Please, someone help me. The previous question was - Ammonium nitrite decomposes to give off nitrogen gas and liquid water. How many grams of ammonium nitrite must have reacted if 2.58 L of gas was collected over water in a gas collecting tube at 21.0°C and 97.8 kPa?
Balanced equation:

Answers
3. The amount of ammonium nitrite that must have reacted is 8.164 grams.
A. If the experiment is done at a significantly higher temperature, the volume of nitrogen gas will increase.B. If the amount of ammonium nitrite is increased, the volume of nitrogen gas will increase. C. If the experiment is not collected over water, the volume of nitrogen gas will remain the same.4a. The limiting reactant is Fe₂(CO₃)₃.
b. The volume of carbon dioxide gas that can be produced is 619 milliliters.
What mass of ammonium nitrite reacted?First, the number of moles of nitrogen gas using the ideal gas law:
PV = nRT
where:
P is pressure (in atm) = 97.8 kPa = 97.8/101.3 = 0.965 atm
V is volume (in liters) = 2.58 L
n is number of moles
R is gas constant = 0.0821 L·atm/(mol·K)
T is temperature (in Kelvin) = 21.0°C + 273.15 = 294.15 K
Solving for n:
n = (PV) / (RT)
n = (0.965 atm * 2.58 L) / (0.0821 L·atm/(mol·K) * 294.15 K)
n ≈ 0.102 moles of nitrogen gas
The moles of ammonium nitrite that reacted from the balanced chemical equation:
NH₄NO₂ → N₂ + 2H₂O
From the mole ratio above, one mole of ammonium nitrite reacts to produce one mole of nitrogen gas
Therefore, the moles of ammonium nitrite reacted is 0.102 moles.
So, the mass of ammonium nitrite that reacted is:
Mass = moles * molar mass
Mass = 0.102 moles * 80.04 g/mol
Mass ≈ 8.164 g
4a. Moles of H₃PO₄ = volume (in liters) * molarity
= 0.900 L * 3.00 mol/L
Moles of H₃PO₄ = 2.70 mol
Moles of Fe₂(CO₃)₃ = mass / molar mass
= 235 g / (2 * 55.85 g/mol + 3 * 12.01 g/mol + 9 * 16.00 g/mol)
= 235 g / 291.88 g/mol
Moles of Fe₂(CO₃)₃ = 0.804 mol
Therefore, Fe₂(CO₃)₃ is the limiting reactant.
b. From the balanced equation: 1 mol Fe₂(CO₃)₃ produces 3 moles of CO₂
Moles of CO₂ = 0.804 mol * 3
Moles of CO₂ = 2.412 moles
the volume of CO₂ will be:
PV = nRT
Where:
P is pressure = 45.5 psi or 3.099 atm
V is volume (in liters)
n is the number of moles = 2.412 mol
R is gas constant = 0.0821 L·atm/(mol·K)
T is temperature (in Kelvin) = 78°C + 273.15 = 351.15 K
Solving for V:
V = (nRT) / P
V = (2.412 mol * 0.0821 * 351.15/ 3.099
V ≈ 0.619 L = 619 mL
Learn more about limiting reactants at: https://brainly.com/question/30879855
#SPJ1
Related Questions
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) is a psychedelic drug that stimulates the reward pathway, among other effects. Which of the following is a possible mechanism of how it affects neurons?
a) LSD molecules block the release of dopamine from axon terminals.
b) LSD molecules promote the reuptake of dopamine into the presynaptic neuron.
c) LSD molecules catalyze the breakdown of dopamine in the synaptic cleft.
d) LSD molecules act as an agonist and bind to dopamine receptors
d) LSD molecules act as an agonist and bind to dopamine receptors
Answers
According to the given statement LSD molecules catalyze the breakdown of dopamine in the synaptic cleft.
The correct option is C.
