PLS ANSWER!!!!
Why do some combinations of ionic compounds form a precipitate while others do not?
Answers
Answer:
Hello!!! Princess Sakura here ^^
Explanation:
The precipitate forms when one of the compounds is insoluble. In double replacement reactions, the positive ions and the negative ions are dissolved reactants that switch places to form the precipitation reaction.
Answer:
because one of the compounds in insoluble
Explanation:
a p e x :)
Related Questions
What is the uncertainty (in ppm) of a 1.00ppm standard solution prepared by pipetting 10uL of a 1000 ppm (s
Answers
The uncertainty % RSD using the given uncertainty values is 1.4%.
Given:
Concentration of the initial solution = 1000 ppm (±1.0 ppm)
Volume pipetted = 10 μL (±0.5 μL)
Volume of the final solution = 10 mL
Uncertainty from pipette:
The uncertainty associated with the pipette is ±0.5 μL.
Uncertainty from dilution:
The dilution is performed in a 10 mL volumetric flask. Class A volumetric flasks typically have a specified tolerance value that depends on the flask size. For a 10 mL class A volumetric flask, a typical tolerance might be ±0.02 mL (±20 μL).
Now, let's calculate the concentration of the final solution:
Concentration of the final solution = (Concentration of the initial solution x Volume of the initial solution) / Volume of the final solution
Concentration of the final solution = (1000 ppm x 10 μL) / 10 mL = 1 ppm
To calculate the uncertainty (u) of the final solution, we can use the formula:
u = √(u_pipette/Volume pipetted)² + (u_dilution/Volume of the final solution)²)) x Concentration of the final solution
u = √((0.5 μL/10 μL)² + (20 μL/10 mL)²)) x 1 ppm
Calculating the uncertainty (u):
u = √((0.5 μL/10 μL)² + (20 μL/10 mL)²)) x 1 ppm ≈ 0.014 ppm
To calculate the % RSD, we use the formula:
% RSD = (u / Concentration of the final solution) x 100
% RSD = (0.014 ppm / 1 ppm) x 100 ≈ 1.4%
Therefore, the uncertainty (in % RSD) of the 1.00 ppm standard solution prepared by pipetting 10 μL of a 1000 ppm (s=1.0 ppm) and diluting it to the mark in a 10 mL class A volumetric flask is approximately 1.4%.
The correct question is:
What is the uncertainty (in % RSD) of a 1.00ppm standard solution prepared by pipetting 10uL of a 1000 ppm (s=1.0ppm) using a 10-100 uL Eppendorf pipet and diluting to the mark in a 10mL class A volumetric flask?
To know more about relative standard deviation (RSD) visit: brainly.com/question/24499671
#SPJ4
write a
paragraph or two on electromagnetism.
Answers
Answer:
Electromagnetism is the study of the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It includes the electric force, which pushes all charged particles, and the magnetic force, which only pushes moving charges.It is used in many electrical appliances to generate desired magnetic fields. It is even used in a electric generator to produce magnetic fields for electromagnetic induction to occur.
Explanation:
tell me if this helped, ill try and explain better
draw the molecular orbital diagrams for b2 and calculate the bond order of the molecule. would the molecule be stabilized by adding or removing an electron. explain why.
Answers
To draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2, we need to consider the atomic orbitals of two boron atoms (B) and their interaction.
First, let's consider the electron configuration of boron (B) which is 1s² 2s² 2p¹. Since we have two boron atoms, we can represent their atomic orbitals as follows:
B₁: σ(1s)² σ*(1s)² σ(2s)² σ*(2s)² π(2p)¹
B₂: σ(1s)² σ*(1s)² σ(2s)² σ*(2s)² π(2p)¹
Now, let's fill the molecular orbitals by pairing the electrons:
σ(1s)² σ*(1s)² σ(2s)² σ*(2s)² π(2p)²
The molecular orbital diagram for B2 would look like this:
σ*(2p) π*(2p)
↑ ↑
↑ ↑
σ(2s) ↑ ↑ π(2p)
↑ ↑
↑ ↑
σ(1s) ↑ ↑
Based on the molecular orbital diagram, we can see that there are 2 electrons in bonding orbitals (σ(2s), π(2p)), and no electrons in antibonding orbitals (σ*(2p), π*(2p)). The bond order can be calculated by subtracting the number of electrons in antibonding orbitals from the number of electrons in bonding orbitals and dividing the result by 2:
Bond Order = (Number of electrons in bonding orbitals - Number of electrons in antibonding orbitals) / 2
Bond Order = (2 - 0) / 2 = 1
Therefore, the bond order of B2 is 1, indicating a single bond between the two boron atoms.
