Let 84.0 J of heat be added to a particular ideal gas. As a result, its volume changes from 90.0 to 144.0 cm3 while the pressure remains constant at 1.0 atm. By how much did the internal energy of the gas change?
a)What is the molar specific heat at constant pressure?
b)Find the molar specific heat at constant volume.
Answers
The molar heating value in normal pressure is 116.49 J/molK or the molar heating value under continuous volume is 124.42 J/molK, according to the declaration.
Why does heat form?Small units known as atoms, molecules, and ions make up all matter. These little particles vibrate back and forth or run into each other constantly. All is among a type of energy termed as heat (or thermal) energy, which is produced by the movement of particles.
Briefing:Internal energy change:
Q = 84.0 J, V = 90 cm³ = 9.0E-5 m³, V' = 144.0 cm³ = 1.44E-4 m³, P = 1 atm
W = P(V'-V) = (1.013E5)(1.44E-4 - 9.0E-5) = 5.61 J
U = Q-W = 84.0-5.61 = 78.39 J
a). Molar specific heat
Q = nCp(T' - T) = (Cp/R) nR(T' - T) = (Cp/R) P(V' - V)
so Cp = RQ/[P(V' - V)] = 8.31*84.0 / 5.61 = 124.42 J/molK
b). Molar specific heat (constant v)
Cv=Cp - R = 124.8-8.31 = 116.49 J/molK
To know more about Heat visit:
https://brainly.com/question/29753339
#SPJ4
Related Questions
a basketball weighing 0.5 kg is flying through the air at 10 m/s. what is its kinetic energy
Answers
Answer:
KE=(mv^2)/2. So (.5)(10^2)/2 = 25 J
Explanation:
. In a classic clip on America’s Funniest Home Videos, a sleeping cat rolls gently off the top of a warm TV set. Ignoring
air resistance, calculate (a) the position and (b) the velocity of the cat after 0.100 s, 0.200 s, and 0.300 s.
Answers
After 0.100 s, the cat would be 0.049 m below its initial position, with a velocity of 0.98 m/s. After 0.200 s, the cat would be 0.196 m below its initial position, with a velocity of 1.96 m/s. Finally, after 0.300 s, the cat would be 0.441 m below its initial position, with a velocity of approximately 2.94 m/s.
To calculate the position and velocity of the sleeping cat after certain time intervals, we need to make some assumptions and use basic principles of physics.
Assuming the cat falls vertically downward due to gravity and ignoring air resistance, we can apply kinematic equations to solve the problem.
(a) Position:
Using the equation for the position of an object in free fall, h = (1/2)gt^2, where h is the height, g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s^2), and t is time, we can determine the position of the cat.
After 0.100 s: h = (1/2)(9.8 m/s^2)(0.100 s)^2 = 0.049 m (approximately)
After 0.200 s: h = (1/2)(9.8 m/s^2)(0.200 s)^2 = 0.196 m (approximately)
After 0.300 s: h = (1/2)(9.8 m/s^2)(0.300 s)^2 = 0.441 m (approximately)
(b) Velocity:
The velocity of the cat can be calculated using the equation v = gt, where v is the velocity and t is time.
After 0.100 s: v = (9.8 m/s^2)(0.100 s) = 0.98 m/s (approximately)
After 0.200 s: v = (9.8 m/s^2)(0.200 s) = 1.96 m/s (approximately)
After 0.300 s: v = (9.8 m/s^2)(0.300 s) = 2.94 m/s (approximately)
To learn more about velocity
https://brainly.com/question/80295
#SPJ8
Humans interpret visible light as colors.
Colors are the result of objects reflecting and absorbing
light.
How to combine these sentences
Answers
Answer:
humans interpret visable light as colors which is the result of objects reflecting and absorbing
light.
Explanation:
Answer:
The color of an object is actually the wavelengths of the light reflected while all other wavelengths are absorbed.
Explanation:
Color, in this case, refers to the different wavelengths of light in the visible light spectrum perceived by our eyes.
