Answers
Answer:
Angle-Angle-Angle(AAA)Side-Angle-side(SAS)Step-by-step explanation:
Let's see what is similar in both triangles
<A=<F<B=<E<C=<DSo Angle-Angle-Angle similarly theorem verified
AB=EDFD=BCBC=EFSo Side-Angle-side or Side-Side-Side similarity theorem verified
Related Questions
Explain how many solutions the equation 2×+1=2(×+1) and 2×+2=2(×+1) have use vocabulary words in your explanation
Answers
Step-by-step explanation:
The equation 2x+1=2(x+1) can be simplified to 2x+1=2x+2 since the right-hand side of the equation can be expanded to 2x+2. By subtracting 2x from both sides of the equation, we get 1=2, which is not true for any value of x. Therefore, the equation 2x+1=2(x+1) has no solution.
On the other hand, the equation 2x+2=2(x+1) can be simplified to 2x+2=2x+2 by expanding the right-hand side of the equation to 2x+2. We can see that both sides of the equation are equal, so the equation is true for any value of x. Therefore, the equation 2x+2=2(x+1) has infinitely many solutions, meaning that any value of x will satisfy the equation.
In summary, the equation 2x+1=2(x+1) has no solution, while the equation 2x+2=2(x+1) has infinitely many solutions. The term "solution" refers to the value of x that makes the equation true, while "infinitely many solutions" means that there are an infinite number of values of x that satisfy the equation.
Refer to Table 4-1. Suppose that D2 and S1 are the prevailing demand and supply curves for a product. If the demand schedule changes from D2 to D1, then:
Price D 1 D 2 S 1 S 2
$12 5 9 19 14
$10 8 12 17 12
$8 11 15 15 10
$6 13 18 13 8
$4 16 21 11 6
$2 18 24 9 4
equilibrium price increases from $6 to $8.
equilibrium quantity increases from 13 to 18
equilibrium quantity decreases from 15 to 13.
equilibrium price decreases from $6 to $4.
Answers
The correct option is A, equilibrium price increases from $6 to $8.
What do you mean by Equilibrium?In economics, equilibrium is a state in which the supply and demand for a product or service are balanced, resulting in a stable price. This can occur in a free market, where the price of a good or service is determined by the interaction of buyers and sellers.
Overall, equilibrium is a fundamental concept in many different fields, representing a state of balance or stability in a system or situation.
If the demand schedule changes from D2 to D1, then the demand curve shifts to the left. As a result, the new equilibrium point will be where the new demand curve (D1) intersects with the supply curve (S1).
From the table, we can see that the new equilibrium point is at a price of $8 and a quantity of 15. Therefore, the equilibrium price increases from $6 to $8, but the equilibrium quantity decreases from 15 to 13.
So the correct answer is: equilibrium price increases from $6 to $8.
