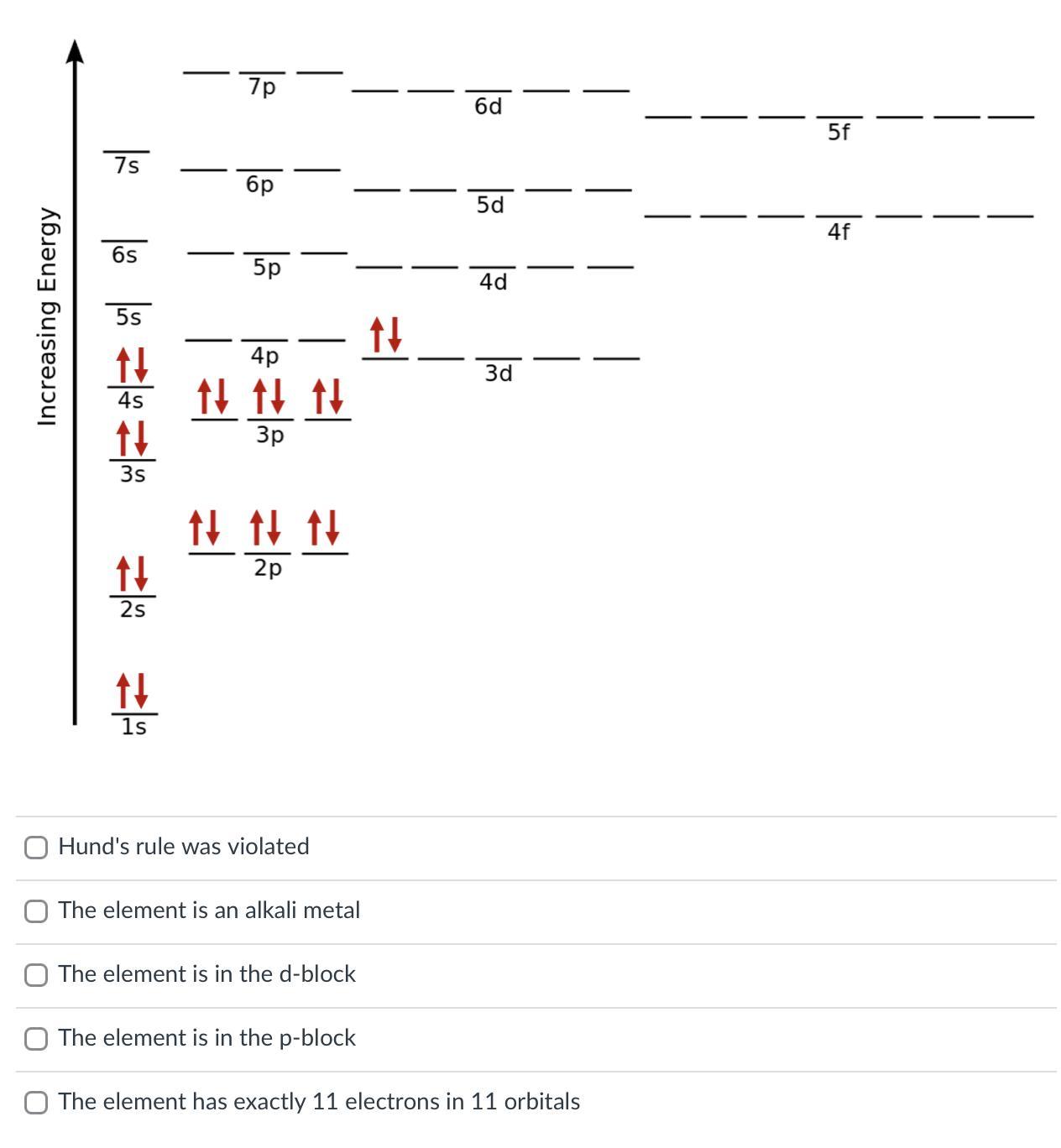
Answers
Answer
Hunde's rule was violated
The element is in the d-block
Explanation
From the orbital diagram, it can be observed that the 2 electrons of the 3d violate Hunde's rule.
Hund's rule states that every orbital in a subshell is singly occupied with one electron before any one orbital is doubly occupied, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals have the same spin.
Also, the total number of electrons in the orbital diagram is 22 electrons and this corresponds to the number of electrons of Titanium at ground states.
Hence, the element is in the d-block.
Related Questions
How many grams is 5.00 moles of carbon dioxide?