Now, let's consider whether the molecule would be stabilized by adding or removing an electron. In B2, all the bonding orbitals are fully occupied, resulting in a stable configuration.
Adding an electron would lead to an imbalance and an increase in the number of antibonding electrons, which could destabilize the molecule. Removing an electron would also disrupt the balance between bonding and antibonding orbitals.
Therefore, B2 is already in a stable configuration, and neither adding nor removing an electron would stabilize the molecule further.
To know more about electrons , refer here :
https://brainly.com/question/12001116#
#SPJ11
Which negative quality does Deborah exhibit?
Answers
Answer: Disdain
Explanation: Deborah believes that people of other nationalities are inferior to her. she treats them with disdain and does not miss an opportunity to abuse them.
If 2.09 mol of ethane (C₂H6) undergo combus-
tion according to the unbalanced equation
C₂H6+ O2 CO₂ + H₂O,
how many moles of O₂ is required?
Answer in units of mol. Answer in units of
mol.
Answers
For every mole of C2H6 you’ll get 2 moles of CO2 and 3 moles of H2O
We know this because the carbon and hydrogen has to be equivalent on both sides.
2.09 * 2 = 4.18 moles of CO2
2.09 * 3 = 6.27 moles of H2O
4.18 * 2 + 6.27 = 8.36 + 6.27 = 14.63 moles of O
14.63/2 = 7.32 moles of O2
"Which of the following reagents would oxidize Zn to Zn2+, but not Sn to Sn2+?Br2Br-Ca^2+Co^2+CaCo"
Answers
The only reagent that could potentially oxidize Zn to Zn²⁺ without oxidizing Sn to Sn²⁺ is Br₂ (bromine).
To determine which reagent would oxidize Zn to Zn²⁺ but not Sn to Sn²⁺, we need to compare the reduction potentials (E°) of the elements involved. The reagent with a higher reduction potential will have a greater tendency to accept electrons and oxidize the other element.
The reduction potential for Zn²⁺/Zn (Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻ ⇌ Zn) is approximately -0.76 V, while the reduction potential for Sn²⁺/Sn (Sn²⁺ + 2e⁻ ⇌ Sn) is approximately -0.14 V. Since the reduction potential for Zn²⁺/Zn is lower than that of Sn²⁺/Sn, Zn is less easily oxidized compared to Sn.
Now, let's examine the given reagents:
Br₂: Bromine (Br₂) has a higher reduction potential than Zn²⁺/Zn. It could potentially oxidize Zn to Zn²⁺. However, it can also oxidize Sn to Sn²⁺ because its reduction potential is higher than both Zn²⁺/Zn and Sn²⁺/Sn.
Br-: Bromide ion (Br-) has a lower reduction potential than both Zn²⁺/Zn and Sn²⁺/Sn. It would not oxidize either Zn or Sn.
Ca²⁺+: Calcium ion (Ca²⁺) has a lower reduction potential than both Zn²⁺/Zn and Sn2+/Sn. It would not oxidize either Zn or Sn.
Co²⁺: Cobalt(II) ion (Co²⁺) has a lower reduction potential than both Zn²⁺/Zn and Sn²⁺/Sn. It would not oxidize either Zn or Sn.
CaCo: This combination does not represent a known reagent or species and cannot be evaluated in terms of its oxidation potential.
Based on the given options, the only reagent that could potentially oxidize Zn to Zn²⁺ without oxidizing Sn to Sn²⁺ is Br₂ (bromine). However, it's important to note that in practical scenarios, multiple factors can influence redox reactions, so careful experimental considerations may be required to determine the actual outcome.
To know more about reduction potential, refer to the link below:
https://brainly.com/question/31362624#
#SPJ11
Which chemical or physical change is a endothermic process
Answers
Answer:
Examples of physical endothermic processes: The melting of ice, the evaporation of water.
PLS MARK ME BRAINLIEST
Explanation:
What is the key bond being formed in a Grignard reaction? A. Carbon-Magnesium B. Magnesium-Bromine
C. Carbon-Carbon D. Carbon-Oxygen
Answers
Answer:
carbon-magnesium
Explanation:
H3C - Mg - Br
rank the following molecules in order of increasing dipole moments: bcl3 , bcl2h , bclh2.
Answers
The molecules can be classified in the order of increasing dipole moment as follows: BCl₃ < BCl₂H < BClH₂.