To know more about equilibrium price visit:
https://brainly.com/question/28527601
#SPJ1
Kindly help to solve questions
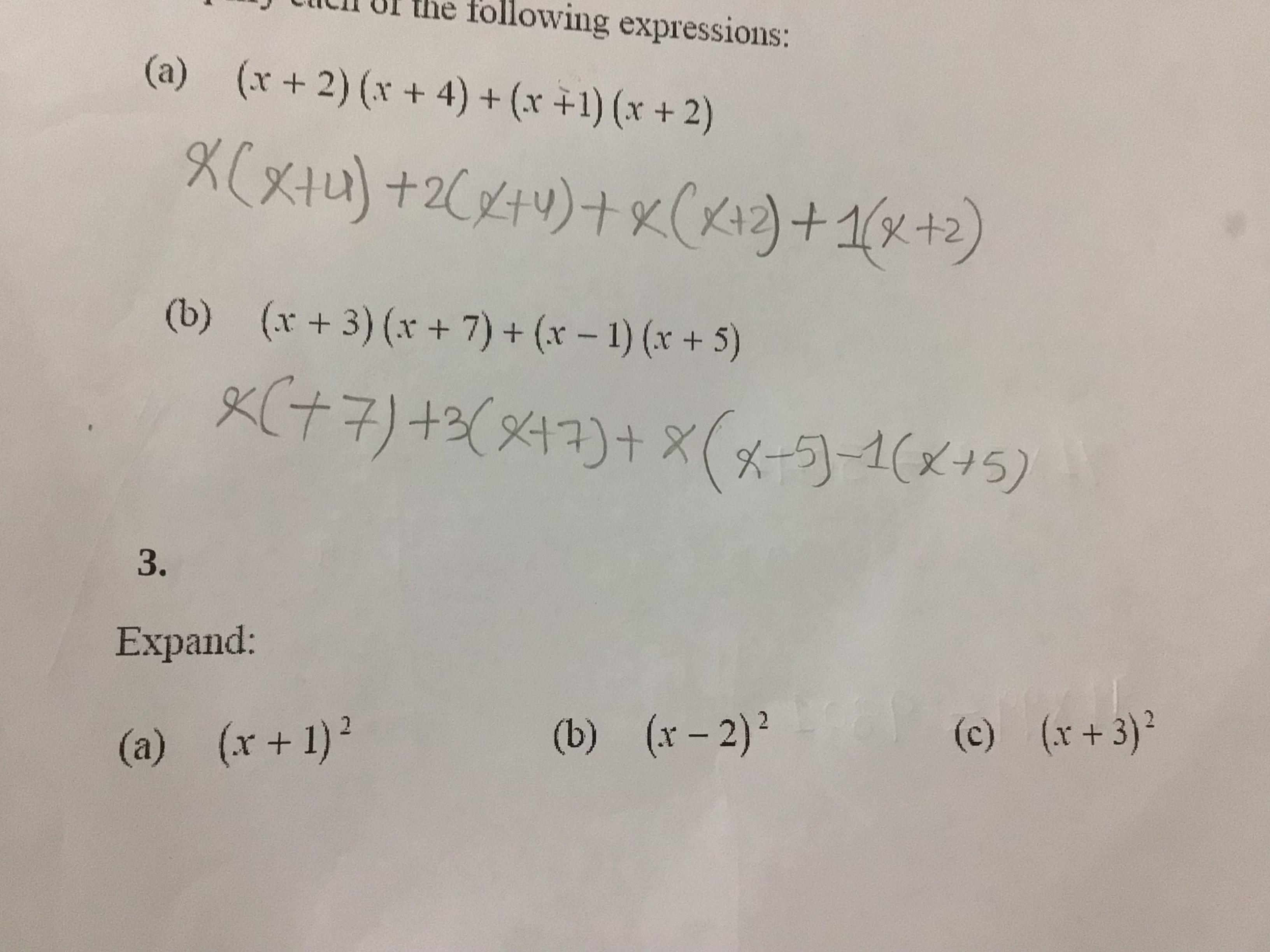
Answers
Applying notable products, the expanded expressions are given by:
a) (x + 1)² = x² + 2x + 1.
b) (x - 2)² = x² - 4x + 4.
c) (x + 3)² = x² + 6x + 9.
What is the notable product for the square of the sum?The notable product for the square of the sum is given by:
(a + b)² = a² + 2ab + b².
Hence:
a) (x + 1)² = x² + 2x + 1.
c) (x + 3)² = x² + 6x + 9.
What is the notable product for the square of the subtraction?The notable product for the square of the subtraction is given by:
(a - b)² = a² - 2ab + b².
That is, just the middle term changes compared to the square of the sum.
Hence:
b) (x - 2)² = x² - 4x + 4.
More can be learned about notable products at https://brainly.com/question/14577819
#SPJ1
Which trig ratio will be helpful in finding the missing side length sin(24)
Answers
The sin ratio will be helpful in finding the missing side length and the missing side length is 29.50 units.