Answers
Answer:
220.1 grams of CO2.
Use the periodic table to determine the number of valence electrons in each of the following elements.
Na:
E:
V:
Ar:
Answers
Answer:
Na: 1
F: 7
V: 5
Ar: 8
C: 4
Explanation:
The number of valence electrons by using periodic table are Na has 1, F has 7, V has 5, Ar has 8 and C has 4 valence electron.
What is periodic table ?The chemical elements are arranged in rows and columns in the periodic table, sometimes referred to as the periodic table of the elements. It is frequently used in physics, chemistry, and other sciences, and is frequently regarded as a symbol of chemistry.
Because of the orderly arrangement of the elements, it is known as the periodic table. They're arranged in rows and columns, as you'll see. Periods and groups are the names given to the horizontal rows and the vertical columns, respectively.
A system for arranging the chemical elements is the periodic table. The fundamental components of all matter are the chemical elements. The atomic number is a distinct characteristic of each chemical element. This figure is based on how many protons there are in each of the element's atoms.
Thus, The number of valence electrons by using periodic table are Na has 1, F has 7, V has 5, Ar has 8 and C has 4 valence electron.
To learn more about the periodic table, follow the link;
https://brainly.com/question/11155928
#SPJ2
Determine what product will be produced at the negative electrode for the following reaction:
2KCl(aq) + 2H20(1) -> H2(g) + Cl2(g) + 2KOH(aq)
A. H2
B. Cl2
с. КОН
D. K
Answers
Answer:
Choice A. \(\rm H_{2}\) would be produced at the negative electrode.
Explanation:
Ionic equation for this reaction:
\(2\, {\rm K^{+}} + 2\, {\rm Cl^{-}} + {2\, \rm H_{2} O} \to {\rm H_{2}} + {\rm Cl_{2}} + 2\, {\rm K^{+}} + {\rm 2\, OH^{-}}\).
Net ionic equation:
\(2\, {\rm Cl^{-}} + 2\, \rm H_{2} O} \to {\rm H_{2}} + {\rm Cl_{2}} + 2\, {\rm OH^{-}}\).
Half-equations:
\(2\, {\rm Cl^{-}} \to {\rm Cl_{2}} + 2\, {e^{-}}\).
(Electrons travel from the solution to an electrode.)
\(2\, {\rm \overset{+1}{H}_{2} O} + 2\, {e^{-}} \to \overset{0}{\rm H}_{2} + 2\, {\rm O\overset{+1}{H}\!^{-}}\).
(An electrode supply electrons to the solution to reduce some of the \(\rm H\) atoms from \(\rm H_{2}O\).)
In a DC circuit, electrons always enter the circuit from the negative terminal of the power supply and return to the power supply at the positive terminal.
The negative electrode is connected to the negative terminal of the power supply. Electrons from the power supply would flow into the solution through this electrode.
This continuous supply of electrons at the negative electrode would drive a reduction half-reaction. In this question, that corresponds to the reduction of water: \(2\, {\rm \overset{+1}{H}_{2} O} + 2\, {\rm e^{-}} \to \overset{0}{\rm H}_{2} + 2\, {\rm O\overset{+1}{H}\!^{-}}\). Hence, \(\rm H_{2}\) would be produced at the negative electrode.
burning 12g of urea raise temp of water by 30C what is the enthalpy of combustion for 1kg urea
Answers
The enthalpy of combustion for 1kg of urea is -1223525.84 J/mol.
Urea is a compound that is used in fertilizers and in some plastics.The enthalpy of combustion for urea is the amount of energy that is released when urea is burned. In order to calculate the enthalpy of combustion for 1kg of urea, we need to use the information that is provided to us in the question. Let us start by writing down the balanced equation for the combustion of urea: CO(NH2)2 + 3/2 O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + N2
The balanced equation shows that 1 mole of urea reacts with 1.5 moles of oxygen gas to produce 1 mole of carbon dioxide, 2 moles of water, and 1 mole of nitrogen gas. The enthalpy change for this reaction is equal to the amount of energy that is released when 1 mole of urea is burned.
The heat of combustion (ΔHc) of urea is -632.6 kJ/mol. This means that 632.6 kJ of energy is released when 1 mole of urea is burned. We know that 12g of urea raised the temperature of water by 30°C. We can use this information to calculate the amount of energy that was released when 12g of urea was burned.
The specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J/g°C. This means that it takes 4.18 J of energy to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1°C. Therefore, it takes 4.18 x 1000 = 4180 J of energy to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°C.