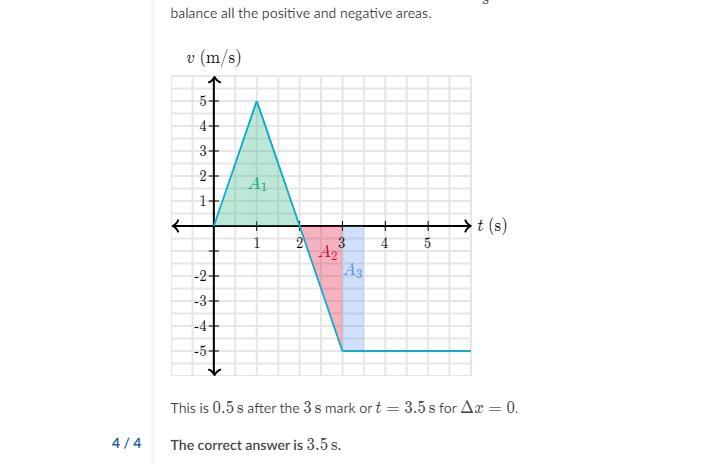
A penguin is trying to cross the street. It’s velocity v as a function of time t is given in the graph below where rightwards is the positive velocity given. At what time does the penguib have the same positition as t = 0s?
Answers
Answer:
3.5
Explanation:
Khan Academy gives the answer here.
A block of mass 2.80 kg is placed against a horizontal spring of constant k = 785 N/m and pushed so the spring compresses by 0.0750 m.

Answers
1) The electric potential energy of the block-spring system is approximately 22.03 J.
2) The block's speed after leaving the spring is approximately 2.165 m/s.
1) To calculate the electric potential energy of the block-spring system, we need to consider the potential energy stored in the spring when it is compressed. The formula for the potential energy stored in a spring is given by:
\(PE =\) \((1/2) k x^2\)
where PE is the potential energy, k is the spring constant, and x is the displacement (compression) of the spring.
Given that the spring constant, k, is 785 N/m and the displacement, x, is 0.0750 m, we can substitute these values into the formula:
\(PE =\) \((1/2) * 785 * (0.0750)^2\) = 22.03125 J
2) When the block is released, it will experience a conversion of potential energy stored in the spring into kinetic energy as it accelerates. Since the surface is frictionless, there are no dissipative forces, and the conservation of mechanical energy can be applied.
The potential energy stored in the spring is given by the equation:
\(PE =\) \((1/2) mv^2\)
where m is the mass of the block and v is its velocity.
By equating the initial potential energy to the final kinetic energy, we can solve for the velocity of the block:
\((1/2) k x^2 = (1/2) mv^2\)
Simplifying the equation:
\(v^2 = k/m * x^2\)
\(v = sqrt(k/m) * x\)
Substituting the given values:
v = sqrt(785/2.8) * 0.0750 ≈ 2.165 m/s
For such more questions on potential
https://brainly.com/question/30052338
#SPJ8
This is 30% of my overall grade
Earth has a greater mass than the moon. If the mass of the moon was as great as the earth’s mass, how would it affect the moon’s orbit?
A - The moon will end out crashing into the earth.
B - The moon will continue to orbit as usual.
C - The moon will take a larger loop around the earth.
D - The moon will circle closer to the earth, but not crash into it.
Answers
Answer: C
Explanation:
Answer: C - The moon will take a larger loop around the earth.
Explanation:
can the speed of the car immediately before the braked are applied be determined without accelerartion
Answers
Without accelerating, it is feasible to ascertain a car's speed before the brakes are used. The magnitude of the shift in location depends on an object's speed in kinematics and daily use.
Given that it calculates how much its position has changed in respect to time, it is a scalar quantity. The average speed of an object during a time interval is calculated as the distance travelled in that time interval divided by the interval's duration. The maximum size and direction of an object are referred to as magnitude in physics. Magnitude is a factor that is shared by both vector and scalar values. We are aware that scalar quantities are those that only have a single property—magnitude.
Learn more about speed here
https://brainly.com/question/28224010
#SPJ4
Why is impulse and momentum important in sports like cricket??
