The diagram shows a tennis ball being thrown vertically into the air. When the ball just left the players hand it is at the speed of 5.0 m/s . The tenis ball has the mass of 0.058 kg. Write down the equation that links kinetic energy to mass and speed
Answers
Answer:
1. KE = ½mv²
2. The kinetic energy of the tennis ball is 0.725 J
Explanation:
The following data were obtained from the question:
Mass (m) = 0.058 kg
Velocity (v) = 5.0 m/s
Kinetic energy (KE) =.?
1. Defining an expression which relates kinetic energy, mass and speed of an object.
Kinetic energy is simply defined as the energy possess by an object in motion. Mathematically, kinetic energy can be represented as:
KE = ½mv²
Where
KE => is the kinetic energy.
m => is the mass of the object.
v => is the velocity of the object.
2. Determination of the kinetic energy of the tennis ball.
Mass (m) = 0.058 kg
Velocity (v) = 5.0 m/s
Kinetic energy (KE) =.?
KE = ½mv²
KE = ½ × 0.058 × 5²
KE = 0.029 × 25
KE = 0.725 J
Thus, the kinetic energy of the tennis ball is 0.725 J.
Related Questions
calculate the volume of a liquid with a density of 5.45g/cm³ or centimeter square and a mass of 65g.
Answers
Answer:
12 ml
Explanation:
The thing to remember about a substance's density is that it tells you the mass of every unit of volume of said substance.
a 0.25 kg ideal harmonic oscillator has a total mechanical energy of 4.0 j. if the oscillation amplitude is 28.1 cm what is the oscillation frequency?
Answers
The oscillation frequency of the ideal harmonic oscillator is approximately 3.216 Hz.
To find the oscillation frequency of the ideal harmonic oscillator, we can use the formula:
E = (1/2) × k × A²
Where:
E = Total mechanical energy
k = Spring constant
A = Amplitude
First, we need to determine the spring constant (k). Rearranging the formula, we have:
k = 2 × E / A²
Plugging in the given values, we get:
k = 2 × 4.0 J / (0.281 m)²
k = 2 × 4.0 J / (0.281² m²)
k = 2 × 4.0 J / 0.078961 m²
k ≈ 102.394 N/m
Now, we can find the oscillation frequency using the formula:
f = 1 / (2π) × √(k / m)
Where:
f = Frequency
π ≈ 3.14159
m = Mass
Given that the mass (m) is 0.25 kg, we can substitute the values:
f = 1 / (2π) × √(102.394 N/m / 0.25 kg)
f = 1 / (2π) × √(409.576 N/kg)
f ≈ 1 / (2π) × 20.236 Hz
f ≈ 3.216 Hz
Learn more about the oscillation frequency at
https://brainly.com/question/13112321
#SPJ4
In a dynamic random access memory (dram) computer chip, each memory cell chiefly consists of a capacitor for charge storage. each of these cells represents a single binary-bit value of 1 when its 35-ff capacitor (1ff=10−15f) is charged at 1.5 v, or 0 when uncharged at 0 v. when it is fully charged, how many excess electrons are on a cell capacitor's negative plate?
Answers
In a dynamic random access memory (DRAM) computer chip, each memory cell chiefly consists of a capacitor for charge storage.
Each of these cells represents a single binary-bit value of 1 when its 35-ff capacitor (1ff=10−15f) is charged at 1.5 V or 0 when uncharged at 0 V. When it is fully charged, there are approximately 105 electrons on a cell capacitor's negative plate.
Given,Capacitance of memory cell,
C = 35 fF = 35 × 10⁻¹⁵ F
Charge on negative plate,
q = CV …..(1)Voltage, V = 1.5 V
Substituting the value of V in equation (1),
q = (35 × 10⁻¹⁵) × (1.5)q = 52.5 × 10⁻¹⁵ C
Charge is given by,
q = ne
Where,n = Number of electronsand,
e = Electronic charge = 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C
Therefore,Number of electrons,
n = q / e = (52.5 × 10⁻¹⁵) / (1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹)≈ 10⁵ (approx)
Hence, there are approximately 105 electrons on a cell capacitor's negative plate when it is fully charged.