What is the trigonometric ratio?The trigonometric ratio is defined as the ratio of the pair of a right-angled triangle.
We have a right-angle triangle in the figure in which:
Length of the hypotenuse = x unit
Length of the side opposite to the angle = 12
And the angle is given between sides adjacent to the angle to the hypotenuse = 24°
We know the:
\(\rm sin\theta = \frac{Side \ opposite \ to \ the \ angle}{hypotenuse }\)
\(\rm sin24 = \frac{12}{x}\)
\(\rm x = \frac{12}{sin24}\)
x = 29.50 units
Thus, the sin ratio will be helpful in finding the missing side length and the missing side length is 29.50 units.
Know more about trigonometry here:
brainly.com/question/26719838

Please help with number 17, I’m lost on how to even start it

Answers
Let j=+5 - 5+ |-5 x 1/5
What is the value of+J?
Answers
Answer:
j=|x|
Step-by-step explanation:
What is the value of 11g - 9k + 3 when g = 9 and k = 11?
Neatly show your work.
Answers
Answer:
3
Step-by-step explanation:
11g - 9k + 3
Let g = 9 and k =11
11 * 9 - 9*11 +3
Multiply
99 - 99 +3
Add
3
Answer:
3
General Formulas and Concepts:
Pre-Algebra
Order of Operations: BPEMDAS
Brackets Parenthesis Exponents Multiplication Division Addition Subtraction Left to RightStep-by-step explanation:
Step 1: Define
Identify
11g - 9k + 3
g = 9
k = 11
Step 2: Evaluate
Substitute in variables: 11(9) - 9(11) + 3Multiply: 99 - 99 + 3Subtract: 3How are the areas of triangles and parallelograms in the coordinate
plane calculated?
Answers
Answer:
___________________________________________________________
By finding the product of a point's x coordinate times the next point's y coordinate, then subtracting the y coordinate of the first point times the x coordinate of the second coordinate and dividing by two, you will find the area of the polygon.
___________________________________________________________
In the diagram below, \overline{MN}
MN
is parallel to \overline{JK}
JK
. If MNMN is 1212 more than LNLN, LK=33LK=33, and JK=55JK=55, find the length of \overline{LN}
LN
. Figures are not necessarily drawn to scale. State your answer in simplest radical form, if necessary.
Answers
The value of the missing length LN of the similar triangles is; LN = 18
How to solve Similar Triangles?Similar triangles are defined as triangles that have the same shape, but their sizes may vary. This means therefore that, if two triangles are similar, then we can say that their corresponding angles are congruent and also their corresponding sides are in equal proportion.
In the given triangle attached, we can say that if we apply the concept of similar triangles, we will get;
LN/LK = MN/JK
We are told that;
MN is 12 more than LN. Thus; MN = 12 + LN
LK = 33
JK = 55
Thus;
LN/33 = (12 + LN)/55
55LN = 33(12 + LN)
55LN = 396 + 33LN
22LN = 396
LN = 396/22
LN = 18
Read more about Similar Triangles at; https://brainly.com/question/14285697
#SPJ1

angles x and y are supplementary. angle x is 3 times the measure of angle y. what is the measure of angle x? 45° 60° 120° 135°
Answers
Answer:
x = 135°
Step-by-step explanation:
x and y are supplementary angles, that is they sum to 180° , then
x + y = 180 ← substitute x = 3y into the equation
3y + y = 180
4y = 180 ( divide both sides by 4 )
y = 45
then
x = 3y = 3 × 45° = 135°
Construct an algebraic proof for the given statement. Cite a property from Theorem 6.2.2 for every step. (A - B) u (An B) = A Theorem 6.2.2 Set Identities Let all sets referred to below be subsets of a universal set U. 1. Commutative Laws: For all sets A and B, (a) AUB = BUA and (b) An B = BNA. 2. Associative Laws: For all sets A, B, and C, (a) (A U BUC = AU (BUC) and (b) (ANB) NC = An (BNC). 3. Distributive Laws: For all sets, A, B, and C, (a) AU (BNC) = (AUB) N (AUC) and (b) A N (BUC) = (ANB) U (ANC). 4. Identity Laws: For all sets A, (a) A UØ = A and (b) A NU = A. 5. Complement Laws: (a) AU AC = U and (b) An A = 0. 6. Double Complement Law: For all sets A, (A) = A. 7. Idempotent Laws: For all sets A, (a) AU A = A and (b) An A = A. 8. Universal Bound Laws: For all sets A, (a) A UU = U and (b) Ang=0. 9. De Morgan's Laws: For all sets A and B, (a) (AUB) = A n Bº and (b) (ANB) = ACU B. 10. Absorption Laws: For all sets A and B, (a) A U(ANB) = A and (b) AN (AUB) = A. 11. Complements of U and Ø: (a) U = 0 and (b) Ø¢ = U. 12. Set Difference Law: For all sets A and B, A - B = ABC.