Answers
==============================
\( \large \sf \underline{Question:}\)
Why is impulse and momentum important in sports like cricket??==============================
\( \large \sf \underline{Answer:}\)
Impulse and momentum are important in sports like cricket because from the word "momentum" it describe itself like you're getting used of it or you know what to do like there's no stopping you.
==============================
How are impulse and momentum related?
brainly.com/question/2193212brainly.com/question/904448==============================
A car was moving at 14 m/s. After 30 s, its speed increased to 20 m/s. What was the acceleration during this time?
Answers
Answer: 0.2 m/s²
Explanation:
Acceleration= (20-14)/30 = 0.2 m/s²
I really need help with this question someone plz help !

Answers
Answer:weight
Explanation:weight
Explosion
1) Two swimmers are floating on a raft that is motionless. One swimmer has a mass of 50 kg and
the other at 80 kg. They both push off the raft at the same time. The 80 kg swimmer moves
away at 3 m/s. What velocity does the 50 kg swimmer move away with?
M1 = 50 kg
M2 = 80 kg
v2' = 3 m/s
Equation: 0= m1 (v1') + m2 (v2')
v1' =
―
Answers
Answer:
We can use the law of conservation of momentum to solve this problem, which states that the total momentum of a system before an event (in this case, pushing off the raft) is equal to the total momentum of the system after the event, assuming no external forces act on the system.
Before the push-off, the raft and the two swimmers have a total momentum of zero, since they are motionless. After the push-off, the total momentum of the system is still zero.
Let's assume that the 50 kg swimmer moves away from the raft with a velocity of v1' after the push-off. The 80 kg swimmer moves away from the raft with a velocity of 3 m/s, in the opposite direction.
Using the law of conservation of momentum, we can write:
0 = m1 * v1' + m2 * v2'
where m1 is the mass of the 50 kg swimmer, m2 is the mass of the 80 kg swimmer, and v2' is the velocity of the 80 kg swimmer after the push-off.
Substituting the values given in the problem, we get:
0 = 50 kg * v1' + 80 kg * (-3 m/s)
Solving for v1', we get:
v1' = (80 kg * 3 m/s) / 50 kg
v1' = 4.8 m/s
Therefore, the 50 kg swimmer moves away from the raft with a velocity of 4.8 m/s after the push-off.
2H, +0,-> 2H,0
How many hydrogen atoms are on the left side of the equation?
Answers
Answer:
4
Explanation:
The reaction between hydrogen and oxygen gives water (H2O)
2H,+O, -> 2H2O
Oxygen is a gas O, = O2
Balancing both sides
let , be x
2x = 4
\(x = \frac{4}{2} \)
x= 2
Therefore, 2H2 = 4 hydrogen
EASY POINTS:Which element is magnetic? calcium chromium carbon cobalt
Answers
Answer:
D
Explaination:
I got it right on the quiz
Answer:
The answer is D. cobalt! :)
Part C Now, grab Tracker’s protractor tool (the green angle in the video frame) and measure the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for the frame numbers specified in the table below. Hints: To advance the video a frame at a time, use the step buttons on the right. Position the vertex of the protractor exactly at the origin of the coordinate axis. Move the arms of the protractor so that one arm is on the vertical axis (above or below, as appropriate) and the other on the light ray.
Answers
In order to measure the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction using Tracker's protractor tool (the green angle in the video frame), the following steps should be followed:
Step 1: Open the video in Tracker software.
Step 2: Click on the "Measure" button on the toolbar at the top of the software.
Step 3: From the dropdown menu, select "Angle".
Step 4: Click on the "protractor tool" icon (the green angle in the video frame).
Step 5: Position the vertex of the protractor exactly at the origin of the coordinate axis and move the arms of the protractor so that one arm is on the vertical axis (above or below, as appropriate) and the other on the light ray.
Step 6: Measure the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for the frame numbers specified in the table below by using the step buttons on the right to advance the video a frame at a time.