How a molecule is formed?A molecule is the term used to describe the aggregate of atoms that results from the formation of covalent bonds. Therefore, we might claim that what an atom is the most basic component of a covalent composite. The two atoms Na+ and Cl- form a crystal-like lattice in salt, an ionic compound. There are many sodium chloride molecules in salt water.
How come salt is not a molecule?Table salt (NaCl) is a complex because it contains two different types of elements (sodium and chlorine), but it also not a molecule because of the ionic bond that holds it together. A lot of atoms are bound together to form gas molecules.
To know more about Molecule visit:
https://brainly.com/question/1446104
#SPJ4
In a laboratory experiment, the reaction of 3.0 mol of H2 with 2.0 mol of I2 produced 1.0 mol of HI. Determine the theoretical number of moles that could be produced in this reaction.
Answers
The reaction that is occurring in this question is:
H2 + I2 -> 2 HI
As we can see, the molar ratio for H2 and I2 is 1:1, one mole of H2 for each mole of I2, and the molar ratio between any reactant and HI is 1:2, which means the number of moles of product will be two times more than the number of moles of the reactants
We have:
3.0 moles of H2
2.0 moles of I2
1.0 moles of HI
According to the molar ratio, we should have the name number of moles of I2 and H2, which means that H2 is in excess and I2 is the limiting reactant with 2 moles
If we have 2 moles of I2, and the molar ratio of I2 and HI is 1:2, we should have 4 moles of HI being produced
Therefore the theoretical number of moles is 4.0 moles of HI from 2.0 moles of I2
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid EDTA is 41.09% C, 5.53% H, 9.58%N, and 43.8% O. What is the empirical formula of EDTA?
Answers
Answer:
41.09% B N. The formula in EDTA
Explanation:
what is the percent yield of sulfur dioxide if the burning of 25.0 g of carbon disulfide produces 40.5 g of sulfur dioxide?
Answers
Answer:
25-54-46-36 619-73 77-88-50
The birdseed above is a mixture of several different types of sizes of seeds. Is the mixture a…
A) homogeneous
B) heterogeneous
Answers
Answer:
Answer B: Heterogeneous
Explanation:
im pretty sure this is it if its not im really sorry
1. What can you conclude about the figure?
a. The arrow locations represent precision.
b. The arrow locations represent both high accuracy and
good precision.
c. The arrows have been thrown accurately toward the
bulls-eye.
d. The arrow locations represent neither accuracy
nor precision.

Answers
Answer : The correct option is, (d) The arrow locations represent neither accuracy nor precision.
Explanation :
Precision : It is defined as the closeness of two or more measurements to each other.
For Example: If we measure a length 4 times and we get 5.8 m each time. Then the measurement is very precise.
Accuracy : It is defined as the closeness of a measured value to a standard or known value.
For Example: If the weight of the substance is 40 kg and one person measures 39.9 kg and another person measures 39.8 kg. Then, the weight measured by first person is more accurate.
Hence, we from this we conclude that the arrow locations represent neither accuracy nor precision.
Answer : The correct option is, (d) The arrow locations represent neither accuracy nor precision.
Explanation :
Precision : It is defined as the closeness of two or more measurements to each other.
For Example: If we measure a length 4 times and we get 5.8 m each time. Then the measurement is very precise.
Accuracy : It is defined as the closeness of a measured value to a standard or known value.
For Example: If the weight of the substance is 40 kg and one person measures 39.9 kg and another person measures 39.8 kg. Then, the weight measured by first person is more accurate.
Hence, we from this we conclude that the arrow locations represent neither accuracy nor precision.
determine the new temperature in °c for a sample of neon with the initial volume of 2.5 l at 15 °c, when the volume is changed to 3550 ml. pressure is held constant.
a. -252 °C b. 21.3 °C c. 136 °C d. 294 °C e. 409 °C
Answers
The new temperature in °C for the sample of neon is 21.3 °C.
The correct answer is b. 21.3 °C.
To solve this problem, we can use the formula for the ideal gas law:
PV = nRT
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles of gas, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
Since the pressure is held constant, we can simplify the equation to:
V1/T1 = V2/T2
where V1 is the initial volume, T1 is the initial temperature, V2 is the final volume, and T2 is the final temperature.