To learn more about dynamic random access memory
https://brainly.com/question/28303339
#SPJ11
a) A cell of dry air is moved vertically from its original position under adiabatic conditions. Depending on the temperature profile of the surrounding atmosphere, this gas cell can keep on moving in the same direction, or it may come back to its original position. Considering the temperature profile of the atmosphere, change of the air cell temperature as it moves up and down in the surrounding atmosphere, as well as relative densities of the air cell and atmosphere, explain why and when the atmosphere is considered to be convectively stable and convectively unstable. In answering this question, use diagrams of temperature change with altitude. (13 marks) b) Explain why the adiabatic lapse rate of dry air is different from the adiabatic lapse rate of wet saturated air. Show them both in a diagram. (5 marks) c) Wet unsaturated air rises from the ocean surface. The ambient lapse rate is higher than the adiabatic lapse rate for dry air. There is a temperature inversion layer at higher altitudes. Show in a schematic diagram how the temperature of the wet air changes with altitude, in comparison with the ambient temperature. Explain at what altitudes the cumulus clouds are formed and why. (7 marks)
Answers
The question addresses the stability of the atmosphere and the factors that determine convective stability or instability. It also explains the difference between the adiabatic lapse rate of dry air and wet saturated air.
a) The stability of the atmosphere is determined by the temperature profile and relative densities of the air cell and atmosphere. If the temperature of the surrounding atmosphere decreases with altitude at a rate greater than the adiabatic lapse rate of the air cell, the atmosphere is considered convectively stable.
In this case, the air cell will return to its original position. Conversely, if the temperature of the surrounding atmosphere decreases slower than the adiabatic lapse rate of the air cell, the atmosphere is convectively unstable. The air cell will continue moving in the same direction.
b) The adiabatic lapse rate refers to the rate at which temperature decreases with altitude for a parcel of air lifted or descending adiabatically (without exchanging heat with its surroundings). The adiabatic lapse rate of dry air is higher (around \(9.8^0C\) per kilometer) compared to the adiabatic lapse rate of wet saturated air (around 5°C per kilometer).
This difference arises because when water vapor condenses during the ascent of saturated air, latent heat is released, reducing the rate of temperature decrease. A diagram can illustrate the difference between the two lapse rates, showcasing their respective slopes.
c) When wet unsaturated air rises from the ocean surface, its temperature decreases at a rate equal to the dry adiabatic lapse rate. However, if the ambient lapse rate (temperature decrease with altitude) is higher than the adiabatic lapse rate for dry air, a temperature inversion layer forms at higher altitudes.
In this inversion layer, the temperature increases with altitude instead of decreasing. A schematic diagram can depict the temperature changes of the wet air in comparison to the ambient temperature, showing the inversion layer.
Cumulus clouds form at the altitude where the rising moist air reaches the level of the temperature inversion layer. These clouds are formed due to the condensation of water vapor as the air parcel cools to its dew point temperature.
Learn more about adiabatic lapse rates here:
https://brainly.com/question/30023377
#SPJ11
assume that you come in contact with a 120 v electrical circuit. the current (in milliamps) with the above voltage through wet (contact resistance of 1,000 ohms) hands is:
Answers
The current through wet hands when in contact with a 120 V electrical circuit would be 120 milliamps (mA).
Voltage (V) = 120 V
Resistance (R) = 1,000 ohms
According to Ohm's law, the voltage across two places is precisely proportional to the current flowing through a conductor between them. According to Ohm's Law, we can compute the electrical current in a circuit by dividing the voltage by the resistance. If the resistance is reduced, the current will alter.
Calculating the current by using Ohm's law -
I = V / R
Substituting the values:
I = 120 / 1,000
= 0.12 A
Converting 0.12 A to milliamps by multiplying by 1,000 -
= 0.12 x 1,000
= 120
Read more about current on:
https://brainly.com/question/30435424
#SPJ4
No matter how well we get along with our parents as adolescents, there comes a time when we need to break away and assert our own independence. There are several ways in which we do this, some of them deliberate and intentional and some of them not so intentional. Describe several ways you use or have used to break away from your parents. Briefly describe your parents' reactions.
