3CO−2(aq)
Answers
The pH of the 2.20 M solution of the weak acid CH3CO2H can be calculated using the equilibrium expression and the dissociation constant (Ka) of the acid.
What is the pH of the solution?To determine the pH of the solution, we need to consider the dissociation of the weak acid CH3CO2H. The equilibrium expression shows the formation of H3O+ ions (hydronium ions) and CH3CO−2 ions (acetate ions) from the dissociation of CH3CO2H in water.
The Ka value represents the acid dissociation constant and is given as 1.76×10−5. This value indicates the degree of dissociation of the acid. Since the acid is weak, it only partially dissociates, and we can assume that the initial concentration of CH3CO2H remains relatively unchanged.
To find the pH, we need to determine the concentration of H3O+ ions. Since CH3CO2H is a weak acid, we can approximate the concentration of H3O+ ions to be equal to the concentration of the acid that dissociates. Therefore, the concentration of H3O+ ions is approximately 2.20 M.
Using the equation pH = -log[H3O+], we can calculate the pH of the solution.
In this case,
\(pH = -log(2.20) = -log(2.20) = 0.657.\)
Therefore, the pH of the 2.20 M solution of CH3CO2H is approximately 0.657.
Learn more about pH
brainly.com/question/32445629
#SPJ11
Status
Exam
HF is
an acid
a base
neither an
acid nor a
base
Copyright © 2003 - 2020 Acellus Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Is HF a base, acid or non
Answers
Answer:
HF is an acid as it losses hydrogen into the sollution on hydrolysis.
Explanation:
WILL MARK BRAINLY IF GOOD ANSWER :)
Chlorine and oxygen are both gases at room temperature. What are some characteristic properties of chlorine that distinguish it from oxygen?
Answers
Answer:
Well one characteristic is electical energy transforms into thermal energy and gases and the state of matter(one of the distinct form i which matter exist)
the pressure of 5.0 l of gas increases from 1.50 atm to 3.1 atm. what is the final volume of the gas, assuming constant temperature?
Answers
The volume of the gas at constant temperature would be 4.60 L.
How this is done?
P1 = 1.5 atm
V1 = 5 lit
P2 = 1240 mm Hg = 1.63 atm
V2 = ?
P1V1 = P2V2
1.5 X 5 = 1.63 X V2
V2 = 7.5
The volume of a fixed mass of a gas decreases on cooling it and increases by increasing the temperature.
V1 / T1 = V2 / T2 (Sometimes known as Charles's Law)
V1 = is the starting volume
T1 = is the starting temperature
V2 = is the finishing volume
T2 is the finishing temperature
To know more about Charles law from the following link
https://brainly.com/question/12708400
#SPJ4
Which is a distinction between an epidemic and a pandemic?
A.
the species of organisms infected
B.
the geographical area affected
C.
the symptoms of the disease
D.
the season in which the disease spreads
Answers
Answer:
B.
a pandemic would be like COVID-19 as it spread world wide
a epidemic would be like Japanese small pox incident because it was mostly in Japan
Why must the halogenated acetanilide 5 be transformed into the amine 6 before introducing iodine into the ring? Explain in terms of the activating power of amide vs amino groups, and the electrophilicity of the iodonium ion
Answers
The halogenated acetanilide 5 must be transformed into the amine 6 before introducing iodine into the ring because of the differences in activating power between amide and amino groups, as well as the electrophilicity of the iodonium ion.
Step 1: Understand activating power.
Activating power refers to the ability of a substituent to increase the reactivity of an aromatic ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS). Amide groups (as in acetanilide) are weakly activating, while amino groups are strongly activating.
Step 2: Consider electrophilicity.
Electrophilicity refers to the ability of a molecule or ion to accept electrons from another molecule or ion. The iodonium ion is a highly electrophilic species, which means it readily accepts electrons from nucleophiles.
Step 3: Explain the transformation.
Since the iodonium ion is highly electrophilic, it requires a strongly activating group on the aromatic ring to facilitate the reaction. The amide group in halogenated acetanilide 5 is only weakly activating, which makes it difficult for the iodonium ion to react with the aromatic ring. By transforming the halogenated acetanilide 5 into the amine 6, you introduce a strongly activating amino group, which greatly increases the reactivity of the aromatic ring towards the electrophilic iodonium ion, allowing for the successful iodination of the ring.
To learn more about electrophilicity https://brainly.com/question/31051319
#SPJ11