We know that 12g of urea raised the temperature of water by 30°C. Therefore, the amount of energy that was released when 12g of urea was burned is:
Energy = mass x specific heat capacity x temperature change
Energy = 0.012 kg x 4180 J/kg°C x 30°C
Energy = 1497.6 J
We can now use this information to calculate the enthalpy of combustion for 1kg of urea:
Enthalpy of combustion = energy released / moles of urea burned
Enthalpy of combustion = 1497.6 J / (0.012 kg / 60.06 g/mol)
Enthalpy of combustion = - 1223525.84 J/mol
for such more questions on enthalpy
https://brainly.com/question/14047927
#SPJ8
Using the chemical formula CaO + 2 NaCl → Na2O + CaCl2, calculate how many moles of CaCl2 you would produce if you used up 5.4 moles of CaO?
Answers
Answer:
5.4 moles CaO 1 mole CaCl₂ 5.4 mole CaCl₂
1 mole CaO
Explanation:
What type of pressure means the air around you is densely packed
Answers
When the air around you is densely packed, it means the pressure is high.
Pressure and air densityThe atmospheric pressure is directly proportional to air density.
When the air around a place is densely packed, it is an indication of high atmospheric pressure.
On the other hand, if the air around is loosely packed, it means the atmospheric pressure is also low.
More on pressure and density can be found here: https://brainly.com/question/5218385
#SPJ1
A 54.2 g sample of polystyrene, which has a specific heat capacity of 1.880 J-gc, is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at
right) that contains 100.0 g of water. The temperature of the water starts off at 21.0 °C. When the temperature of the water stops
changing it's 34.3 °C. The pressure remains constant at 1 atm.
Calculate the initial temperature of the polystyrene sample. Be sure your answer is rounded to the correct number of significant
digits.
thermometer.
insulated
container
water
sample.
a calorimeter
Answers
Tthe initial temperature of the polystyrene sample is 39.4°C.
Given: Mass of polystyrene sample = 54.2 gSpecific heat of polystyrene = 1.880 J-g°CWater mass = 100.0 g Initial water temperature = 21.0°CWater final temperature = 34.3°CPressure remains constant at 1 atmFormula used:Heat gained by water = heat lost by polystyreneHence,Heat lost by polystyrene = Heat gained by water=> mcΔT = mcΔTwhere,m = mass of polystyrene or waterc = specific heat capacityΔT = change in temperatureThe temperature change is ΔT = 34.3°C - 21.0°C = 13.3°CNow we can use this temperature change to calculate the initial temperature of the polystyrene.Taking the water's specific heat capacity, c = 4.184 J/g°CHeat gained by water = (100.0 g)(4.184 J/g°C)(13.3°C) = 5574 JHeat lost by polystyrene = 5574 JTaking the polystyrene's specific heat capacity, c = 1.880 J/g° ) = 13.3°C Now let's calculate the mass of polystyrene using the specific heat capacity formula.5574 J = (54.2 g)(1.880 J/g°C)(13.3°C - Ti)Ti = 39.4°C
for more questions on polystyrene
https://brainly.com/question/15913091
#SPJ8
The element __ is the most similar to oxygen in chemical and physical properties.
Answers
Answer:
the element air is the most similar to oxygen in chemical. and physical properties
Calculate the standard entropy change
C2H2 (g) + 2H2 (g) → C2H6 (g
C2H2= 201
H2=131
C2H6 = 230
Answers
Entropy is a notion that essentially refers to the universe's propensity for chaos or the spontaneous changes that take place in everyday happenings. Here the standard entropy change for the given reaction is -233.
Entropy is typically referred to as a measurement of a system's randomness or disorder. In the year 1850, a German physicist by the name of Rudolf Clausius first proposed this idea. Entropy is a thermodynamic property that is used to characterize how a system behaves in terms of temperature, pressure, entropy, and heat capacity.
Here the standard entropy change is:
Entropy of products - entropy of reactants
ΔS = 230 - (201 + 2 ( 131)) = -233
To know more about entropy, visit;
https://brainly.com/question/17172535
#SPJ1
. A pipet is a type of glassware that is used to deliver a specified volume of liquid. A 5 mL pipet has major scale divisions marked for every milliliter and minor scale divisions marked for every 0.1 mL. What is the uncertainty (in mL) made using this pipet? Would it be proper to report that the pipet was used to deliver 3.2 mL of liquid? Explain why or why not
Answers
Answer:
Measure of uncertainty thousands place or .01 mL
Yes it would be proper.