Answers
Answer: I never said anything to them but if i did it would be "I need a break from you, i love you but sometimes I have to find the path on my own." i would say this if i wasn't scared to hurt them.
Explanation:
Two cars collide head on while each is traveling at 70 km/h. Suppose all their kinetic energy is transformed into the thermal energy of the wrecks. What is the temperature increase of each car? Part A You can assume that each car's specific heat is that of iron. Express your answer with the appropriate units
Answers
To determine the temperature increase of each car, we can use the principle of conservation of energy. The total kinetic energy of the cars before the collision is converted into thermal energy (heat) after the collision.
The formula to calculate the temperature increase is:
ΔT = (ΔE) / (m * c)
Where:
ΔT is the temperature increase,
ΔE is the change in thermal energy (equal to the initial kinetic energy of the cars),
m is the mass of each car, and
c is the specific heat capacity of iron.
Since the specific heat capacity of iron is approximately 450 J/(kg·°C), and the mass of each car is not given in the question, we cannot determine the specific temperature increase without that information. Therefore, the answer cannot be expressed with the appropriate units without knowing the mass of the cars.
To know more about , kinetic energy, click here https://brainly.com/question/999862
#SPJ11
A ball of mass 0.25 kg falls from a height of 50 m. Using energy
considerations, find the final velocity. Let g = 9.8 m/s
A . 2.97 m/s
B . 21.0 m/s
C . 33.3 m/s
D . 44.1 m/s
Answers
Therefore, the velocity of the ball just before it hits the ground is approximately 22.1 m/s. Therefore, the closest value to this option is 21.0 m/s.
When a ball of mass 0.25 kg falls from a height of 50 m, we can calculate its velocity using the principle of conservation of energy. According to this principle, the sum of the potential and kinetic energy of an object remains constant.
Therefore, we can equate the potential energy at the initial height to the kinetic energy at the final velocity.Let's calculate the potential energy of the ball at the initial height
:Eg = mghEg = 0.25 kg × 9.81 m/s² × 50 m
Eg = 122.625 J
This is the energy that the ball has due to its position. As it falls, this energy is transformed into kinetic energy. At the moment the ball reaches the ground, all the potential energy has been transformed into kinetic energy
.Ek = 1/2mv²Ek = Egv² = 2Ek/mv = √(2Ek/m)
Let's plug in the values we obtained:Eg = 122.625 Jm = 0.25 kgv = √(2Ek/m)
We obtain:v = √(2 × 122.625 J / 0.25 kg)v = √(245.25 J/kg)v = 22.116 m/s
For such more question on kinetic energy
https://brainly.com/question/8101588
#SPJ8
Why should Mike repeat this investigation?
Mike needs to make sure that all the skateboards are not affected by friction.
Mike needs to have more than one set of numbers to make an accurate graph
The investigation needs multiple trials to determine which board is the control.
The investigation needs to be repeated several times to have the most accurate data.
Answers
Answer:
D
Explanation:
What are the x / y-components? I'd also like a step-by-step explanation please.
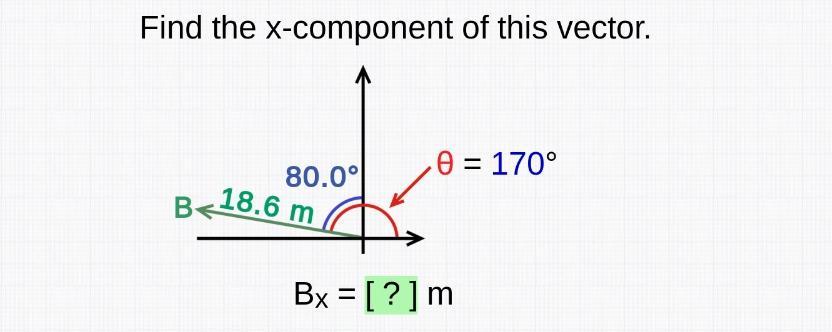
Answers
The x and y component of the vector are -18.32 m and 3.23 m respectively.