Plugging in the given values, we get:
2.5 L / (15 + 273.15 K) = 3550 mL / T2
Solving for T2, we get:
T2 = (3550 mL / 2.5 L) * (15 + 273.15 K) = 21.3 °C
Learn More about neon here :-
#SPJ11
. Strong acid-titrated with strong base. Suppose the titration was reversed in question 2. You titrate 20.0 mL of 0.15 M HCl with 0.15 M NaOH. A. Add this curve to your sketch in question 2 part A. B. Then, determine the pH (a) at the start of the titration and (b) at the equivalence point. (c) What is the total volume of solution at the equivalence point
Answers
Answer:
a) attached below
b) i) 0.82 ii) 7
c) 40 mL
Explanation:
A) Titrate 20 mL of 0.15 M HCL with 0.15 M NaOH
sketch attached below
B) Determine PH at
i) start of titration
conc of H^+ = 0.15 M
HCL ------- > H^+ + CL^-
∴ pH = - log ( H^+ ) = - log ( 0.15 ) = 0.82
ii) equivalence point
at equivalence point the moles of acid = moles of base hence pH at equivalence = 7
C) Determine the total volume of solution at the equivalence point
volume of base at equivalence point
= Ma Va = Mb Vb
∴ Vb = ( Ma * Va ) / Mb
= ( 0.15M * 20 mL ) / 0.15
= 20.0 mL
Total volume of solution at equivalence point = Ma + Mb = 20 + 20 = 40 mL

A sample of gas occupies 20 mL at -109 degree C. What volume does the sample
occupy at 65 °C?
Answers
Answer: V2= 41.2mL
Explanation:
Givens:
* V1= 20ml
* T1 = -109 ⁰C --> K= ⁰C + 273.15 --> 164.15 K
* V2 = ??
* T2= 338.15 K
Use Charles law V1/T1 = V2/T2
Since we are looking for V2 we can rearrange the formula to
V2= (T2 x V1) /T1
V2= (338.15K x 20mL) / 164.15 K
V2= 41.2mL
NOTE:
Temperature should always be in K not in ⁰C or ⁰F
To convert from C to K use
*K= ⁰C + 273.15
Enter your C value in the ( ⁰C ) and you can get K
In the Bronsted-Lowry model of acids and bases, an _____ is a hydrogen donor and a _____ is a hydrogen acceptor.
Answers
Answer:
According to Bronsted-lowry concept an acid is a hydrogen donnor and a base is a hydrogen acceptor.
Explanation:
9.73 g of lead(iv) chloride contains enough cl- ions to make ____ g of magnesium chloride.
Answers
5.31g of magnesium chloride.
We'll start with the lead (IV) chloride formula. as well as how many chloride ions are present. Lead is in the 4+ oxidation state, as indicated by the (IV). Because the chloride ion is monovalent, it will require four chloride ions to balance the charge.
Pb(Cl)4
This means that for every mole of lead(IV) chloride present, there are four moles of chloride ions available. 349g/mol is the molar mass. The chloride moles are then:
\(9.73g \times \frac{1mol}{349g} \times \frac{4mol \: { cl}^{ - } }{1mol \: {pbcl}4 } = 0.1115mol \: {cl}^{ - } \)
we need 0.1115 moles of chloride ions.
magnesium is a 2+ cation and formula for magnesium chloride is : MgCl2
the molar mass is 95.2g/mol. 1 mol of magnesium chloride
gives 2 mole of chloride ions. to calculate mass of magnesium chloride needed to supply 0.1115moles of chloride,
\(0.111mol {cl}^{ - } \times \frac{1mol \: mgcl2}{2mol \: cl} \times \frac{95.2g}{1mol} = 5.31g \: mgcl2 \)
visit to learn more about molar mass,
https://brainly.com/question/7585012
#SPJ4
How would increasing the magnitude of the charges on two charged particles and decreasing the distance between the particles affect the strength of the electric force between the particles?