The dipole moment of a molecule relies on the difference in electronegativity between its constituent atoms and the molecular geometry. A larger difference in electronegativity and a more asymmetric molecular shape lead to a higher dipole moment.
BCl₃ (boron trichloride) is a trigonal planar molecule with a central boron atom bonded to three chlorine atoms. Chlorine is more electronegative than boron, creating polar bonds. However, due to the symmetric arrangement of the chlorine atoms around boron, the dipole moments of individual bonds cancel each other out, resulting in a net dipole moment of zero for the molecule. So, BCl₃ has the lowest dipole moment among the given molecules.
BCl₂H (dichloro borane) has a bent molecular shape due to the presence of an additional hydrogen atom compared to BCl₃. The electronegativity difference between boron and chlorine creates polar bonds and the bent molecular geometry results in a net dipole moment. So, BCl₂H has a higher dipole moment than BCl₃.
BClH₂ (chloroborane) has a linear molecular shape with a central boron atom bonded to two chlorine atoms and one hydrogen atom. The electronegativity difference between boron and chlorine leads to polar bonds. The linear shape creates a larger dipole moment compared to BCl₂H, as the hydrogen atom adds to the asymmetry of the molecule.
Learn more about electronegativity here:
https://brainly.com/question/29545875
#SPJ4
A 10. 0 gram sample of water at 23. 0°C absorbs 209 joules of heat. What is the final temperature of the water sample? (c of water is 4. 18 J/g°C)
Answers
To determine the final temperature of the water sample, we can use the heat transfer equation:
q = m * c * ΔT
Where:
q is the heat absorbed (in joules),
m is the mass of the substance (in grams),
c is the specific heat capacity of the substance (in J/g°C),
ΔT is the change in temperature (in °C).
Given:
q = 209 J
m = 10.0 g
c (specific heat capacity of water) = 4.18 J/g°C
The initial temperature of the water sample = 23.0°C
We can rearrange the equation to solve for ΔT:
ΔT = q / (m * c)
Substituting the given values:
ΔT = 209 J / (10.0 g * 4.18 J/g°C)
ΔT ≈ 4.99°C
To find the final temperature, we add the change in temperature to the initial temperature:
Final temperature = Initial temperature + ΔT
Final temperature = 23.0°C + 4.99°C
Final temperature ≈ 27.99°C
Therefore, the final temperature of the water sample is approximately 27.99°C.
Learn more about heat transfer equation here:
https://brainly.com/question/30526730
#SPJ11
How many moles are in 7.9 grams of P 2 O 5?
Answers
Answer: 0.0556555468903552 moles, you can estimate that to its nearest hundreth, or thousandth.
Explanation:
im just naturally a genius
calculate the number of hydrogen atoms in a 90.0g sample of camphor c10h16o. be sure your answer has a unit symbol if necessary, and round it to 3 significant digits.
Answers
The number of hydrogen atoms in a 90.0g sample of camphor C₁₀H₁₆O is 5.68 X 10²⁴.
The mass of 1 mole of a chemical is indicated by its molar mass. It provides you with the amount of grams per mole of a substance, to put it another way.
Given,
Mass of sample of camphor (C₁₀H₁₆O), m = 90.0g
To find: No. of hydrogen atom in given sample.
Molecular mass of camphor is:
M = 152 g/mol
Moles of camphor,
n = m/M
n = 90/152 = 0.59
1 mole of camphor contains 16 moles of Hydrogen
so, 0.59 moles of camphor contains 9.44 moles of hydrogen
1 mole of any substance contain 6.022 X 10²³ no. of atoms/molecule
So, no. of atoms in 9.44 moles of hydrogen is
N = 6.022 X 10²³ X 9.44
N = 56.84 X 10²³
N = 5.68 X 10²⁴
Hence, The number of hydrogen atoms in a 90.0g sample of camphor C₁₀H₁₆O is 5.68 X 10²⁴.
Learn more about the molecular mass with the help of the given link:
https://brainly.com/question/18446366
#SPJ4
Tim would like to know the mass of two boxes. Instead of Tim looking at the boxes to determine their mass, what should Tim use to accurately
determine the mass of each box
Answers
Answer:
The triple beam balance
0. 01 M HCl solution has a pH of 2. Suppose that during the experiment, both the universal pH indicator and the cabbage indicator turn orange-red for 0. 01 M HCl. What can you conclude about the the cabbage indicator key? It matches the universal pH indicator and is indicating the proper pH. It should completely match the universal indicator key for all pH values greater than 7 (base). It should completely match the universal indicator key for all pH values. There was some sort of experimental error, because the indicators should never match.