Step 7: Record the measured angles in the table below. Note that the angle of incidence should be measured on the incident ray (the ray that is coming from the left), and the angle of refraction should be measured on the refracted ray (the ray that is coming from the right).In conclusion, by following these steps, one can measure the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction using Tracker's protractor tool.
For more question Tracker’s protractor tool.
https://brainly.com/question/16772121
#SPJ8
You have two contentious friends, Chris and Pat, and you’ve quickly discovered that they need you to resolve arguments they have about physics concepts. Chris says, "The spacing between two dots tells you the speed at the time of the first dot," but Pat says, "The spacing tells you the speed at the time of the second dot. How do you resolve this debate?"
Answers
Answer:
v_average = (d₂-d₁) / Δt
this average velocity is not necessarily the velocity of the extreme points,
Explanation:
To resolve the debate, it must be shown that the two have part of the reason, the space or distance between the two points divided by time is the average speed between the points.
v_average = (d₂-d₁) / Δt
this average velocity is not necessarily the velocity of the extreme points, in the only case that it is so is when there is no acceleration.
Therefore neither of them is right.
Suppose you need your silicon circuit element to run continuously for 3 minutes before it shuts off long enough to cool back down to its initial temperature. If the circuit element can withstand a temperature change of 5.1 ∘C without being damaged, what is the maximum rate at which energy can be added to the circuit element?
Answers
The maximum rate at which energy can be added to the circuit element mathematically given as
\(MER=5.044 \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{~J} / \mathrm{sec}\)
What is the maximum rate at which energy can be added to the circuit element?Generally, the equation for P is mathematically given as
\(P=\ln s \frac{\Delta T}{\Delta t}\)
Therefore
\(Rate\ of\ Change\ of\ Temp =\frac{p}{lnS}\)
\(\frac{p}{lnS}=\frac{7.4 \times 10^{-3}}{23 \times 10^{-6} \times 705}\)
\(\frac{p}{lnS}=0.456^{\circ \mathrm{c}} / \mathrm{sec}\)
Max temp Change
\(MaxT=5.6^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\)
\(\text { time }=3 \times 60\)
t=180s
In conclusion, Max Energy Rate
\(MER =23 \times 10^{-6} \times \frac{301 \times 5.6}{180}\)
\(MER=5.044 \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{~J} / \mathrm{sec}\)
Read more about Energy
https://brainly.com/question/13439286
#SPJ1
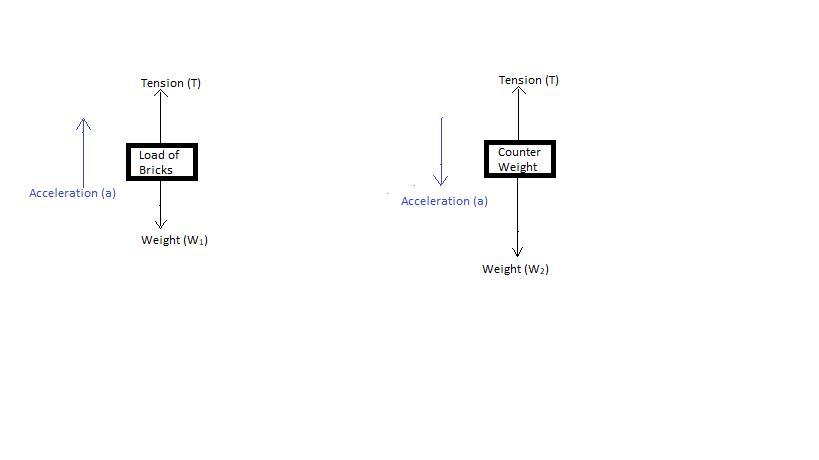
A 15.0 kg load of bricks hangs from one end of a rope that passes over a small, frictionles pulley. A 28.0 kg counterweight is suspended from the other end of the rope . the system is released from rest. A0 draw two free-body diagrams, one for the load od bricks and one for the counterweight. B) What is the magnitude of the upward acceleration of the load of bricks
Answers
Answer:
A) The free body diagrams for both the load of bricks and the counterweight are attached.
B) a = 2.96 m/s²
Explanation:
A)
The free body diagrams for both the load of bricks and the counterweight are attached.