Type your answer here:
How can iron fillings provide evidence that can be used to explain how two magnets exert forces on each other even though the magnets are not in contact with each other?
Type your answer here:
Answers
(a) Increasing the magnitude of the charges on two charged particles and decreasing the distance between the particles increases the strength of the electric force between the particles.
(b) Iron filings can provide evidence that can be used to explain how two magnets exert forces on each other because each of the magnet can attract the iron filings.
Force between two particles
The electrostatic force between two particles is determined from Coulomb's law as shown below;
F = kq₁q₂/r²
where;
q₁ is magnitude of the first chargeq₂ is magnitude of the second charger is the distance between the two chargesThus, from the equation above, increasing the magnitude of the charges on two charged particles and decreasing the distance between the particles increases the strength of the electric force between the particles.
Force between two magnets by iron filingsIron filings can provide evidence that can be used to explain how two magnets exert forces on each other because each of the magnet can attract the iron filings.
Learn more about iron filings here: https://brainly.com/question/7692322
#SPJ1
Answer:
unit quiz k12
Explanation:
Iron filings can provide evidence that can be used to explain how two magnets exert forces on each other because each of the magnets can attract iron filings. Another thing is that the patterns of the iron fillings show lines of force that make the magnet's magnetic field. For example, when a magnet is placed in a container and you place iron fillings over the lid it makes a pattern showing the lines of forces making the magnetic field
Which solute, an electrolyte or a nonelectrolyte, has the greater effect on the boiling point when a given amount of each
solute is dissolved in the same mass of water?
O The nonelectrolyte does because it disperses into molecules.
O The electrolyte does because it disperses into molecules.
O The nonelectrolyte does because it dissociates into ions.
O The electrolyte does because it dissociates into ions.
Answers
The solute wether electrolyte or a nonelectrolyte, has the greater effect on the boiling point when a given amount of each solute is dissolved in the same mass of water The nonelectrolyte does because it dissociates into ions.
What is a solute?Solute refers to substances or liquid which can readily dissolve in a solvent. It's concentration is lower to that of solvent.
Therefore, The solute wether electrolyte or a nonelectrolyte, has the greater effect on the boiling point when a given amount of each solute is dissolved in the same mass of water The nonelectrolyte does because it dissociates into ions
Learn more about solute below.
https://brainly.com/question/16083884
#SPJ2
Answer:
D: The electrolyte does because it dissociates into ions.
Explanation:
The smallest unit of an element that maintains properties of that element is called a(n)
A
neutron
B
proton
С
atom
D
electron
Answers
Answer:
try c atom i hope this helps!! : )
Explanation:
The formula of a compound is M(OH)2 . Given that the Mr of compound is 98 , calculate Ar of M. (Ar of O = 16 , H = 1 ) WITH WOKING OUT
Answers
Answer:
The atomic weight Ar, of M is 64
Explanation:
The formula of the given compound is M(OH)₂
Mr, is the molecular weight of a compound and for the given compound, Mr is equal to 98.
Ar, is the atomic weight of the elements in the compound
The molecular weight, Mrof a compound is the mass of one mole mole of that compound. It can be obtained by summing the atomic masses of all elements in that compound. For elements that has more than one atom in the compound, the atomic weight of that element is multiplied by the number of atoms of the element present in the compound and then the sum of the weight of each element gives the molecular weight of the compound.
Onnthe compound above,the atomic weight of the unknown element M, is to be obtained.
Ar of the other elements inn he compound is given : Ar of O = 16, Ar of H = 1.
Molecular weight of the compound, Mr = 98
Calculating for the Ar of M:
(M × 1) + (16 × 2) + (1 × 2) = 98
M +32 + 2 = 98
M + 34 = 98
M = 98 -34
M = 64
Therefore, the atomic weight Ar, of M is 64
Some greenhouse gases, such as fluorocarbons (CFCs, HFCs, PFCs, etc.), are human-made. Others, such as water, methane, and carbon dioxide, are naturally produced. Which type of greenhouse gas (human-made or natural) is more difficult to control and eliminate? Which types are easier? In three to five sentences, provide evidence for your argument.(4 points)
Answers
The natural types of greenhouse gases are more difficult to control and eliminate while the human-made type are easier.