Answers
Answer:
a.) It matches the universal pH indicator and is indicating the proper pH.
Explanation:
it says its the answer.
Answer:
Explanation:
An object is thrown vertically from the ground upwards with a speed of 10 m/s. Considering g = 10 m/s2, the maximum height that the object reaches from the ground, in meters, will be:
a) 15.0.
b) 10.0.
c) 5.0.
d) 1.0.
e) 0.5.
Oxygen can be produced in the laboratory by the reaction
2KClO3———-> 2KCl+3O2
How much potassium chlorate is needed to produce 2.75 L of oxygen, collected over water at 37°C and 94.9 kPa? The vapor pressure of water at 37°C is 6.28 kPa.
Answers
Answer:
5.2g potassium chlorate is needed to do so
what are the names given to each part of the picture indicated above

Answers
(IMAGE ATTATCHED)
Help plssss this is due in 3 hours
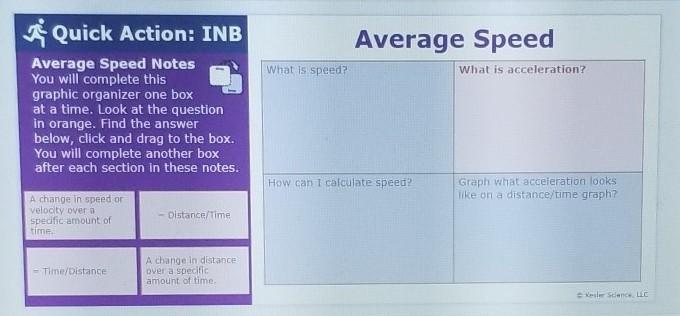
Answers
You can calculate speed by dividing distance and time
And you can solve acceleration by dividing time by distance
How do the different processes of a rock cycle change a rock? Which processes will form an igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rock
Answers
Hope this helps (:
2 C2H6 + 7 O2 -> 4 CO2 + 6 H2O
Use the given equation for the following questions:
If 20 moles of fuel are combusted in the above equation, how many moles of O2 are consumed?
If 20 moles of fuel are combusted in the above equation, how many moles of CO2 are produced?
Answers
Answer:
Hope it's correct
Explanation:
2 mol of C2H6 = 7 mol of O2
So 20 mol of C2H6 = ? (20/2)*7 = 70 mol
How does the temperature change when a layer of glass is added?
Answers
Answer:
thermal shock
Explanation:
the temperatures inside the glass jar should have continued to increase over time. Internal stresses due to uneven heating. This is also known as “thermal shock”.
In general, the thicker the glass, the more prone it will be to breaking due to the immediate differences in temperature across the thickness of glass.
Borosilicate glass is more tolerant of this, as it has a higher elasticity than standard silicon glass.
You may also note that laboratory test tubes and flasks are made with thinner walls, and of borosilicate glass, when designated for heating.
Which substance can be decomposed by chemical means? a. calcium b. argon c. sodium chloride d. aluminum
Answers
What is called exothermic
Answers
An exothermic process is one that gives off heat.
Explanation:
This heat is transferred to the surroundings. An endothermic process is one in which heat has to be supplied to the system from the surroundings.
Wool does not hold electrons as tightly as rubber, so when a wool sweater and a rubber balloon are rubbed together, electrons transfer from the (sweater/balloon) to the (sweater/balloon).
Answers
When a wool sweater and a rubber balloon are rubbed together, their surfaces come into contact and the friction causes electrons to be transferred from one surface to the other.
Wool does not hold onto electrons as tightly as rubber, so electrons transfer from the sweater to the balloon. This results in the sweater becoming positively charged and the balloon becoming negatively charged. This transfer of electrons is known as static electricity, which can create a spark or shock when discharged. The strength of the static electricity generated depends on the materials involved, their surface area, and the amount of friction applied.
Learn more about friction:
brainly.com/question/13000653
#SPJ4
burning fossil fuels causes atmospheric pollution write one effect for each pollutant in table 2.
Answers
Burning fossil fuels releases a variety of pollutants into the atmosphere, including carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, mercury, etc.
What is pollution?Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that traps heat in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. Burning fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is the largest source of human-generated carbon dioxide emissions. When fossil fuels containing sulfur are burned, they release sulfur dioxide into the air. Sulfur dioxide can react with other compounds in the atmosphere to form acid rain, which can damage crops, forests, and buildings. Burning fossil fuels also releases nitrogen oxides, which contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain. Nitrogen oxides can also react with other compounds in the atmosphere to form ozone, which is harmful to human health.
