Answers
Answer:
the resistance of the longer one is twice as big as the resistance of the shorter one.
Explanation:
Given that :
For the shorter cylindrical resistor
Length = L
Diameter = D
Resistance = R1
For the longer cylindrical resistor
Length = 8L
Diameter = 4D
Resistance = R2
So;
We all know that the resistance of a given material can be determined by using the formula :
\(R = \dfrac{\rho L }{A}\)
where;
A = πr²
\(R = \dfrac{\rho L }{\pi r ^2}\)
For the shorter cylindrical resistor ; we have:
\(R = \dfrac{\rho L }{\pi r ^2}\)
since 2 r = D
\(R = \dfrac{\rho L }{\pi (\frac{2}{2 \ r}) ^2}\)
\(R = \dfrac{ 4 \rho L }{\pi \ D ^2}\)
For the longer cylindrical resistor ; we have:
\(R = \dfrac{\rho L }{\pi r ^2}\)
since 2 r = D
\(R = \dfrac{ \rho (8 ) L }{\pi (\frac{2}{2 \ r}) ^2}\)
\(R = \dfrac{32\rho L }{\pi \ (4 D) ^2}\)
\(R = \dfrac{2\rho L }{\pi \ (D) ^2}\)
Sp;we can equate the shorter cylindrical resistor to the longer cylindrical resistor as shown below :
\(\dfrac{R_s}{R_L} = \dfrac{ \dfrac{ 4 \rho L }{\pi \ D ^2}}{ \dfrac{2\rho L }{\pi \ (D) ^2}}\)
\(\dfrac{R_s}{R_L} ={ \dfrac{ 4 \rho L }{\pi \ D ^2}}* { \dfrac {\pi \ (D) ^2} {2\rho L}}\)
\(\dfrac{R_s}{R_L} =2\)
\({R_s}=2{R_L}\)
Thus; the resistance of the longer one is twice as big as the resistance of the shorter one.
Related Questions
A racing car has a uniform acceleration of 6 m/s2. In 10s it will cover:
Answers
distance = initial velocity x time + (1/2) x acceleration x time^2
Since the car starts from rest (initial velocity = 0 m/s), the formula simplifies to:
distance = (1/2) x acceleration x time^2
Substituting the given values, we get:
distance = (1/2) x 6 m/s^2 x (10 s)^2
distance = 300 meters
The racing car will cover a distance of 300 meters in 10 seconds with a uniform acceleration of 6 m/s^2.
A pulse of sound takes 1 second to travel about 25 feet to the seafloor
100
and back. A ship stops in an area where the seafloor extends to the bottom
of the Sunlight Zone. At this spot an echosounder gives a pulse of sound
that takes 26 second to travel to the seafloor and back. How deep is the
100
ocean at the bottom of the Sunlight Zone?
HELP!!! I’m stumped!! Get max points ( if it lets me! )
Answers
Answer: The depth of the ocean is 650 feets at the bottom of the sunlight zone.
The distance travelled by echo sound is given by the formula -
Speed = 2×distance/time
So, calculating the speed of sound from the formula using distance and time
Speed = 2×25/(1/100)
Speed = 50×1000
Speed of sound = 5000 feet/second
Now, calculating the distance or depth of ocean at the bottom of the sunlight zone -
Distance = (speed×time)/2
Distance = (5000×26/100)/2
Distance = 1300/2
Distance = 650 feets
Hence, the depth of ocean is 650 feets.
Learn more about echo -
brainly.com/question/19579065
Answer:
We can start by using the formula:
distance = speed x time
where distance is twice the depth of the ocean at the bottom of the Sunlight Zone (since the pulse travels down to the seafloor and then back up), speed is the speed of sound in water, and time is the round-trip time of the pulse.
The speed of sound in water is approximately 1,500 meters per second (or 4,921 feet per second).
Converting the round-trip time to seconds, we have:
26 seconds - 1 second = 25 seconds
Substituting the values into the formula:
2 x depth = 4,921 feet/second x 25 seconds
2 x depth = 123,025 feet
depth = 61,512.5 feet
Therefore, the ocean at the bottom of the Sunlight Zone is about 61,512.5 feet deep.
onsider laminar flow of a fluid through a square channel with smooth surfaces. now the average velocity of the fluid is doubled. determine the change in the head loss of the fluid. assume the flow regime remains unchanged
Answers
The head loss doubles when the average velocity is doubled.