What are greenhouse gases?Greenhouse gases are specific type of gases that have the ability to trap and release heat in their bonds.
Greenhouse gases are the cause of global warming, which is the gradual increase in temperature of the Earth's atmosphere.
However, greenhouse gases can either occur naturally or be synthesized artificially. The naturally-occuring greenhouse gases like CO2 are more difficult to control because they are not produced by humans.
Learn more about greenhouse gases at: https://brainly.com/question/14131369
#SPJ1
What is the electron configuration for vanadium (V)? The Periodic Table A. 1s22s22p63s23p64s24d3 B. 1s22s22p63s23p63d5 C. 1s22s22p63s23p64s24p3 D. 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d3
Answers
The electronic configuration for vanadium (V) in the periodic table is as follows: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3 (option D).
What is electronic configuration?Electronic configuration is the the arrangement of electrons in an atom, molecule, or other physical structure like a crystal.
Vanadium is the 23rd element on the periodic table and has chemical symbol V with atomic number 23. It is a transition metal, used in the production of special steels.
This suggests that the electronic configuration of Vanadium will be written as follows: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3
Therefore, the electronic configuration for vanadium (V) in the periodic table is as follows: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3.
Learn more about electronic configuration at: https://brainly.com/question/14283892
#SPJ1
What is the oxidation number of zinc in zncl2?
Answers
The oxidation number of the zinc in the ZnCl₂ is the +2.
The oxidation number, is also called as the oxidation state, the total number of the electrons that an atom either will gains or will loses in order to form the chemical bond with the another atom.
The oxidation number of the chlorine = -1
The oxidation number of the Zn is as follows :
Zn + 2( -1 ) = 0
Zn - 2 = 0
Zn = + 2.
The Oxidation number of an atom can be defined as the charge that the atom appears will have on forming the ionic bonds with the other heteroatoms.
To learn more about oxidation number here
https://brainly.com/question/29257381
#SPJ4
pls help
will give the brainliest!
Please answer correctly
Urgent!!!!

Answers
a)Green color appears.
Burning splint test tells us us that it is hydrogen gas.
b)\(Ni+ H_2SO_4 \longrightarrow NiSO_4 + H_2 \uparrow\)
c)There would be an effervescence. Upon passing the gas through lime water it turns milky $\implies$ gas is Carbon Dioxide.
d)$\NiCO_3+ H_2SO_4 \longrightarrow NiSO_4 + CO_2 +H_2O$
The system below was at equilibrium and
then some O2 gas was added to the
container. What change will occur for the
system?
2SO₂(g) + O₂(g) ⇒ 2SO3(g) + 198 kJ

Answers
The reaction will shift toward the products (right) and increase the concentration of SO₃.
What is Le Chatelier's principle?A crucially significant idea within chemistry is Le Chatelier's principle. When exposed to alterations such as changes in temperature, pressure, or concentrations of chemicals within a system at equilibrium; this principle explicates how said system reacts.
The fundamental postulate maintains that it shall respond by opposing any such modification so that stability can be reinstated once again.