Hence, Burning fossil fuels releases a variety of pollutants into the atmosphere, including carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, mercury, etc.
Learn more about pollution here.
https://brainly.com/question/2208840
#SPJ2
carbon dioxide has one more resonance form than ozone. explain why this structure is not possible for ozone.
Answers
Carbon dioxide has one more resonance form than ozone.
Define resonance.
In resonance, more than one or two Lewis structures can each represent a single substance (or molecule). The overall Lewis structure of a chemical (or molecule) is a mix of the two.
One of the three resonance structures in carbon dioxide, or CO2, is a significant contributor. Four valence electrons from carbon and six from each oxygen atom make up the total of 16 in the CO2 molecule. All three resonance structures have full octets of atoms, however structure 1 will be more stable and so contribute more because it lacks charge separation.
Because both oxygen atoms have formal charges, structures 2 and 3 exhibit charge separation. Furthermore, the stability of these two complexes is further diminished by oxygen having a positive charge.
We have two significant resonance structures for ozone, both of which are equally important to the molecule's overall hybrid structure. The required 18 valence electrons are provided by both configurations (6 from 3 bonds and 12 as lone pairs placed on the oxygen atoms).
To learn more about valence electrons use link below:
https://brainly.com/question/371590
#SPJ4

A severe systemic reaction to an allergen causing serious symptoms that develop very quickly is known as.
Answers
Answer: Anaphylaxis
Explanation:
I have a nut allergy, and this has happened to me once. The doctors also told me a lot about anaphylaxis, and I like to learn about myself.
I hope this helps!! :)
The following is a chemical reaction for _______ with ozone. Reaction 1: C l O B r O right-arrow C l B r O 2. Reaction 2: C l O 3 right-arrow C l O O 2. Reaction 3: B r O 3 right-arrow B r O O 2. A. Chlorofluorocarbons b. Halons c. UV radiation d. None of the above Please select the best answer from the choices provided A B C D.
Answers
The following is a chemical reaction for Halons with ozone.
The correct answer is option B
The chemical reaction for Halons with ozone is given below:Reaction 1: C l O B r O right-arrow C l B r O 2.Reaction 2: C l O 3 right-arrow C l O O 2.Reaction 3: B r O 3 right-arrow B r O O 2.The Halons consist of organic molecules that contain bromine and chlorine atoms that react with ozone. Halons are made up of bromine and chlorine atoms that are heavy and highly reactive.
The stratosphere, which is the second layer of the atmosphere, contains ozone that absorbs harmful UV radiation. The Halons react with the ozone, resulting in a decrease in the amount of ozone present. This results in an increase in UV radiation that reaches the earth's surface. Hence, the correct answer is option B, Halons.
To know more about Halons visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/31871001
#SPJ11
How is an electromagnet similar to and different from a regular magnet?
Answers
Answer:
that the electromagnet can have a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it and disappears when the flow of the current stops, while permanent magnets are made up of magnetic material that can be easily magnetized and can create
Explanation:
what happens when ammonia passes through copper sulphate solution ??
Answers
Explanation:
what happens when ammonia passes through copper sulphate solution
which of the following best explains what resonance structures are? select the correct answer below: a molecule whose lewis structure could be described by more than one resonance structure possesses an electronic structure equal to that of the most stable resonance form. a molecule whose lewis structure could be described by more than one resonance structure possesses an electronic structure equal to that of a combination of the resonance structures, with the more stable structures contributing more to the average structure. a molecule whose lewis structure could be described by more than one resonance structure possesses an electronic structure that fluctuates between the possible structures over time. a molecule whose lewis structure could be described by more than one resonance structure could have any of the different resonance structures. each different resonance is a different compound. feedback
Answers
A molecule whose lewis structure could be described by more than one resonance structure possesses an electronic structure equal to that of a combination of the resonance structures, with the more stable structures contributing more to the average structure (option b).
Resonance structures are different Lewis structures that can be drawn for a molecule, where the placement of electrons is shifted.
The molecule does not exist as any one of these structures, but rather as a combination or average of all of the resonance structures.
The more stable resonance structures contribute more to the overall electronic structure of the molecule. Therefore, resonance structures help us understand the true electronic structure of a molecule and how it behaves in chemical reactions.
A molecule whose Lewis structure could be described by more than one resonance structure possesses an electronic structure equal to that of a combination of the resonance structures, with the more stable structures contributing more to the average structure.
Thus, the correct choice is b.
For more question on electronic structure
https://brainly.com/question/29698483
#SPJ11