The velocity formula: why?
The vector quantity velocity (v), denoted by equation v = s/t, quantifies dislocation (or shift in position, s), over change in time (t).
How do velocity and speed differ?Velocity is the pace and direction of the an object's movement, whereas speed is the timekeeping at which an object is travelling along a path.In other words, velocity is a vector, whereas speed is indeed a scalar value.
To know more about velocity visit:
https://brainly.com/question/18084516
#SPJ4
The heating element in an electric kettle is rated as 2.0 kW. If the water in the kettle is at 100.0 °C, what volume of water will be converted into steam in one minute? The specific latent heat of vaporization of the water is 2,257,000 J/kg and the
3 density of water is 1,000 kg/m .
Answers
Answer:
The volume is \(V =5.32 *10^{-5} \ m^3\)
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The power of the heating element is \(P = 2.0 kW = 2.0 *10^3 \ W\)
The temperature of the water in the kettle is \(T _w = 100^oC\)
The time to convert water to steam is t = 1 minute = 60 sec
The specific latent heat of vaporization is \(H_v = \ 2,257,000 J/kg\)
The density of water is \(\rho_w = 1000\ kg/m^3\)
The power of the heating element is mathematically represented as
\(P = \frac{E}{t}\)
Where E Energy generated by the heating element in term of heat
\(E = Pt\)
substituting values
\(E = 2.0 *10^{3} * 60\)
\(E = 120000 J\)
Now
The latent heat of vaporization is mathematically represented as
\(H_v = \frac{E}{m}\)
Where m is the mass of water converted to steam
So
\(m = \frac{E}{H_v}\)
substituting values
\(m = \frac{120000}{2257000}\)
\(m = 0.0532\ kg\)
The volume of water converted to steam is mathematically evaluated as
\(V = \frac{m }{\rho_w}\)
substituting values
\(V = \frac{0.0532}{1000}\)
\(V =5.32 *10^{-5} \ m^3\)
ASSIGNMENT what is the length of wire whose resistivity 3x10^-6ohm with the r=0.2mm with a given Value of 15.552 Resistance.
Answers
The length of wire whose resistivity is 3 x 10^-6ohm, and radius is 0.2 mm, with a given value of 15.552 resistance is 6.5268 m.
Given data: r = 0.2 mm = 0.2 x 10^-3m Resistivity = 3 x 10^-6 ohm R = 15.552 ohm
Formula Used: Resistivity (ρ) = (RA)/L
Where, R is resistance, A is the area of cross-section, L is the length of the wire.
Resistance (R) = ρ (L/A)
Multiplying A on both sides, we get
Resistance (R) x A = ρ L ... equation (1)
Area of the cross-section of a wire of radius (r) is given by, A = πr^2
where, π is a constant whose value is 3.14
Substituting the given values, we get
A = πr^2= π (0.2 x 10^-3m)^2= 1.2566 x 10^-7 m^2
Substituting the values of R, A and ρ in equation (1), we get
Length of wire (L) = (Resistance x Area) / Resistivity= (15.552 ohm x 1.2566 x 10^-7 m^2) / (3 x 10^-6 ohm)= 6.5268 m
Therefore, the length of wire whose resistivity is 3 x 10^-6ohm, and radius is 0.2 mm, with a given value of 15.552 resistance is 6.5268 m.
For more such questions on resistivity, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/30934104
#SPJ8
Describe how the boiling point of water on top of a mountain would be different from its boiling point at sea level.
Answers
Answer:
At elevated altitudes, any cooking that involves boiling or steaming generally requires compensation for lower temperatures because the boiling point of water is lower at higher altitudes due to the decreased atmospheric pressure.
Explanation:
Answer:
The Lower the air pressure the lower the boiling point.
Which angle (A,B, or C) is the diffraction angle?
B because it’s closest to the center line

Answers
As waves come into contact with a barrier or aperture, they experience the phenomenon known as diffraction, which causes them to bend and disperse.
Which diffraction angle has the highest value?Diffracted light has maximum intensities at angles m given by dsinm=m when light is usually incident on a diffraction grating. Thus, the 3rd-order maxima can arise at 90° (or a smaller angle) and there won't be any 4th-order maxima because the maximum angle for diffraction maxima is 90°.