Learn about system at equilibrium here https://brainly.com/question/21341070
#SPJ1
PLS HELP QUESTION 5 it’s due today and I already have a bad grade in her class
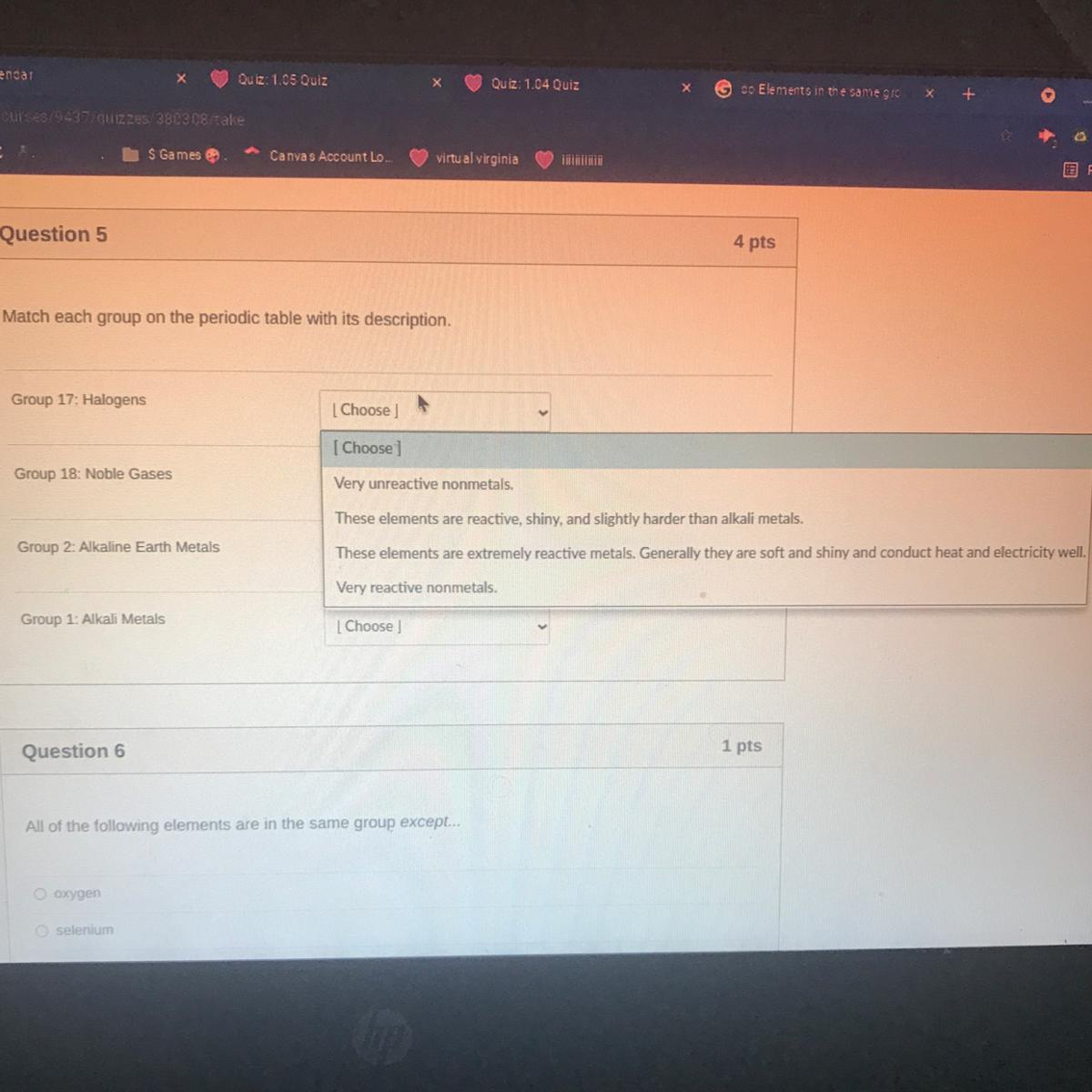
Answers
Answer:
very reactive non metals
Explanation:
keep working on her class
Answer:
very reactive non metals
Explanation:
Hope you do better!
Certain race cars use methanol (CH3OH, also called wood alcohol) as a fuel. The combustion of methanol occurs according to the following equation:
2CH3OH + 3O2 --> 2CO2 + 4H2O
In a particular reaction, 9.8 moles of CH3OH are reacted with an excess of O2. Calculate the number of moles of H2O formed
Answers
Known :
Mole of CH₃OH = 9.8 mole
Coef. of CH₃OH = 2
Coef. of H₂O = 4
Solution :
Mole of H₂O = (Coef. of H₂O / Coef. of CH₃OH) × Mole of CH₃OH
Mole of H₂O = (4/2) × 9.8 mole
Mole of H₂O = 19.6 mole
Which bonding type results in stronger bonds? What is your evidence?