Answers
(A - B) u (A n B) = A is proved using several properties from Theorem 6.2.2. of Set Identities.
How to prove (A - B) u (A n B) = A algebraically?To prove (A - B) u (A n B) = A algebraically, we can use the following steps:
(A - B) u (A n B) // Given
[(A n B) U (A - B)] // Definition of union
[(B n A) U (A - B)] // Commutative law of intersection
[(B U (A - B)) n (A U (A n B))] // Distributive law of union over intersection
[(B U (A n B)') n (A U B)] // Complement law of intersection and De Morgan's law
[(B U (A - B)) n (A U B)] // Complement law of A n B
[(B U (A n B)') n (A U B)] // Definition of A - B
[(B U (A n B)') n (B U A')] // De Morgan's law
[(B n (B U A')) U ((A n B)'' n (B U A'))] // Distributive law of intersection over union
[(B n U) U (Ø n (B U A'))] // Complement law of B U A' and B n (B U A')
B U Ø // Identity law of intersection and complement law of B U A'
B // Identity law of union
Therefore, (A - B) u (A n B) = A is proved. We used several properties from Theorem 6.2.2, including the commutative law of intersection, distributive law of union over intersection, complement law of intersection, De Morgan's law, complement law of A n B, definition of A - B, distributive law of intersection over union, complement law of B U A', and identity law of intersection and union.
Learn more about set identities
brainly.com/question/14974663
#SPJ11
HELP WITH THIS PLSS S

Answers
The statement illustrates the transitive property of congruence, which is a fundamental concept in geometry.
What is transitive property of congruence?This property states that if two geometric figures are congruent to a third figure, then they are congruent to each other.
In the given statement, ΔABC is congruent to ΔDEF, and ΔDEF is congruent to ΔXYZ. By the transitive property, we can conclude that ΔABC is also congruent to ΔXYZ.
This property is important because it allows us to establish relationships between geometric figures based on their congruence. It is used in many geometric proofs and applications, such as proving theorems, solving problems involving similar triangles, and determining the congruence of geometric shapes.
To know more about geometric figures visit:
https://brainly.com/question/5026441
#SPJ1
65%of 320+?=686
Options are:
a) 480
b) 452
c) 461
d) 475
e) none of these
Answers
Answer:
e) none of these
Explanation:
65% * 320 + ? = 686208 + ? = 686? = 686 - 208? = 478Answer:
e) None of these.
Step-by-step explanation:
Let the unknown number be x, then:
0.65*320 + x = 686
208 + x = 686
x = 686 - 208
= 478
Find the convergence set of thegiven power series: ∑n=1[infinity](x−2)nn2 The above series converges for≤x≤
Answers
The convergence set of the power series ∑n=1∞ \((x-2)^n/n^2\) is [1, 3). The series converges for x values in the interval [1, 3), and diverges for x values outside of this interval.
At the endpoints x = 1 and x = 3, the series converges for x = 1 and diverges for x = 3.