What factors affect angle of diffraction?Light's wavelength determines the amount of diffraction, with longer wavelengths diffracted at a greater angle than shorter ones (in effect, red light are diffracted at a higher angle than is blue and violet light).
To know more about diffraction visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/16096548
#SPJ1
Answer:
it is B
Explanation:
If a child of mass 60.6 kg sits in a seat, what is
the tension in the chain (for the same angle)?
Answers
The Tension in the chain is 593.88 N
Tension:This can be defined as a pulling force, transmitted to a rope or a string.
The Tension in the chain can be calculated using the formula below.
Formula:
T = mg................................... Equation 1Where:
T = Tension in the chainm = mass of the childg = acceleration due to gravity.From the question,
Given:
m = 60.6 kgg = 9.8 m/s²Substitute these values into equation 1
T = 60.6(9.8)T = 593.88 NHence, the Tension in the chain is 593.88 N
Learn more about tension here: https://brainly.com/question/24994188
Which of the following would require the
greatest number of calories?
Answers
Answer:
Heating 100 g of water from 10◦C to 50◦C
Explanation:
m₁ ΔT₁ = 2000
m₂ ΔT₂ = 300
m₃ ΔT₃ = 4000
m₄ ΔT₄ = 70
A miniature quadcopter is located at
xi = −1.75 m
and
yi = 2.70 m
at
t = 0
and moves with an average velocity having components
vav, x = 1.70 m/s
and
vav, y = −2.50 m/s.
What are the x-coordinate and y-coordinate (in m) of the quadcopter's position at
t = 2.10 s?
Answers
A miniature quadcopter is located at xi = −1.75 m and yi = 2.70 m at t = 0, so the x-coordinate of the quadcopter's position at t = 2.10 s is -0.185 m, and the y-coordinate is -3.175 m.
What is the quadcopter's position?
The equation that is used here is the kinematic equations to find the position of the quadcopter at time t,
x = xi + vav, x × t
y = yi + vav, y × t
Substituting the given values, one can get:
x = -1.75 m + 1.70 m/s × 2.10 s = -0.185 m
y = 2.70 m - 2.50 m/s × 2.10 s = -3.175 m
Hence, the x-coordinate of the quadcopter's position at t = 2.10 s is -0.185 m, and the y-coordinate is -3.175 m.
Learn more about the quadcopter here.
https://brainly.com/question/29280235
#SPJ1
Compare sound and earthquake waves
Answers
When materials vibrate, waves are created that travel through the substance, and this energy is what we hear as sound. Earthquakes are earth vibrations that cause the (potential) energy held within rocks to be released (as a result of their pressure-generating relative positions). Seismic waves are produced by earthquakes.
How do sound waves and earthquakes compare?
The waves lose energy as they move through the air with sound or through the ground with shaking during an earthquake. Therefore, a band can be heard louder close to the stage than farther away, and an earthquake can be felt more strongly close to the fault than farther away.
In actuality, sound in the air cannot match how quickly earthquake waves move. In rock, the compressional or "P" wave of an earthquake moves at the In actuality, sound in the air cannot match how quickly earthquake waves move. The speed of a P wave is typically 10,000 mph. The speed of sound through air is roughly 750 mph.
To learn more about sound waves use:
https://brainly.com/question/16093793
#SPJ1
what is a water resavore.......................................
Answers
Answer: A Water resavoir is a place where they hold water until needed. Like let's say there was a drought in Arizona, the state would rely on the resavoir's until the drought is gone. I hope I explained it well.
Crystalline germanium (Z=32, rho=5.323 g/cm3) has a band gap of 0.66 eV. Assume the Fermi energy is half way between the valence and conduction bands. Estimate the ratio of electrons in the conduction band to those in the valence band at T = 300 K. (See eq. 10-11) Assume the width of the valence band is ΔΕV ~ 10 eV.