Explanation:
measure of uncertainty is when you as the user have to guess, since the pipette has marks every 0.1 ml then you can guess that the liquid is in between the marks or maybe closer to one mark then the other.
Ethanol in the body is oxidized to acetaldehyde by liver alcohol dehydrogenase (LADH). Other alcohols are also oxidized by LADH. For example, methanol, which is mildly intoxicating, is oxidized by LADH to the quite toxic product of formaldehyde. The toxic effects of ingesting methanol (a component of many commercial solvents) can be reduced by administering ethanol. The ethanol acts as a competitive inhibitor of methanol by displacing it from LADH. This provides sufficient time for the methanol to be harmlessly excreted by the kidneys. If an individual has ingested 30 mL of methanol (a lethal dose), how much 100 proof whiskey (50% ethanol by volume) must be imbibed to reduce the activity of her LADH towards methanol to 5% of its original value? The adult human body contains ~40L of aqueous fluids throughout which ingested alcohols are rapidly and uniformly mixed. The densities of ethanol and methanol are both 0.79 g/cm3. Assume the KM values of LADH for ethanol and methanol to be 10-3 M and 10-2 M, respectively, and that Ki = KM for ethanol
Answers
Answer: The changes are the mL of methanol ingestion (30mL) and the proof of the whiskey (40% ethanol; 80 proof), and the percentage of reduction (1%). I applied the formulas from the last post in reference to this question but am completely lost. The formulas used last time were: 2. Formulas Applied alpha=1 + ([etOH]/KetOH) (V[meOH]/V[etOH])= (Vmax*[meOH]/KmeOH+[meOH])/(Vmax*[meOH]/alpha*KmeOH+[meOH]) which reduces to (V[meOH]/V[etOH])=(alpha*KmeOH+[meOH])/(KmeOH+[meOH]) 3. My attempt Molarity of methanol: 30mL; which equates to 23.7g of methanol; in 40L that is equal to 0.5925 g/L Dividing the molecular weight by 32.04g/mol I get 0.0184925 which is approximately 0.02M; Km is 0.01M Since the molar mass of methanol and ethanol are two fold, I can multiply the g/l by 4. However, unlike the previous problem, I cannot multiply by 2 because I do not have 50% EtOH, so because 40 is less than 50 I assume to multiply by 2.5 yielding: (30mL)(4)(2.5)=300mL 300mL of EtOH to effectively reduce the Methanol to 1%.
Hurricane Andrew hit Florida in 1992, and as a result, caused great amounts of damage to property in Miami. Which of the following terms describes a hurricane?
A. a current
B. a severe storm
C. a stable air mass
D. a jet stream
Answers
B. A severe storm
What is the molar mass of AICI3?
Answers
Answer:
133.34 g/mol
Explanation:
A can of soda is opened at room temperature and a hiss is heard. Which factor has changed inside the container?
Answers
The factor that has changed inside the container would be the pressure.
Pressurized containersSodas in cans are preserved using a gas, carbon dioxide to be precise.
The gas is used to preserve the drink and sealed under pressure.
When a can of soda is opened, the first thing that escapes is the carbon dioxide gas. By doing so, the pressure in the can reduces.
More on canned soda and pressure can be found here: https://brainly.com/question/10301529
#SPJ1
A mystery element has 18 protons. Which one of the following statements is true about the element?
o
A. The element belongs in row 2 of the periodic table and is classified as a halogen.
O
B. The element belongs in row 3 of the periodic table and is classified as a noble gas.
O
C. The element belongs in row 4 of the periodic table and is classified as an alkali metal.
D. The element belongs in row 5 of the periodic table and is classified as an alkaline earth metal.
Answers
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Elements in a group are determined by the number of valence electrons
Elements in a period are determined by the number of electrons shell
The electronic configuration of the element is
2,8,8
the number of valence electron is 8 that means it is in Group 8/O
the number of electron shell is 3 that means it is in period (row) 3
Group 8/O elements are called Noble gases
1. 2Al(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) → Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2(g) a. Determine the volume (mL) of 15.0 M sulfuric acid needed to react with 45.0 g of aluminum to produce aluminum sulfate. b. Determine the % yield if 112 g of aluminum sulfate is produced under the above conditions.
Answers
Answer:
a. 167 mL b. 39.27 %
Explanation:
a. From the chemical equation. 2 mole of Al reacts with 3 mole H₂SO₄ to produce 1 mol Al₂(SO₄)₃.