B)
The acceleration of upward acceleration of the load of bricks is given by the following formula:
a = g(m₁ - m₂)/(m₁ + m₂)
where,
a = upward acceleration of load of bricks = ?
g = 9.8 m/s²
m₁ = heavier mass = mass of counterweight = 28 kg
m₂ = lighter mass = mass of load of bricks = 15 kg
Therefore, using these values in equation, we get:
a = (9.8 m/s²)(28 kg - 15 kg)/(28 kg + 15 kg)
a = 2.96 m/s²
Answer:
2.96 m/s2
Explanation:
Set Up: Apply ∑→ Fy=m → ay to the load of bricks & to the counterweight.
The tension is the same at each end of the rope.
The rope pulls up with the same force T on the bricks & on the counterweight.
The counterweight accelerates downward and the bricks accelerate upward; these accelerations have the same magnitude.
Solve: Apply ∑→ Fy=m → ay to each object. The acceleration magnitude is the same for the two objects.
For the bricks take +y to be upward since vector a (→ a) for the bricks is upward: ∑→ Fy=m → ay
T – m1g = m1a
For the counterweight take +y to be downward since → a is downward: ∑→ Fy=m → ay , m2g – T = m2a
Add the two equations to eliminate T and then solve for a.
m2g ⎯ m1g = m1a + m2a
(m2⎯ m1)g = (m1 + m2)a
a = (m2− m1/ m1 + m2)g
= (28 kg−15 kg/15 kg+28 kg) (9.8 m/s2) = 2.96 m/s2
A coil has resistance of 20 W and inductance of 0.35 H. Compute its reactance and its impedance to an alternating current of 25 cycles/s.
Answers
Answer:
Reactance of the coil is 55 WImpedance of the coil is 59 WExplanation:
Given;
Resistance of the coil, R = 20 W
Inductance of the coil, L = 0.35 H
Frequency of the alternating current, F = 25 cycle/s
Reactance of the coil is calculated as;
\(X_L=\) 2πFL
Substitute in the given values and calculate the reactance \((X_L)\)
\(X_L =\) 2π(25)(0.35)
\(X_L\) = 55 W
Impedance of the coil is calculated as;
\(Z = \sqrt{R^2 + X_L^2} \\\\Z = \sqrt{20^2 + 55^2} \\\\Z = 59 \ W\)
Therefore, the reactance of the coil is 55 W and Impedance of the coil is 59 W
3. An 18.0 N force pulls a cart against a 15.0 N frictional force. The speed of the cart increases 1.0 m/s every 5.0 s. What is the cart's mass?
Answers
Answer:
The total force on the cart is:
F = F(applied) - F(friction) = (18 N) - (15 N) = 3.0 N
The acceleration of the cart is:
a = (change in velocity)/(time) = (1.0 m/s)/(5.0 s) = 0.20 m/s^2
Using F = ma, the mass of the cart is:
m = F/a = (3.0 N)/(0.20 m/s^2) = 15 kg
A quarterback throws a pass at an angle of 35° above the horizontal with an initial speed of 25 m/s. The ball is caught by the receiver 2.55 seconds later. Determine the distance the ball was thrown.
Answers
The distance the ball was thrown is 52.22m by A quarterback throws a pass at an angle of 35° above the horizontal with an initial speed of 25 m/s. The ball is caught by the receiver 2.55 seconds later.
How to calculate distance?Every motion under constant acceleration is projectile motion
Angle above horizontal Ф = 35°, initial speed v1 = 25m/s , time 2.55s
Substituting value in the below equation
x=x₁ + (v₁*cosθ)(t)+1/2 *a*t²
a= 0 as acceleration in horizontal direction is zero
x= 25*cos(35)*2.55
x=52.22 m
Projectile motion is a form of motion in which object influenced when it is launched into the gravitational force from the surface of Earth along a curved path.