Answers
Answer:
= 8.2*10⁻¹²
Explanation:
Probability of finding an electron to occupy a state of energy, can be expressed by using Boltzmann distribution function
\(f(E) = exp(-\frac{E-E_f}{K_BT} )\)
From the given data, fermi energy lies half way between valence and conduction bands, that is half of band gap energy
\(E_f = \frac{E_g}{2}\)
Therefore,
\(f(E) = exp(-\frac{E-\frac{E_g}{2} }{K_BT} )\)
Using boltzman distribution function to calculate the ratio of number of electrons in the conduction bands of those electrons in the valence bond is
\(\frac{n_{con}}{n_{val}} =\frac{exp(-\frac{[E_c-E_g/2]}{K_BT} )}{exp(-\frac{[E_v-E_fg/2}{K_BT} )}\)
\(= exp(\frac{-(E_c-E_v}{K_BT} )\\\\=exp(\frac{-(0.66eV)}{(8.617\times10^-^5eV/K)(300K)} )\\\\=8.166\times10^-^1^2\approx8.2\times10^{-12}\)
A metal object with a mass 5.50 kg is connected to a spring with a force constant of 225 N/m, and it oscillates horizontally with an amplitude of 4.20 cm. (a) What is the total mechanical energy (in J) of the object-spring system? (b) What is the maximum speed (in m/s) of the oscillating object? m/s (c) What is the maximum magnitude of acceleration (in m/s) of the oscillating object? m/s²
Answers
a) Total mechanical energy of the object-spring system = 0.198 J
b) Maximum speed of the oscillating object = 0.269 m/s
c) Maximum magnitude of acceleration of the oscillating object = 1.72 m/s2
What is acceleration?
Acceleration is the name we give to any process where the velocity changes. Since velocity is a speed and a direction, there are only two ways for you to accelerate: change your speed or change your direction—or change both.
Mass of the object = m = 5.5 kg
Force constant of the spring = k = 225 N/m
Amplitude of the motion = A = 4.2 cm = 0.042 m
Total mechanical energy of the object-spring system = E
Total mechanical energy is equal to the maximum potential the spring can store in this motion.
(a) \($E=\frac{1}{2} \times 300 \times 0.037^2$\)
\($$E=0.20535 \text { Joules }$$\)
Maxmium speed, \($v_{\max }=$\) AeO
\($$\begin{gathered}\omega=\sqrt{\frac{k}{m}}=\sqrt{\frac{300}{5.5}} \\\omega=7.3855 \mathrm{rad} / \mathrm{s} \\v_{\max }=0.037 \times 7.3855 \\V=0.273 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\end{gathered}$$\)
(C) Maximim acceleration, \($a_m=A \omega^2$\)
\($$\begin{aligned}a_{\max } & =0.037 \times 7.3855^2 \\a_{\max } & =2.018 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2\end{aligned}$$\)
To learn more about acceleration visit:https://brainly.com/question/12550364
#SPJ4
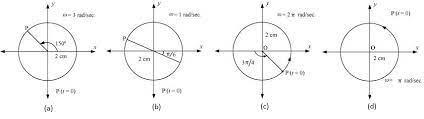
Draw a circle of reference and a time graph for the following SHM: amplitude a = 15 x 10-7 m, period T = 24 × 104 s, and initial phase angle o = 30°. Draw the graphs for two complete vibrations.
Answers
Let's draw a reference circle. The circle of reference is a circle with a radius equal to the motion's amplitude, and it indicates the SHM's maximum displacement. The initial phase angle is the angle formed between the positive x-axis and the radius representing the motion's initial displacement.
To begin sketching the circle of reference, create a horizontal x-axis and a vertical y-axis that intersect at the origin. Then we draw a circle with a radius equal to the amplitude a, centered at the origin. Finally, we draw a radius at an angle with respect to the positive x-axis. This radius represents the motion's initial displacement.
The position of the object experiencing SHM at any given time is represented by the circle of reference. The time graph depicts how the object's position changes over time. The red line depicts the object's displacement from its equilibrium location.
The amplitude of the SHM is given as 15 x 10-7 m, which is indicated by the distance from the center of the reference circle to the outer edge. The SHM has a period of 24 x 104 s, which is the time it takes the item to complete one full cycle of motion. The starting position of the red line on the circle of reference represents the initial phase angle of 30°.
The time graph depicts how the object's displacement from its equilibrium position varies over time during two complete vibrations. The displacement varies between +15 x 10-7 m and -15 x 10-7 m every cycle, with the red line touching the equilibrium position twice. The time graph also shows a period of 24 x 104 s, as it takes nearly that amount of time for the displacement to complete one full cycle.
learn more about vibrations here
https://brainly.com/question/2279743
#SPJ1
These two questions are connected to the figure.