How to determine the convergence set of the power series?To find the convergence set of a power series, we can use the ratio test:
lim[n→∞] |\((x - 2)(n+1)^2 / n^2\)| = lim[n→∞] |\((x - 2)(1 + 2/n)^2\)| = |x - 2| lim[n→∞] \((1 + 2/n)^2\)
Since lim[n→∞] \((1 + 2/n)^2 = 1\), the series converges if |x - 2| < 1, and diverges if |x - 2| > 1.
If |x - 2| = 1, then the ratio test is inconclusive, so we need to check the endpoints x = 1 and x = 3 separately.
For x = 1, the series becomes:
∑n=1infinitynn2 = ∑n=1infinitynn2
which is the alternating harmonic series, which converges by the alternating series test.
For x = 3, the series becomes:
∑n=1infinitynn2 = ∑n=1[infinity]nn2
which diverges by the p-series test with p = 2.
Therefore, the convergence set of the series is:
1 ≤ x < 3
In interval notation, this can be written as:
[1, 3)
Learn more about convergence set of a power series
brainly.com/question/31440916
#SPJ11
Can someone tell me what Pythagorean theorem is? I really need help.
Answers
Answer:
The sum of the squares of the two sides equals the square of the hypotenuse (a² + b² = c²).
Let's say you have a triangle with a 90º angle (also known as a right angle). The two equal legs are a and b while the hypotenuse is the longer side. Hypotenuse is and always will be c.
Here's a problem:
c ⊿ a (12)
b (6)
C is missing, we have to find C, so here's what we do:
Step 1: You square all the numbers in the equation
12² + 6² = c²
↓
144 + 36 = c
Step 2: You add 144 + 36 and you get 180
Step 3: Then you find the square root >> \(\sqrt{180\\\) and you get ≈13.4
Now sometimes, the a or b would be missing, for example:
c (13)⊿ a
b (5)
A is missing (when a or b is missing, use the following formula, do not use the same formula when c is missing)
Step 1: You square all the numbers in the equation
a² + 5² = 13²
a + 25 = 169
For this next part, you must subtract a or b (in this case, b) on both sides, for example:
25 – 25 = 169 - 25
25 – 25 cancels itself out so now we subtract 169 by 25 and we get 144.
Then we find the square root of 144 and we get 12
I hope this helps :)
prove using the well-ordering principle that two consecutive elements of fibonacci's sequence cannot both be divisible by 13. can you generalize your result?
Answers
Our assumption that two consecutive elements of the Fibonacci sequence can be divisible by 13 is false, and the proposition is proved.
We begin with the fact that the Fibonacci sequence is an increasing sequence; that is, each element is greater than the one before it.
The sequence is defined as follows:
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, 610, 987, 1597, 2584, 4181, 6765, 10946, 17711, 28657, 46368, 75025, 121393, 196418, 317811, 514229, 832040, 1346269, 2178309, 3524578, 5702887, 9227465, 14930352, 24157817, 39088169, 63245986, 102334155, 165580141, 267914296, 433494437, 701408733, 1134903170, 1836311903, and so on.
Now, let us prove the proposition by contradiction. Assume that there are two consecutive elements of the Fibonacci sequence that are divisible by 13. Then there must be some integer n such that:
F(n) = 13m, andF(n + 1) = 13p,
where m and p are integers.
Since the Fibonacci sequence is defined recursively by F(n) = F(n-1) + F(n-2), we can obtain an expression for F(n-2) in terms of F(n) and F(n-1):
F(n-2) = F(n) - F(n-1)Since F(n) and F(n-1) are both divisible by 13, their difference must also be divisible by 13.
Therefore, F(n-2) is divisible by 13 as well. However, this contradicts the well-ordering principle, which states that every non-empty set of positive integers has a least element.