What are the x and y components of the vector?The x and y component of the vector is calculated by applying the following formula.
Bx = B cosθ
By = B sinθ
where;
B is the magnitude of the vectorBx is the x componentBy is the y componentθ is the angle of the vector measured above x axisThe vector is located in negative x direction but positive y direction.
The angle of the vector from x axis = 90⁰ - 80⁰ = 10⁰
Bx = B cosθ = -18.6 m x cos ( 10 ) = -18.32 m
By = B sinθ = 18.6 m x sin ( 10 ) = 3.23 m
Learn more about x and y components here: https://brainly.com/question/27996986
#SPJ1
R WORK and LABEL everything correctly.
Joe swings a rope and it cycles 18 times in
36 seconds. What is the frequency and
period of the waves?
Answers
Frequency is the number of cycles per unit time and is calculated using the formula:
Frequency = Number of cycles / Time taken
In this case, the number of cycles is 18 and the time taken is 36 seconds.
Frequency = 18 / 36 = 0.5 Hz
Period is the time taken for one complete cycle and is calculated using the formula:
Period = Time taken / Number of cycles
In this case, the time taken is 36 seconds and the number of cycles is 18.
Period = 36 / 18 = 2 seconds
Therefore, the frequency of the waves is 0.5 Hz and the period of the waves is 2 seconds.
The frequency of the waves is 0.5 Hz and the period of the waves is 2 seconds.
Joe swings a rope and it cycles 18 times in 36 seconds. By calculating the frequency and period of the waves, we can determine that the frequency of the waves is 0.5 Hz and the period of the waves is 2 seconds.
To know more about cycles visit
https://brainly.com/question/30288963
#SPJ11
The oxygen molecule has a total mass of 5. 30 × 10-26 kg and a rotational inertia of 1. 94 ×10-46 kg-m2 about an axis through the center perpendicular to the line joining atoms. Suppose that such a molecule in a gas has a mean speed of 500 meters/sec and that its rotational kinetic energy is two-thirds of its translational kinetic energy. Find its average angular velocity
Answers
The average angular velocity of the oxygen molecule is 1.28 x 10^12 radians/sec.
The total kinetic energy of the oxygen molecule can be expressed as the sum of its translational and rotational kinetic energies:
KE_total = KE_translational + KE_rotational
Given that the rotational kinetic energy is two-thirds of the translational kinetic energy, we can write:
KE_rotational = (2/3)KE_translational
We also know that the total kinetic energy is related to the mean speed by the formula:
KE_total = (1/2)mv²
where m is the mass of the molecule and v is its mean speed.
Substituting the expressions for KE_rotational and KE_total into this equation, we get:
(5/6)KE_translational = (1/2)mv²
Solving for the translational kinetic energy, we obtain:
KE_translational = (3/5)mv²
The moment of inertia of the oxygen molecule can be related to its angular velocity by the formula:
KE_rotational = (1/2)Iω²
where I is the moment of inertia and ω is the angular velocity.
Substituting the expressions for KE_rotational and I, and solving for ω, we get:
ω = √((2/3)KE_translational / I)
Substituting the expressions for KE_translational, I, m, and v, we obtain:
ω = √((2/9)mv² / I)
Finally, substituting the given values, we get:
ω = 1.28 x 10¹² radians/sec.
To know more about the Angular velocity, here
https://brainly.com/question/13770698
#SPJ4
A physical change is a change to the physical properties of a substance. This type of change does
not change the nature of the substance. *
Answers
Answer:
False
Explanation:
in lab, we showed that leds can sometimes act as solar cells when excited by blue, green, amber, and red leds. which color(s) leds (the light sources) will induce a voltage in a green led (acting as the solar cell)?
Answers
Blue lights and some green lights will induce a voltage in green led(acting as a solar cell)
LED working as a solar cell is a photodiode. For photodiodes to produce electric current they need to absorb photons. But they work only when they absorb photons of wavelength equivalent to or less than the specified LED and the wavelength of light it emits.