Answers
Answer:
A, and E
Explanation:
Two blocks, which can be modeled as point masses, are connected by a massless string which passes through a hole in a frictionless table. A tube extends out of the hole in the table so that the portion of the string between the hole and M1 remains parallel to the top of the table. The blocks have masses M1 = 1.9 kg and M2 = 2.8 kg. Block 1 is a distance r = 0.95 m from the center of the frictionless surface. Block 2 hangs vertically underneath. find the speed of m1 assume m2 does not move relative to the table.
Answers
The speed of the block m1 on the frictionless table is 1.34 m/s.
The given parameters;
mass of the first block, m1 = 1.9 kgmass of the second block, m2 = 2.8 kgdistance of block m1, R = 0.95 mThe net torque on both blocks is calculated as;
\(\tau _{net} = I \alpha\)
\(T_2R- T_1 R_1 = I \alpha \\\\\)
where;
T₁ is the tension on first blockI is the moment of inertia of point massα is the angular acceleration\(T_1 = m_1 g + m_1 a\\\\T_2 = m_2 g - m_2 a\)
The acceleration of both blocks is calculated as follows;
\(R(T_ 2- T_1) = MR^2 \times (\frac{a}{R} )\\\\R(T_2 -T_1) = MRa\\\\T_2 - T_1 = Ma\\\\(m_2g - m_2 a) - (m_1 g + m_1 a) = Ma\\\\m_2 g - m_1 g - m_2 a - m_1 a = Ma\\\\g(m_2 - m_1) = Ma + m_2a+ m_1a\\\\g(m_2 - m_1) = a(M+ m_2 + m_1)\\\\where;\\\\M \ is \ mass \ of \ string = 0 \\\\g(m_2 - m_1) = a (0+ m_2 + m_1)\\\\g(m_2 - m_1) = a(m_1 + m_2)\\\\a = \frac{g(m_2 - m_1)}{m_1 + m_2} \\\\a = 1.88 \ m/s^2\)
The speed of the block m1 is calculated as follows;
\(a = \frac{v^2}{r} \\\\v^2 = ar\\\\v = \sqrt{a r} \\\\v = \sqrt{1.88 \times 0.95} \\\\v = 1.34 \ m/s\)
Thus, the speed of the block m1 on the frictionless table is 1.34 m/s.
Learn more here:https://brainly.com/question/9060205
The earth rotates on its axis with a period of 24 hours. What is the frequency in Hertz?
Answers
Answer:
The answer is 0.042 Hz (rounded)
or 0.0417 Hz
Explanation:
Hope it helps
Answer:
The answer is 0.041Hz
Explanation:
The answer is 0.041Hz
I guess
Two students are standing next to one another. One student has a mass of 79.0 kg, and the other has a mass of 93.5 kg. If they are standing so that their centers of mass are a distance of 1.12 m apart, what is the force of the gravitational attraction between them?
A. 4.40 * 10^-7 N
B. 3.93 * 10^-7 N
C. 1.29 * 10^-6 N
D. 8.77 * 10^-6 N
Answers
Answer:
\(F=3.93\times 10^{-7}\ N\)
Explanation:
Mass of student 1, m₁ = 79 kg
Mass of student 2, m₂ = 93.5 kg
The students are 1.12 m apart, d = 1.12 m
We need to find the force of the gravitational attraction between them. The force of gravitational force is given by :
\(F=G\dfrac{m_1m_2}{r^2}\\\\F=6.67\times 10^{-11}\times \dfrac{79\times 93.5}{(1.12)^2}\\\\=3.93\times 10^{-7}\ N\)
So, the force of gravitational attraction between them is \(3.93\times 10^{-7}\ N\). Hence, the correct option is (B).
if a space rover has a mass of 3900 kg, then what is its weight on earth
Answers
Answer:
38 220
Explanation:
Weight =Mg
W=Mg
W = (3900)(9.8)
W = 38 220
What is the frequency of highly energetic ul-
traviolet radiation that has a wavelength of
124 nm?
The speed of light is 3 x 108 m/s.
Answer in units of Hz.
Answers
Frequency = (speed) / (wavelength)
Frequency = (3 x 10⁸ m/s) / (124 x 10⁻⁹ m)
Frequency = 2.42 x 10¹⁵ Hz
astone is thrown upwards with an initial velocity of 25m/s atan angle of 30 to the ground.what is the work out the stones horizantal range ?