For more information on projectile motion kindly visit to
https://brainly.com/question/11049671
#SPJ1
explain with one example that different types of organisums live in one habitation
Answers
Answer:
When you look at a simple koi pond you can find Koi (the secondary consumer) that feeds off of the zooplankton (first consumer), they eat the phytoplankton (producers). All in a simple food chain
Explanation:
Basically, Koi eat the little animal plankton (zooplankton) that then eats the plant plankton (phytoplankton) that can only end when a part of that habitat is removed. If you got rid of the plant plankton then the whole chain would collapse and most likely die.
The diagram below shows snapshots of an oscillator at different times . What is the frequency of the oscillation ?

Answers
In the diagram tha shows snapshots of an oscillator at different times, the frequency of the oscillation is 0.555 Hz.
How to calculate the periodThe period of the oscillation is the time taken for the for the object to return to its original position. (ie. Displacement = 0). From the above snapshot,
Period of oscillation = 1.80s.
From here, finding the frequency is simple as, Frequency = 1/Period. Hence,
Frequency = 1/1.80
= 0.555 Hz (3 sf).
The frequency of the oscillation is indeed 0.555 Hz. The frequency represents the number of oscillations or cycles per second. In this case, the object completes approximately 0.555 oscillations per second.
Learn more about oscillation on
https://brainly.com/question/14628852
#SPJ1
What is one factor that affects the potential energy in a system?
Answers
Given what we know, we can confirm that the potential energy in a system is affected by the height, gravity, and mass of the object in question.
What is potential energy?This is a measurement of energy held by a system. This energy is determined by the position of the system in relation to other systems. The calculation of this system is done by way of gravity, mass, and height of the system and is therefore affected by these three factors.
Therefore, we can confirm that three factors that will affect the potential energy of a system are its mass, height, and gravity.
To learn more about potential energy visit:
https://brainly.com/question/21288807?referrer=searchResults
A string, 0.15 m long, vibrating in the n = 5 harmonic, excites an open pipe, 0.82 m long, into second overtone resonance. The speed of sound in air is 345 m/s. The distance between a node and an adjacent antinode, in the string, in mm, is closest to?
answer: 150 mm
Answers
The distance between a node and an adjacent antinode in the string is closest to 30 mm.
Determining the distanceThe fundamental frequency of the open pipe is given by:
f1 = v/2L
where v is the speed of sound in air and L is the length of the pipe. Substituting the given values, we get:
f1 = 345/(2 x 0.82)
= 210.97 Hz
The second overtone frequency of the pipe is 3 times the fundamental frequency:
f3 = 3f1 = 3 x 210.97
= 632.91 Hz
The frequency of the vibrating string is given by:
fs = n(v/2L)
where n is the harmonic number. Substituting the given values, we get:
fs = 5(345/2 x 0.15)
= 5750 Hz
The wavelength of the sound wave in the pipe that is in second overtone resonance is four times the length of the pipe:
λ = 4L = 4 x 0.82
= 3.28 m
The distance between a node and an adjacent antinode in the string is half of the wavelength of the vibrating string:
d = λ/2 = v/(2fs)
= 345/(2 x 5750)
= 0.03 m
= 30 mm
Learn more on wavelength here https://brainly.com/question/10750459
#SPJ1
Derive an expression of total energy Kinetic energy plus potential energy in rolling motion
Answers
The derivation of the total energy Kinetic energy plus potential energy in rolling motion is shown in the image attached.
What is the total energy Kinetic energy plus potential energy in rolling motion?In rolling motion, the total energy is the sum of the kinetic energy and the potential energy. Rolling motion is a combination of rotational and translational motion, and the energy of rolling can be expressed as follows:
Total energy = Kinetic energy + Potential energy
The derivation has been done and shown in the image attached here.
Learn more about kinetic energy:https://brainly.com/question/26472013
#SPJ1

At a sports car rally, a car starting from rest accelerates uniformly at a rate of 9.0m/s² over a straight-line distance of 100m. The time to beat is 4.5s.
a Does the driver do it?
b. If not, what must the acceleration be to do so?