For LEDs to work as solar cells they must absorb photons of a specific wavelength and these absorbed photons initiate the formation of electron-hole pairs. LEDs have to be reverse-biased to work as solar cells.
Know which is correct about LEDs
brainly.com/question/10546488
#SPJ4
How will this surfboard’s streamlined shape affect its speed?
Answers
Answer: Speed increases
Explanation:
A streamlined shape reduces the surface area making contact with the fluid (in this case, water). Less surface area making contact with the fluid means friction is reduced. The lower the force of friction, the lower the "drag" on the object in motion, hence the faster it can go. The force of friction is always in the opposite direction of the motion of the object.
Sự kiện nào đánh dấu giai đoạn giai cấp tư sản Ấn Độ bước lên vũ đài chính trị?
Answers
I can help you but I can't understand this language please explain it.
A student leaves their history classroom and walks 20 meters north to a drinking fountain. Then the student turns and walks 50 meters south to their art classroom. What is the magnitude of the total distance traveled by the student?
a. 20 m
b. 30 m
c. 50 m
d. 70 m
Answers
Answer:
D
Explanation: Given that a student leaves their history classroom and walks 20 meters north to a drinking fountain. Then the student turns and walks 50 meters south to their art classroom.
The distance is a scalar quantity.
The distance = 50 + 20
distance = 70 metres
Therefore, the magnitude of the total distance traveled by the student is 70 metres. Which is option D
1 Calculate the physiological AG for the reaction: Phosphocreatine+ADP creatine + ATP at 25° C as it occurs in the cytosol of neurons, in which phosphocreatine is present at 4.7 mM, creatine at 1.0 mM, ADP at 0.20 mM, and ATP at 2.6 mm. (B) Why are A Go' and AG different? (A) (C) Consider the following reaction, and determine the tricks utilized by the system, to allow each step of the reaction to proceed in the forward direction. The step numbers are written on each arrow. A¹B²C³ Dª›E AG value for step 1= 20 kJ/mol; for step 2= -1.35 kJ/mol; for step 3= 2.57 kJ/mol; for step 4= -10.67 kJ/mol.
Answers
To calculate the physiological AG (Gibbs free energy change) for the given reaction, we need to use the formula:
AG = AG° + RT * ln(Q)
where AG is the physiological Gibbs free energy change, AG° is the standard Gibbs free energy change, R is the gas constant (8.314 J/(mol·K)), T is the temperature in Kelvin, and Q is the reaction quotient.
For the reaction: Phosphocreatine + ADP → Creatine + ATP
We can write the reaction quotient Q as:
Q = ([Creatine] * [ATP]) / ([Phosphocreatine] * [ADP])
Substituting the given concentrations:
Q = (1.0 mM * 2.6 mM) / (4.7 mM * 0.20 mM)
Q = 13 / 0.94
Q ≈ 13.83
Now, we need the standard Gibbs free energy change AG° for this reaction. Unfortunately, the standard AG° values for this specific reaction are not provided, so it's not possible to calculate the physiological AG without that information.
As for the question of why AG° and AG are different, AG° represents the standard Gibbs free energy change under standard conditions (usually 25°C, 1 atm pressure, and 1 M concentration), assuming all reactants and products are at their standard state.
On the other hand, AG takes into account the actual concentrations of reactants and products under non-standard conditions, using the reaction quotient Q.
Regarding the second question about the tricks utilized by the system to allow each step of the reaction to proceed in the forward direction, it seems that the given information is incomplete.
The step numbers (A, B, C, D, E) and the corresponding AG values are provided, but the details of the individual steps and the tricks utilized are not mentioned. Without that information, it's not possible to determine the specific tricks used by the system for each step.
To learn more about physiological click here brainly.com/question/30063255
#SPJ11
At what conditions acceleration of a body is zero?
Answers
Answer:
when there is uniform velocity the acceleration of a body is zero
Consider two current carrying circular loops. Both are made from the same wire and both carry the same current, but one has twice the radius of the other. If the magnetic field strength at the center of the smaller loop is B, what is the magnetic field strength at the center of the larger loop? A) 8B 4B C) 2B D) B/2 E) B/4
Answers
Your Answer :- The magnetic field strength at the center of the larger loop is B/2, which corresponds to answer choice D.