Now, we calculate the number of moles of Al in 45.0 g Al.
We know number of moles, n = m/M where m = mass of Al = 45.0 g and M = molar mass of Al = 26.98 g/mol.
So n = 45.0 g/26.98 g/mol = 1.668 mol
Since 2 mole of Al reacts with 3 mole H₂SO₄, then 1.668 mole of Al reacts with x mole H₂SO₄. So, x = 3 × 1.668/2 mol = 2.5 mol
So, we have 2.5 mol H₂SO₄.
Now number of moles of H₂SO₄, n = CV where C = concentration of H₂SO₄ = 15.0 M = 15.0 mol/L and V = volume of H₂SO₄.
V = n/C
= 2.5 mol/15.0 mol/L
= 0.167 L
= 167 mL of 15.0 M H₂SO₄ reacts with 45.0 g Al to produce aluminum sulfate.
b. From the chemical reaction, 2 mol Al produces 1 mol Al₂(SO₄)₃
Therefore 1.668 mol Al will produce x mol Al₂(SO₄)₃. So, x = 1 mol × 1.668 mol/2 mol = 0.834 mol
So, we need to find the mass of 0.834 mol Al₂(SO₄)₃. Now molar mass Al₂(SO₄)₃ = 2 × 26.98 g/mol + 3 × 32 g/mol + 4 × 3 × 16 g/mol = 53.96 g/mol + 96 g/mol + 192 g/mol = 341.96 g/mol.
Also number of moles of Al₂(SO₄)₃, n = mass of Al₂(SO₄)₃,m/molar mass Al₂(SO₄)₃, M
n =m/M
So, m = nM = 0.834 mol × 341.96 g/mol = 285.2 g
% yield = Actual yield/theoretical yield × 100 %
Actual yield = 112 g, /theoretical yield = 285.2 g
So, % yield = 112 g/285.2 g × 100 %
= 0.3927 × 100 %
= 39.27 %
The volume (mL) of 15.0 M sulfuric acid needed to react with 45.0 g of aluminum is 166mL and % yield of the reaction is 39.46%.
How do we calculate moles?Moles of any substance will be calculated by using the below formula as:
n = W/M, where
W = given mass
M = molar mass
Given chemical reaction is :
2Al(s) + 3H₂SO₄(aq) → Al₂(SO₄)₃(aq) + 3H₂(g)
Moles of 45g of Al will be calculated as:
n = 45g / 27g/mol = 1.66 mole
From the stoichiometry of the reaction, it is clear that:
1.66 moles of Al = react with 3/2×1.66=2.49 moles of H₂SO₄
By using the formula of molarity we can calculate the volume of H₂SO₄ as:
M = n/V
V = (2.49) / (15) = 0.166L = 166mL
Again from the stoichiometry it is clear that:
1.66 moles of Al = produces 1/2×1.66= 0.83 moles of Al₂(SO₄)₃
Mass of 0.83 moles of Al₂(SO₄)₃ = (0.83mol)(341.96g/mol) = 283.82 g
Given actual yield of Al₂(SO₄)₃ = 112g
% yield will be calculated as:
Percent yield = (Actual yield/Theoretical yield) × 100
% yield = (112/283.82) × 100 = 39.46%
Hence required values are discussed above.
To know more about percent yield, visit the below link:
https://brainly.com/question/8638404
how much energy is required to vaporize 2 kg of copper
Answers
It would require approximately 600 kilojoules of energy to vaporize 2 kg of copper.
To calculate the energy required to vaporize a substance, we need to consider the heat of vaporization, which is the amount of energy required to convert a given amount of substance from its liquid state to its gaseous state at a constant temperature.
The heat of vaporization for copper is approximately 300 kJ/kg (kilojoules per kilogram) at its boiling point, which is around 2567 degrees Celsius (4649 degrees Fahrenheit). This means that for every kilogram of copper, 300 kJ of energy is needed to vaporize it.
Given that you have 2 kg of copper, we can calculate the total energy required as follows:
Energy = Heat of Vaporization × Mass
Energy = 300 kJ/kg × 2 kg
Energy = 600 kJ
Therefore, it would require approximately 600 kilojoules of energy to vaporize 2 kg of copper.