Answers
Answer:
The driver does not do it. The acceleration must be greater than 9.0m/s² in order to beat the time of 4.5s. The acceleration must be calculated using the equation a = (d/t)², where a is the acceleration, d is the distance, and t is the time. In this case, a = (100/4.5)², which is equal to approximately 27.78m/s². Therefore, the acceleration must be greater than 27.78m/s² in order to beat the time of 4.5s.
Explanation:
Water flows at a speed of 13 m/s through a pipe that has a diameter of 1.2 m. What is the
diameter of the smaller end of the pipe that the water comes out with a speed of 30 m/s?
Answers
The diameter of the smaller end of the pipe is approximately 0.78 meters.
To determine the diameter of the smaller end of the pipe, we can use the principle of conservation of mass. According to this principle, the mass flow rate of water should remain constant throughout the pipe.
The mass flow rate is given by the equation:
Mass flow rate = density of water * cross-sectional area * velocity
Since the density of the water remains constant, we can write:
Cross-sectional area1 * velocity1 = Cross-sectional area2 * velocity2
Given that the velocity1 is 13 m/s, the diameter1 is 1.2 m, and the velocity2 is 30 m/s, we can solve for the diameter2 using the equation:
(pi * (diameter1/2)^2) * velocity1 = (pi * (diameter2/2)^2) * velocity2
Simplifying the equation:
(1.2/2)^2 * 13 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
Calculating the equation:
(0.6)^2 * 13 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
0.36 * 13 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
4.68 = (diameter2/2)^2 * 30
Dividing both sides by 30:
0.156 = (diameter2/2)^2
Taking the square root of both sides:
0.39 = diameter2/2
Multiplying both sides by 2:
0.78 = diameter2
To learn more about diameter
https://brainly.com/question/32968193
#SPJ8
Which of the following represents a velocity?
Answers
Answer:
I news an answer choice please
Explanation:
but velocity is basically the speed on something
Answer:
The meaning of velocity of an object can be defined as the rate of change of the object’s position with respect to a frame of reference and time. It might sound complicated but velocity is basically speeding in a specific direction. It is a vector quantity, which means we need both magnitude (speed) and direction to define velocity.
The SI unit of it is meter per second (ms-1). If there is a change in magnitude or the direction in the velocity of a body the body is said to be accelerating.
hope this helps
A candle is sitting in front of a concave mirror at a distance of 18.0 cm. It is found that an image of the ca
25.0 cm. What is the focal length of the mirror?
03.52 cm
07.50 cm
O 10.4 cm
022.1 cm
Answers
Answer:
The focal length of the mirror is 10.4 cm.
Explanation:
The object distance ( d₀ ) ( distance of the candle from the mirror) is -18 cm.The Image distance ( dᵢ ) ( distance of the image from the mirror) is -25.0 cm.The mirror equation is 1/f = 1/d₀ + 1/dᵢ.So substitute the values of object distance and image distance in the mirror equation,
1/f = 1/(-18cm) + 1/(-25.0cm)
1/f = -25cm/(-18cm x -25cm) - 18cm/(-18cm x 25cm)
1/f = ( -25cm - 18cm)/(18cm x 25cm)
1/f = -43.0/450.0
f = -10.4651 cm.
The focal length of the mirror is approximately -10.4 cm.
To know more about Focal Length,
brainly.com/question/31755962
brainly.com/question/2194024
Determine the cost of one no rechargeable alkaline battery ~ and compare with the cost of one rechargeable NiCad battery.
Answers
Answer:
$2.7
$0.9225
Explanation:
According to the question, the computation is shown below:
AA NiCad rechargeable batteries cost for 4 pack is $10.80.
So for one NiCad rechargeable battery is
\(= \frac {Total\ cost}{Number\ of\ pack}\)
\(= \frac{\$10.80}{4}\)
= $2.7
Now
AA NiCad non-rechargeable batteries cost for 4 pack is $3.69
So for one NiCad rechargeable battery is
\(= \frac {Total\ cost}{Number\ of\ pack}\)
\(= \frac{\$3.69}{4}\)
= $0.9225
So as we can see that cost of one NiCad rechargeable batteries is more than the cost of NiCad non-rechargeable batteries