The magnetic field strength (B) at the center of a current-carrying circular loop can be calculated using the formula:
B = μ₀ * I / (2 * π * R)
Where:
- μ₀ is the permeability of free space (4π × 10^(-7) Tm/A),
- I is the current,
- R is the radius of the loop.
Given that both loops are made from the same wire and carry the same current, the magnetic field strength at the center of the smaller loop is B. The radius of the larger loop is twice that of the smaller loop (2R).
To find the magnetic field strength at the center of the larger loop, we can use the same formula:
B_larger_loop = μ₀ * I / (2 * π * (2R))
Simplify the equation:
B_larger_loop = (μ₀ * I) / (4 * π * R)
Since B = μ₀ * I / (2 * π * R), we can rewrite the equation as:
B_larger_loop = (1/2) * B
So, the magnetic field strength at the center of the larger loop is B/2, which corresponds to answer choice D.
learn more about "magnetic field strength":-https://brainly.com/question/26257705
#SPJ11
an object of mass 1kg has a P.E. of 1 joule relative to the ground it is at height of

Answers
Answer:
Potential Energy = mgh = 1
m= 1
g= 9.8
mgh = 1 x 9.8 x h = 1
height = 1/9.8
height = 0.102 m
When do scholars think kites were invented?
A. 2000 AD
B. 1000 BC
C. 12,000 BC
D. Never, there's no such thing as a kite
Answers
Answer:
kites where invented 2000 AD
so its A. 2000 AD
srry if it's wrong
Answer:
I guess no. A
Explanation:
approximately 2,800 years ago.
A telescope mirror is part of a sphere with a radius of 3 m. what is the focal length of the mirror?
Answers
The focal length of the mirror will be 0.33 m
Focus is defined as the point through which the reflected light rays pass (or appear to pass) when incident light rays are parallel to the principal axis. It is located at the midpoint of pole and center of curvature. The distance between the pole and the focus of the mirror is called the focal length of the mirror.
F =2R or focal length of a mirror is half of its radius of curvature.
The radius of curvature of convex or concave mirror is equal to two times of the focal length of convex or concave mirror. The radius of curvature is the radius of sphere formed by the convex or concave mirror. It is also equal to the distance between the pole and center of curvature.
F = 1/R
R = 3 m (given )
F = 1 / 3 = 0.33 m
To learn more about focal length here
https://brainly.com/question/16188698
#SPJ4
Two ropes are tied to a steel ring, and a student holds the free end of each rope. The students then pull on the ropes in a tug-of-war. If the forces exerted by the students are unbalanced, what happens to the ring ?
A. The ring remains at rest.
B. The ring moves at a constant velocity.
C. The ring accelerates in the direction of the net unbalanced force.
D. The ring accelerates in the direction opposite the net unbalanced force.
Answers
The ring accelerates in the direction of the net unbalanced force. Thus option C is the correct answer.
According to Newton's second law of motion, the net force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration. If the forces exerted by the two students in the tug-of-war are unbalanced, there will be a net force acting on the steel ring.
The direction of this net force will be in the direction of the stronger force. As a result, the ring will accelerate in the direction of the net unbalanced force. This means that the ring will begin to move, and its velocity will change as long as the net force is applied.
Since the steel ring is accelerating, it can no longer be at rest, and it will not move at a constant velocity. The ring will move in the direction of the stronger force until the forces exerted by the students are balanced again.
To learn more about Force,
https://brainly.com/question/28012687
#SPJ4
Two plane metal plates 4 cm long are held horizontal 3 cm apart in a vacuum one being vertically one above other. The upper plate is at a p.d 300 volt and the lowered is earthed. Electrons having velocity of 10^7 m/s are injected horizontally midway between the plate and in a direction parallel to the 4cm edge. Calculate the vertical deflection of the electron beam as it emerges from the plates. (e/m=1.8 x 10^11Ckg^- 1).