Answers
Answer:
Covalent bonds are the strongest bonds in nature and under normal biological conditions have to be broken with the help of enzymes. This is due to the even sharing of electrons between the bonded atoms and as with anything equally shared there is no conflict to weaken the arrangement.
Explanation:
Bonding electrons are described as electrons that participate in chemical bonds. Chemical bond, a strong attraction between atoms, ions, or molecules, might be the subject here. Atoms sharing electron pairs form a covalent or molecular connection. An attraction between the atomic orbitals of atoms in a molecule is called a bonding molecular orbital.
Which bonding type results in stronger bonds? What is your evidence?
A covalent bond is created when the difference between two atoms' electronegativities is too small for an electron transfer to occur and produce ions. Bonding electrons are collectively referred to as the electrons that are present between the two nuclei. The "glue" that binds the atoms into molecular structures is the bound pair.
It is the most powerful link. By sharing an electron, the two atoms in such a bond are joined together.
One Hydrogen atom with one valence electron and one Chlorine atom with seven valence electrons, for instance, make up the HCL molecule. In this instance, hydrogen and chlorine share an electron to create a single bond.
To know more about Electron bonding, click on the link below:
https://brainly.com/question/12732708
#SPJ1
A gas cylinder contains exactly 15 moles of oxygen gas (O2). How many molecules of oxygen are in the cylinder?A sample of sugar (C12H22O11) contains1.505 × 1023 molecules of sugar. How many moles of sugar are present in the sample? Answer without doing any calculations.
Answers
A gas cylinder containing 15 moles of oxygen gas (O2) would contain a total of 9.03 x 10^23 molecules of oxygen. This can be calculated by multiplying the number of moles by Avogadro's number (6.022 x 10^23 molecules/mol) as follows:
Number of molecules = 15 moles x 6.022 x 10^23 molecules/mol = 9.03 x 10^23 molecules
For the sample of sugar (C12H22O11), the number of molecules given (1.505 x 10^23 molecules) can be converted to moles by dividing by Avogadro's number as follows:
Number of moles = 1.505 x 10^23 molecules ÷ 6.022 x 10^23 molecules/mol
Without doing any calculations, we can see that the numerator (1.505 x 10^23) is approximately 2.5 times smaller than the denominator (6.022 x 10^23). Therefore, the number of moles of sugar in the sample is less than 1 mole and can be estimated to be about 0.25 moles.
To know more about moles, please click on:
https://brainly.com/question/15209553
#SPJ11
animal cells have a vacuole but plant cells also have a vacuole but is it called the...
what?
Answers
What type of chemical reaction is ammonia + oxygen -> nitric acid + water?
Answers
The type of chemical reaction of ammonia + oxygen -> nitric acid + water is a combustion reaction.
What is the chemical reaction?The chemical reaction between ammonia (NH₃) and oxygen (O₂) to form nitric acid (HNO₃) and water (H₂O) is an oxidation-reduction reaction, specifically a combustion reaction.
The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
4NH₃ + 5O₂ → 4NO + 6H₂O
followed by the oxidation of NO to form NO₂ and then the formation of nitric acid by the reaction of NO₂ with water:
2NO + O₂ → 2NO₂
3NO₂ + H₂O → 2HNO₃ + NO
So, while the overall reaction involves oxidation and reduction, the formation of nitric acid involves an acid-base reaction.
Learn more about chemical reaction here: https://brainly.com/question/25769000
#SPJ1
When magnesium chloride reacts with water, 5.85 L HCI(g) is produced by the reaction:
MgCl₂(s) + H₂O(g) → MgO(s) + 2HCl(g)
How many moles of HCI was produced?
moles of HCI
How many moles of MgCl, reacted?
moles of MgCl₂
What mass of MgCl, reacted?
g MgCl₂
Answers
The mole of HCl produced is 0.26 mole.