It's worth noting that the heat of vaporization can vary slightly depending on the purity of the copper and the specific conditions, such as temperature and pressure. The value provided here is an approximation. Additionally, it's important to handle copper and any high-temperature processes with caution, as they can pose safety hazards.
for more questions on vaporize
https://brainly.com/question/24258
#SPJ8
Atomic mass is an average of the elements_____.
Answers
Specific chemical element
Answer:
The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of the atoms of an element measured in atomic mass unit (amu, also known as daltons, D). The atomic mass is a weighted average of all of the isotopes of that element, in which the mass of each isotope is multiplied by the abundance of that particular isotope.
Explanation:
You come across the following container while working in the lab: Answer the following questions in the space below: 1. Identify the WHMIS symbols. 2. What precautions should you take and why?
Answers
Type #1 Flame symbols are among the WHMIS emblems.
Type 2: Symbols with a flame above a circle.
Exploding bomb symbols are of type 3.
Compressed gas symbols are of type 4.
Corrosion symbols are type #5.
Skull and water the water symbols are type #6.
Exclamation mark symbols are type #7.
Health hazard symbols are type #8.
Because workplaces require a defined technique to detect hazardous items, WHMIS labels are crucial.
What does the WHMIS stand for?The national ’s hazard standard for Canada is the Health And Safety At work System (WHMIS). Hazard categorization, cautionary container labeling, the distribution of safety data sheets, and worker information and training programs are the system's main components.
What does WHMIS look like in the US?The U.S. Ohs Hazard Identification Standard and WHMIS are quite similar.
To know more about WHMIS visit:
https://brainly.com/question/28542158
#SPJ1
Hi, what are you doing?
Answers
Answer:
i am dancing and you ok hom
Assume that you have tested an unknown sample with both biuret solution and Benedict's solution and that both tests result in a blue color. What have you learned?
Answers
The sample is neither protein nor reducing sugars.
Benedict’s test is a chemical test that can be used to check for the presence of reducing sugars in a given analyte.
Biuret reagent is made of Copper sulphate (CuSO4), sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and sodium-potassium tartrate (also known as Rochelle salt).
When the sample retains the blue color of the Biuret's and Benedict's reagents, it indicates that the sample has no elements of proteins and reducing sugars in it. If it could be having proteins, then the sample could have to change the color of the Biuret reagent from blue to purple, and in the case of reducing sugars, Benedict's solution could have changed from blue to green to orange and finally red. There it tells that the sample is neither protein nor reducing sugars.
To know more about the Benedict's solution, here
brainly.com/question/14731281
#SPJ4
the number of protons in an ato
Answers
Answer:
The number of protons in the nucleus of the atom is equal to the atomic number
(Z). The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons .
The mass number of the atom (M) is equal to the sum of the number of protons
and neutrons in the nucleus.
the work function of magnesium metal is 5 86/10J
a, calculate the minimum frequency of required to release elections from the metal.
b, calculate the kinetic energy of the ejected electronic light of frequency 2.00/10 s is used to irradiating the metal.
Answers
a) To calculate the minimum frequency of electromagnetic radiation required to release electrons from the metal, you can use the following formula:
f = W / h
where f is the minimum frequency of electromagnetic radiation required, W is the work function of the metal in joules, and h is the Planck constant in joules per second.
Plugging in the values for W and h, you get:
f = (5.86 x 10^-19 J) / (6.626 x 10^-34 J/s) = 8.9 x 10^14 Hz
This is the minimum frequency of electromagnetic radiation required to release electrons from the magnesium metal.
b) To calculate the kinetic energy of the ejected electronic light of frequency 2.00 x 10^14 Hz, you can use the following formula:
KE = hf - W
where KE is the kinetic energy of the ejected electron, h is the Planck constant in joules per second, f is the frequency of the electromagnetic radiation in hertz, and W is the work function of the metal in joules.
Plugging in the values for h, f, and W, you get:
KE = (6.626 x 10^-34 J/s) * (2.00 x 10^14 Hz) - (5.86 x 10^-19 J) = 1.32 x 10^-19 J - 5.86 x 10^-19 J = -4.54 x 10^-20 J
This is the kinetic energy of the ejected electron when light of frequency 2.00 x 10^14 Hz is used to irradiate the magnesium metal. Since the kinetic energy is negative, this means that the electron is not released from the metal when irradiated with this frequency. The frequency of the electromagnetic radiation needs to be higher than the minimum frequency required to release the electron in order for the electron to be ejected from the metal.