Answers
With Newton's second law and kinematics we find the deflection of the electron beam is y = 1.44 cm
given parameters
the voltage of each upper plate V = 300 V, the lower one zero volts the length of the plates, l = 4 cm (1 m / 100 cm) = 0.04 m the separation between the plates d = 3 cm = 0.03 m the velocity of the electrons v = 10⁷ m/s parallel to the plates the relationship e / m = 1.8 10 11 C / kg
to find
the deflection (y) of electrons
the electric field and the electric potential are related
V = -E d
E = - V / d
where E is the electric field, V the electric potential and d the separation between the plates
E = - 300 / 0.03
E = -1 10⁴ N / C
Let's solve this exercise in parts
1st part. Let's set a reference system with the horizontal axis in direction to the length of the plates and the y axis in the vertical direction, the zero is located at the initial point of the plate and half of its separation.
Let's use Newton's second law to find the acceleration in the y-axis of the electrons
F = m a
electric force is
F = q E
q E = m a
a = q / m E
the face of electrons is negative q = -e
a = - e / m E
a = - 1.8 10¹¹ (- 1 10⁴)
a = 1.8 10¹⁵ m /s²
this acceleration is directed upwards, that is, the electrons approach the positive plate.
2nd part. We use kinematics to find the time it takes for electrons to pass the plates; on the x-axis there is no acceleration, so we use the uniform motion relationships
v = x / t
t = x / v
t = 0.04 / 1 10⁷
t = 4 10⁻⁹ s
For the y-axis, let it be known that the electrons are initially in the middle between the plates, so y₀ = 0 and the velocity eg this axis is zero, we look for the deflection at the end of the plate
y = y₀ + v_{oy) t + ½ a t²
y = 0 + 0 + ½ a t²
y = ½ (1.8 10¹⁵) ( 4 10⁻⁸ )²
y = 14.4 10⁻³ m = 1.44 10⁻² m
y = 1.44 cm
We can use Newton's second law and kinematics to find the distance that the electron beam deviates from the middle of the plate is y = 1.44 cm, therefore the beam of electrons leaving the plates
learn more about Newton's second law and kinematics here: brainly.com/question/13016721
Answer:
The vertical deflection of the beam of an electron beam is 1.44×〖10〗^(-2) m.
Explanation:
Velocity (v) = 〖10〗^7 m/s
p.d. (V) = 300 V
Length of metal plates (x) = 4cm = 0.04 m
Separation (d) = 3 cm = 0.03 m
Specific charge of an electron (e/m) = 1.8×〖10〗^11 C/kg
Vertical deflection (y) = ?
The vertical deflection of electron inside the electric field is
y=1/2 at^2
=1/2 eE/m (x/v)^2
=1/2 (e/m) V/d (x/v)^2
=1/2×1.8×〖10〗^11×300/0.03×(0.04/〖10〗^7 )^2
⸫ y=1.44×〖10〗^(-2) m
Hence, the vertical deflection of the beam of an electron beam is 1.44×〖10〗^(-2) m.
which of the following collisions are inelastic? which of the following collisions are inelastic? a ball of clay dropped onto the floor. the clay sticks to the floor. a golf club hitting a golf ball. a bullet colliding with a block of wood. the bullet is embedded in the wood. a rubber ball dropped onto the floor.
Answers
The collisions that are considered inelastic are the ball of clay dropped onto the floor (clay sticks to the floor) and the bullet colliding with a block of wood (bullet embedded in the wood).
The collision of a golf club hitting a golf ball and the rubber ball dropped onto the floor are not specified as inelastic in the given options.An inelastic collision is one in which kinetic energy is not conserved, meaning that the total kinetic energy of the system before the collision is different from the total kinetic energy after the collision. In the case of the ball of clay dropped onto the floor, the clay sticks to the floor, resulting in a loss of kinetic energy and deformation of the clay, indicating an inelastic collision.
Similarly, when a bullet collides with a block of wood and gets embedded, there is a loss of kinetic energy and deformation, indicating an inelastic collision. On the other hand, the golf club hitting a golf ball and the rubber ball dropped onto the floor do not provide sufficient information to determine if the collisions are specifically inelastic.