The mole of MgCl₂ that reacted is 0.13 mole.
The mass of MgCl₂ that reacted is 12.38 grams.
Stoichiometric problemFrom the equation of the reaction:
MgCl₂(s) + H₂O(g) → MgO(s) + 2HCl(g)
The mole ratio of MgCl₂ and HCl is 1:2, while the mole ratio of H₂O and HCl is also 1:2.
5.85 L of HCl was produced. Based on the assumption that the gas was produced at STP.
1 mole of gas at STP = 22.4 L
Thus, 5.85 L of HCl would be equivalent to:
5.85 x 1/22.4 = 0.26 mole.
In other words, the mole of HCl produced is 0.26 mole.
The moles of MgCl₂ produced can be obtained from the mole ratio of MgCl₂ and HCl (2:1):
0.26/2 = 0.13 mole
The mass of MgCl₂ produced can be obtained from the formula:
mass = mole x molar mass
Molar mass of MgCl₂ = 95.211 g/mol
mass of 0.13 mole MgCl₂ = 0.13 x 95.211
= 12.38 grams
In other words, 12.38 grams of MgCl₂ reacted to produce 5.85 L of HCl according to the equation.
More on stoichiometric problems can be found here: https://brainly.com/question/28297916
#SPJ1
How much kinetic energy does a 2kg object have if it is traveling at a velocity of 2m/s?
Answers
Answer:
Given, Mass of an object, m = 2kg
velocity, v = 2m/s
We have,
KE = 1/2 m v²
= 1/2 × 2 (2)²
= 1/2 × 8
= 4J
Hence, 4J is the required Kinetic energy.
In a solution with a pH of 3 a. Litmus Is blue and phenolphthalein is colorless b. Litmus is blue phenolphthalein is red c. Litmus Is red phenolphthalein is colorless d. Litmus is red phenolphthalein is red.
Answers
Answer
c. Litmus Is red phenolphthalein is colorless
Explanation
A solution with a pH of 3 is acidic. The main use of litmus is to test whether a solution is acidic or basic, blue litmus turns red under acidic conditions, and red litmus turns blue under basic or alkaline conditions. Phenolphthalein is often used as an indicator in acid–base titrations. phenolphthalein, it turns colorless in acidic solutions and pink in basic solutions.
Therefore, the correct option for a solution with a pH of 3 is:
c. Litmus Is red phenolphthalein is colorless
rank the following organic acids in order of acidity, from strongest to weakest. (hint: consider how resonance and electronegativity will influence the stability of the conjugate base.)
Answers
The order of acidity from strongest to weakest is: Trifluoroacetic acid > Chloroacetic acid > Acetic acid > Phenol > Methanol.
The order of acidity from strongest to weakest would be:
1. Trifluoroacetic acid (CF3COOH) - This compound has strong electron-withdrawing fluorine atoms attached to the carbonyl group, making the conjugate base more stable through resonance delocalization of the negative charge.
2. Chloroacetic acid (ClCH2COOH) - The chlorine atom also has some electron-withdrawing effects, but not as strong as fluorine. The conjugate base is still relatively stable due to resonance.
3. Acetic acid (CH3COOH) - This compound has a weaker electron-withdrawing effect than the previous two due to the presence of a methyl group. The conjugate base is stabilized through resonance, but not as much as the previous two compounds.
4. Phenol (C6H5OH) - While phenol has a relatively acidic hydrogen atom, it is not as strong as the previous three compounds due to the stability of the conjugate base being limited by the lone pair on the oxygen atom rather than resonance.
5. Methanol (CH3OH) - Methanol has a relatively weak acidity as its conjugate base is stabilized through hydrogen bonding rather than resonance.
Learn more about order of acidity here :-
https://brainly.com/question/29608425
#SPJ11