1. In consideration of the following acids.
HCI, H,SO, HPO, Acetic acid, Formic Acid, HF, carbonic acid, ammonium ion, water, nitric acid
a. Find conjugate bases
b. Provide complete/partial ionized equations
c. Group them as strong and weak acids
Answers
Conjugate acid-base pair is the combination of two compounds which can accept and donate hydrogen ions.
The compounds are HCI, H₂SO₄, HPO, Acetic acid, Formic Acid, HF, carbonic acid, ammonium ion, water, nitric acid.
a.
Conjugate bases of HCl is Cl⁻.
Conjugate bases of H₂SO₄ is HSO₄⁻.
Conjugate bases of HPO₄²⁻ is PO₄³⁻.
Conjugate bases of CH₃COOH is CH₃COO⁻.
Conjugate bases of formic acid is formate ion.
Conjugate bases of HF is F⁻.
Conjugate bases of carbonic acid is the bicarbonate.
Conjugate bases of ammonium ion ammonia.
Conjugate bases of water is H₃O⁺.
Conjugate bases of HNO₃ is NO₃⁻.
b.
HCl ⇄ H⁺ + Cl⁻
H₂SO₄ ⇄ 2H⁺ + SO₄²⁻
H₃PO₄ ⇄ H⁺ + PO₄³
CH₃COOH ⇄ H⁺ + CH₃COO⁻
HCOOH ⇄ H⁺ + HCOO⁻
HF ⇄ H⁺ + F⁻
H₂CO₃ + H₂O ⇄ HCO₃⁻ + H₃O⁺
Ammonia does not ionizes in water.
H₂O ⇄ H₃O⁺ + OH⁻
HNO₃ ⇄ H⁺ + NO₃⁻
c.
Strong acids: HCl, H₂SO₄, HNO₃,
Weak acids: H₃PO₄, CH₃COOH, HCOOH, HF, H₂CO₃, ammonium ion
Water is both weak and strong acid.
Learn more about conjugate bases from the link given below.
https://brainly.com/question/12883745
#SPJ1
b) 2.38 gm of a metal on treatment with nitric acid and sub sequent ignition gave 3.022 gm of the oxide. Specific heat of the metal is 0.055, calculate the extra atomic weight.
Answers
The extra atomic weight in a metal on treatment with nitric acid is 100.361 g/mol.
How to calculate extra weight?The first step is to calculate the mass of oxygen in the oxide formed:
Mass of oxygen = Mass of oxide - Mass of metal
Mass of oxygen = 3.022 g - 2.38 g
Mass of oxygen = 0.642 g
Use the specific heat of the metal to determine its identity:
specific heat = 6.4 / atomic weight
Solving for atomic weight:
atomic weight = 6.4 / specific heat
atomic weight = 6.4 / 0.055
atomic weight = 116.36 g/mol
The atomic weight to calculate the extra atomic weight:
extra atomic weight = atomic weight - atomic weight of oxygen
extra atomic weight = 116.36 g/mol - 15.999 g/mol
extra atomic weight = 100.361 g/mol
Therefore, the extra atomic weight is 100.361 g/mol.
Find out more on nitric acid here: https://brainly.com/question/22698468
#SPJ1
One gram of a compound requires the following quantities of solvent to dissolve: 47 mL of water, 8.1 mL of chloroform, 370 mL of diethyl ether, or 86 mL of benzene. Calculate the solubility of the compound in these four solvents (as g/100 mL). Estimate the partition coefficient of the compound between chloroform and water, ethyl ether and water, and benzene and water. Which solvent would you choose to extract the compound from an aqueous solution
Answers
Answer:
Chloroform.
Explanation:
Given,
Solvent requires 1g of compound per 100 mL
For water,
= 1g/47ml
= 2.1
For Chloroform,
= 1 g/8.1 mL
= 12.345679
For Diethyl ether,
= 1 g/370 mL
= 0.27
For Benzene,
= 1 g/86 mL
= 1.2
Partition coefficients:
Water = -
chloroform = 5.9
Diethyl = .13
Benzene = .57
The solvent chloroform would be chosen for drawing out the compound out of an aqueous solution as it has the maximum solubility.
How much water has to be evaporated from 250 mL of 1 M Ca(OH)2 to make it 3 M?
Answers
Approximately 166.67 mL of water needs to be evaporated from 250 mL of 1 M Ca(OH)2 to make it 3 M.
To find the amount of water that needs to be evaporatedThe relationship between the initial and final concentrations and volumes must be taken into account.