Ton learn more about Collisions : brainly.com/question/13138178
#SPJ11
Name two ways to decrease the electric force between two charged objects.
Answers
Answer:
Inverse relationships are common in nature. In electrostatics, the electrical force between two charged objects is inversely related to the distance of separation between the two objects. Increasing the separation distance between objects decreases the force of attraction or repulsion between the objects.
Explanation:
Two ways to decrease the electric force between two charged objects:
by lessen charge of the test objects.by increasing distance between test change and source charge.What is coulomb force?As a result of their electric charge, particles or objects are attracted to or repelled by the Coulomb force, also known as electrostatic force or Coulomb interaction. Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, a French scientist who published the findings of an experimental inquiry into the proper quantitative description of this force in 1785, gave the electric force its name. The electric force is one of the fundamental physical forces.
Positive or negative electric charges that are similar to one another repel one another in a straight line between their centers. Positive and negative charges that are opposite each other are drawn together along a straight line connecting their centers.
Learn more about coulomb force here:
https://brainly.com/question/11141051
#SPJ5
The development of current atomic theory has changed over time as result of different proposed models and experiments. Place these in chronological order.

Answers
Answer:
b????
Explanation:
hope its right
The development of the current atomic theory has changed over time as a result of different proposed models and experiments as per the chronological order of the development of the atomic models, the correct answer is option B
What are atomic models?There are some models that are used to explain the arrangements of subatomic particles inside the atom based on the atomic theory of atom are known as the atomic models.
As given in the problem statement The development of the current atomic theory has changed over time as a result of different proposed models and experiments. The chronological order of the atomic model is given as follows
John Dalton's atomic model
The Plum Pudding Model, developed by J.J. Thomson,
Using the alpha particle bombardment experiment on a thin sheet of gold, Rutherford's model
Niels Bohr's model explained the revolving nature of the electrons in the different shells around the nucleus of the atom.
Erwin Schrodinger's model explains the arrangement of the subatomic particles as the electron Cloud Model
Thus, the correct answer is option B.
Learn more about the atomic models here,
brainly.com/question/9145431
#SPJ2
At a certain distance from a charged particle, the magnitude of the electric field is 460 V/m and the electric potential is -3.60 kV. (a) What is the distance to the particle? (b) What is the magnitude of the charge?
Answers
Answer:
(a) the distance to the particle is 7.83 m
(b) the magnitude of the charge is 3.13 x 10⁻⁶ C
Explanation:
Given;
magnitude of the electric field, E = 460 V/m
magnitude of the electric potential, V = 3.6 kV = 3,600 V
(a) the distance to the particle is calculated as;
Er = V
r = V/E
r = 3,600/460
r = 7.83 m
(b) the magnitude of the charge is calculated as;
\(E =\frac{kQ}{r^2} \\\\Q = \frac{Er^2}{k} \\\\Q = \frac{460 \times (7.83)^2}{9\times 10^9} \\\\Q = 3.13 \times 10^{-6} \ C\)
14.
Car A travels at a velocity of 80 km/hr with a mass of 1200 kg. Car B's velocity is 20 km/hr with a
mass of 2400 kg. Which car has the greatest momentum?
Formula
Work
Answer with units
Answers
The momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object. The momentum of object A is greater than object B.
What is Momentum?The momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object. Momentum is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude as well as a direction. If 'm' is an object's mass and 'v' is the velocity, then the object's momentum p is:
p = mv
Momentum of Car A, p = mv
m = 1200 kg,
v = (80 × 1000)/ (60 × 60) = 22.22 m/s
p = mv
p = 1200 × 22.22 = 26664 kg.m/s
Momentum of Car B, p = mv
m = 2400 kg,
v = (20 × 1000)/ (60 × 60) = 5.55 m/s
p = mv
p = 2400 × 5.55 = 13333.33 kg.m/s
Therefore, the momentum of Car A is greater than car B.
Learn more about Momentum here:
https://brainly.com/question/30487676
#SPJ9