Answers
Answer:
Range is 62.5 metres
Explanation:
Time of flight
\(t = \frac{2u \sin( \theta) }{g} \)
for range, acceleration is zero
from second newton's equation:
\(S = ut + \frac{1}{2} {at}^{2} \)
but a = 0:
let range be x:
\(x = ut \\ x = \frac{2 {u}^{2} \sin( \theta) }{g} \\ \\ x = \frac{ \{2 \times 25 {}^{2} \sin(30 \degree) \}}{10} \\ \\ x = 62.5 \: metres\)
[ taken g to be 10 m/s² ]
Hi! I need help quick!
Explain the difference between the first day of fall and the first day of winter
Answers
Answer:
We usually travel in January or Feb for our tropical get-a-way. For those of you that have traveled in the fall and winter...
What is the real difference...Like in the floral and fauna, weather, and the capacity of the resorts between these 2 times of the year.
Two 4.72 kg masses are 3.12 m apart on a frictionless table. Each has 85.5 microCoulombs of charge. What is the initial acceleration of each mass if they are released and allowed to move?
Answers
We are given the following information
Mass of objects: m = 4.72 kg
Distance between objects: r = 3.12 m
Charge: q = 85.5 μC
We are asked to find the initial acceleration of each mass.
Recall from Newton's second law of motion,
\(F=m\cdot a\)Where F is the force between two masses, m is the mass, and a is the acceleration.
First, let us find the force between the two masses.
Recall from Coulomb's law,
\(F=\frac{k\cdot q_1\cdot q_2}{r^2}\)Where k is the Coulomb's law constant that is k = 9×10⁹ Nm²/C²
Substitute the given values into the above formula
\(\begin{gathered} F=\frac{9\times10^9\cdot85.5\times10^{-6}\cdot85.5\times10^{-6}}{3.12^2} \\ F=6.7587\;N \end{gathered}\)Finally, the initial acceleration of each mass is
\(\begin{gathered} F=m\cdot a \\ a=\frac{F}{m} \\ a=\frac{6.7587}{4.72} \\ a=1.43\;\frac{m}{s^2} \end{gathered}\)Therefore, the initial acceleration of each mass is 1.43 m/s^2
a student stands several meters in front of a smooth reflecting wall, holding a board on which a wire is fixed at each end. the wire, vibrating in its third harmonic, is 75.0cm long, has a mass of 2.25g, and is under a tension of 400 N. a second student, moving towards the wall, hears 8.30 beats per second. what is the speed of the student approaching the wall? (solve without calculus)
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The length of the wire is \(L = 75.0cm = \frac{75}{100} = 0.75 \ m\)
The mass of the wire is \(m = 2.25 \ g = \frac{2.25}{1000} = 0.00225 \ kg\)
The tension is \(T = 400 \ N\)
The frequency of the beat heard by the second student is
\(f_b = 8.30\ beat/second\)
The speed of the wave generated by the vibration of the wire is mathematically represented as
\(v = \sqrt{\frac{TL}{m}}\)
substituting values
\(v = \sqrt{\frac{400 *0.75}{0.00225}}\)
\(v = 365.15 m/s\)
The wire is vibrating in its third harmonics so the wavelength is
\(\lambda = \frac{2L}{3}\)
substituting values
\(\lambda = \frac{2*0.75}{3}\)
\(\lambda = 0.5 \ m\)
The frequency of this vibration is mathematically represented as
\(f = \frac{v}{\lambda }\)
substituting values
\(f = \frac{365.15}{0.5 }\)
\(f = 730.3 Hz\)
The speed of the second student (Observer) is mathematically represented as
\(v_o = [\frac{f_b}{2f} ] * v\)
substituting values
\(v_o = [\frac{8.30}{2* 730.3} ] * 365.15\)
\(v_o = 2.08 \ m/s\)
Say an impulse is applied opposite the go-kart's direction of travel. What happens to
the go-kart if its momentum + impulse = 0?
The go kart stops comes to a stop.
The go kart slows down but keeps moving.
The go kart speeds up.
There is no change in the speed of the go kart.
Answers
If the impulse is strong enough and lasts for a sufficient amount of time, the go-kart will eventually come to a stop.
Option A is correct.
What is meant by impulse?impulse is described as the integral of a force, F, over the time interval, t, for which it acts. Since force is a vector quantity, impulse is also a vector quantity.