Given: Initial concentration \((C^1) = 1 M Initial volume (V^1) = 250 mL\)
\((C^2) = 3 M final concentration\)
We can use the equation:
\(C^1 * V^1 = C^2 * V^2\)
Where:
\(V^2\)is the final volume of the solution
Rearranging the equation to solve for V2:
\(V^2 = (C^1 * V^1) / C^2\)
Substituting the given values:
\(V^2 = (1 M * 250 mL) / 3 M\)
\(V^2 = 250 mL / 3\)
\(V^2\) ≈ \(83.33 mL\)
To find the amount of water that needs to be evaporated, we subtract the final volume from the initial volume:
Amount of water to be evaporated = \(V^1 - V^2\)
Amount of water to be evaporated = 250 mL - 83.33 mL
Amount of water to be evaporated ≈ 166.67 mL
Therefore, approximately 166.67 mL of water needs to be evaporated from 250 mL of 1 M Ca(OH)2 to make it 3 M.
Learn more about Initial concentration here: brainly.com/question/30720317
#SPJ1
• How does the name of the salt tell us that:
a) there is just one other element combined with the metal?
b) there is oxygen present in the salt?
Answers
The name of the salt tells us that:
a) there is just one other element combined with the metal by looking at the suffix of the salt's name.
b) the presence of oxygen in a salt can be indicated by the name of the salt.
a) The name of a salt can tell us that there is just one other element combined with the metal by looking at the suffix of the salt's name. If the salt name ends in "-ide," it indicates that the salt is composed of a metal and a single non-metal element.
For example, sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium bromide (KBr) are salts where the metal (sodium and potassium) is combined with a single non-metal element (chlorine and bromine, respectively). The "-ide" suffix suggests the presence of only one other element in the salt.
b) The presence of oxygen in a salt can be indicated by the name of the salt. If the salt name includes the element oxygen, it suggests that oxygen is present in the salt compound.
For example, sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃) and calcium sulfate (CaSO₄) contain the element oxygen in their chemical formulas. The presence of oxygen in the salt is implied by the name and the combination of elements in the compound.
Therefore, the name of salt tells us that there is just one other element combined with the metal and there is oxygen present in the salt
Learn more about salt here:
https://brainly.com/question/31814919
#SPJ 1
One gallon of gasoline (C8H18) weights about 6.3 pounds. Burning gasoline with excess of oxygen forms water and carbon dioxide. When 3.1 gallons of gasoline burn, how many pounds of CO2 emit into the air?
FW: C = 12; H = 1; O = 16.
Answers
Answer:
60 pounds of CO₂ are emited into the air
Explanation:
The combustion of gasoline occurs as follows:
C₈H₁₈(l) + 25/2O₂(g) ⇄ 8CO₂(g) + 9H₂O
Where 1 mole of gasoline produce 8 moles of CO₂
To solve this question we must find the moles of gasoline in 3.1 gallons. 8 times these moles are the moles of CO₂ produced. With the moles of CO₂ we can find its pounds as follows:
Pounds gasoline:
3.1 gallons * (6.3 pounds / gallon) = 19.53 pounds
Grams gasoline:
19.53 pounds * (453.592g / pound) = 8859g
Moles gasoline -Molar mass C8H18: 114.23g/mol-
8859g * (1mol / 114.23g) = 77.55 moles gasoline
Moles CO₂:
77.55 moles gasoline * (8 mol CO₂ / mol Gasoline) = 620.4 moles CO₂
Mass CO₂ - Molar mass: 44.01g/mol-
620.4 moles CO₂ * (44.01g / mol) = 27304g CO₂
Pounds CO₂:
27304g CO₂ * (1lb / 453.592g) =
60 pounds of CO₂ are emited into the air13.0 mL of hydrochloric acid (HCl) required to neutralize 36.11 ml of 0.045 M sodium hydroxide (NaOH). What is the molarity of hydrochloric acid?
Answers
Answer:
Molarity of HCl = 0.12 M
Explanation:
Given data:
Volume of HCl = 13.0 mL
Volume of NaOH = 36.11 mL
Molarity of NaOH = 0.045 M
Molarity of HCl = ?
Solution:
Formula:
M₁V₁ = M₂V₂
M₁= Molarity of HCl
V₁ = Volume of HCl
M₂ = Molarity of NaOH
V₂ = Volume of NaOH
M₁ × 13.0 mL = 0.045 M × 36.11 mL
M₁ = 1.62 M.mL / 13.0 mL
M₁ =0.12 M