If the force is insufficient to stop the go-kart entirely, it will slow down but continue to move. The force and duration of the impulse, along with the mass and speed of the go-kart, will all affect how much deceleration occurs.
Given that momentum plus impulse equals zero, the go-kart's change in momentum as a result of the impulse will be equal in amount but will move in the opposite direction of its original momentum.
As a result, the go-kart's final momentum will be zero, suggesting that it has either stopped or is travelling very slowly.
Learn more about impulse at: https://brainly.com/question/229647
#SPJ1
What is the work done from X =0m to 5.0m?
Answers
If the applied force is 20 N and the displacement is from X=0m to X=5.0m, the work done is 100 Joules.
What is the work done?
To determine the work done by a force, you need to know the displacement and the component of the force parallel to the displacement.
In this case, if the force applied is 20 N and the displacement is from X=0m to X=5.0m, you need to determine if the force is parallel to the displacement.
If the force is parallel to the displacement, then the work done is simply the product of the force and the displacement, which is:
Work = Force x Displacement
Work = 20 N x (5.0 m - 0 m)
Work = 100 Joules
Learn more about work done here: https://brainly.com/question/2270290
#SPJ1
The complete question is below:
What is the work done from X =0m to 5.0m? if the applied force is 20 N
An automobile moves forward and backward on the street highway. The graph shows the velocity of this automobile as a function of time. At t equals five seconds, how far is the automobile from its t = 0 initial position? (round to 3 significant digits)

Answers
The velocity of this automobile as a function of time. At t = 5 seconds, the automobile is 90 meters from its initial position.
To determine the distance traveled by the automobile from its t = 0 initial position, we need to calculate the area under the velocity-time graph up to t = 5 seconds.
The graph shows the velocity of the automobile as a function of time. Let's assume that positive velocity represents forward motion, and negative velocity represents backward motion.
Since velocity represents the rate of change of displacement, the area under the velocity-time graph represents the displacement or distance traveled. In this case, the area will consist of two parts: the area above the x-axis (forward motion) and the area below the x-axis (backward motion).
To calculate the area, we can break it down into two separate integrals:
1. The area above the x-axis (forward motion):
Since the velocity is constant at 20 m/s for the first 4 seconds, the area is a rectangle:
Area1 = velocity * time = 20 m/s * 4 s = 80 m
2. The area below the x-axis (backward motion):
The velocity changes to -10 m/s at t = 4 seconds. From t = 4 seconds to t = 5 seconds, the velocity is -10 m/s. The area is a rectangle:
Area2 = velocity * time = -10 m/s * 1 s = -10 m
To find the total distance traveled, we add the absolute values of the areas:
Total distance = |Area1| + |Area2| = |80 m| + |-10 m| = 80 m + 10 m = 90 m
For more such information on: velocity
https://brainly.com/question/80295
#SPJ8
If the car was initially traveling at 96 km/h and came to a stop in 5.0 s along a straight, level road, what was the magnitude of the average force applied to the passenger by the seatbelt? The shoulder strap seatbelt holds a 56kg passenger in place.
Answers
The average force exerted by seatbelts on the passenger is 1493.3N.
initial velocity of the car, u = 96km/h
time taken by the car, s = 5.0 sec
final velocity of the after coming to rest, v = 0
mass of the passenger, m = 56 kg
to find out the acceleration of the car we use equation of motion
v = u+ at
0 = 96km/h + ax 5s
a = - 96 x 18/5x5
a = -26.6m/s²
The deceleration of the car is 26.6 m/s²
The force exerted on the passenger by the backward action of the car is calculated as
F = ma
where
m is mass
a is acceleration
F = 56 x 26.6
F = 1493.3 N
Therefore, the average force exerted by seatbelts on the passenger is 1493.3N.
To know more about force.
https://brainly.com/question/11027219
#SPJ1
What is 165,000 meters to cm, simplified too
Answers
165,000 meters to cm is 16,500,000 cm
What is Distance ?Distance is the measured length between two point. It is measured in meters
Distance can also be measured in
millimeters mmdecimeters dmcentimeters cmkilometers kmetcConversion of meter to centimeter can be done by multiplying the value by 100
What is 165,000 meters to cm ?
165,000 meters × 100 = 16,500,000 cm
Therefore, 165,000 meters to cm is 16,500,000 cm
Learn more about Unit Conversion here: https://brainly.com/question/97386
#SPJ1