Since the Fibonacci sequence is an increasing sequence, there must be some least element k such that F(k) is divisible by 13 but F(k-1) is not. But this means that F(k-2) cannot be divisible by 13, which contradicts our assumption that both F(n) and F(n-1) are divisible by 13.
for such more question on Fibonacci sequence
https://brainly.com/question/29764204
#SPJ11
Hello, I am very confused about this problem. Would it be possible to receive some help on it?

Answers
A quadratic equation that is given in the form:
\(ax^2+bx+c=0_{}\)can be solved using the quadratic formula:
\(undefined\)Write an equation in point-slope form for a line with a slope of 2/3 that passes through (-4,1)
Answers
Answer:
y-1=2/3(x+4)
Step-by-step explanation:
YOUR WELCOME SJJDJDJ
500.000 times 0.045 what is the answer and explained

Answers
Answer:22.5
Step-by-step explanation:think of 500.000 as an 500 then multiply 0.045 so I got 22.5
Answer:
22.5
Step-by-step explanation:
500.000
x 0.045
22.5
You just have to use long multiplication
a spinner is divided into five colored sections that are not of equal size: red, blue, green, yellow, and purple. the spinner is spun several times, and the results are recorded below: spinner results color frequency red 10 blue 12 green 2 yellow 19 purple 12 if the spinner is spun 1000 more times, about how many times would you expect to land on purple? round your answer to the nearest whole number.
Answers
Based on the recorded results, purple appeared 12 times out of a total of 55 spins. If the spinner is spun 1000 more times, we can estimate that purple would appear approximately 218 times.
In the recorded results, the spinner was spun a total of 55 times, with purple appearing 12 times. To estimate the expected frequency of purple in 1000 additional spins, we can calculate the probability of landing on purple based on the recorded frequencies. The probability of landing on purple can be calculated by dividing the frequency of purple (12) by the total number of spins (55):
Probability of landing on purple = Frequency of purple / Total number of spins = 12 / 55
We can use this probability to estimate the expected frequency of purple in the additional 1000 spins:
Expected frequency of purple = Probability of landing on purple * Total number of additional spins
≈ (12 / 55) * 1000
≈ 218
Therefore, based on this estimation, we would expect purple to appear approximately 218 times if the spinner is spun 1000 more times.
Learn more about Probability here:
https://brainly.com/question/32560116
#SPJ11
Round to the nearest hundred 16,537
Answers
Answer:
16,500
Step-by-step explanation:
thats it
What is the measure of ∠spq in this rhombus? m∠spr=(2x 15)° m∠qpr=(3x−5)° enter your answer in the box. m∠spq= °
Answers
The required measure of the angle ∠spq of a rhombus is 110°.
What are the angle?Orientation of the one line with respect to the horizontal or other respective line is known as a measure of orientation and this measure is known as the angle.
Here,
For rhombus,
m∠spr=(2x + 15)°
m∠qpr=(3x−5)°
And,
m∠spr = m∠qpr
2x + 15 = 3x - 5
x = 20
Now,
∠spq = m∠spr + m∠qpr
= 2x + 15 + 3x - 5
= 5x + 10
= 5(20) + 10
= 110°
Thus, the required measure of the angle ∠spq of a rhombus is 110°.
Learn more about Angles here:
https://brainly.com/question/13954458
#SPJ1
2 1/4kms = how many meters?
Answers
Answer:
2 1/4kms = how many meters?
2250 metersStep-by-step explanation:
You're welcome.
Answer:
M = 2250
Step-by-step explanation:
First of all solve the mixed number which is 9/4 and as a decimal it is 2.25
Now as the meters it is....
2250!!!!
Hope this helps, have a great day!!!!!!
(Multiply 2.25 times 1000 and that gives you 2250)
Use the quadratic formula to solve the equation. x^2+7x-4=0 Enter your answers as decimals rounded to the nearest tenth in the boxes. It does not matter which answer goes in which box. Question 1 options: Blank # 1 Blank # 2
Answers
Answer:
I got −7.53112887414 and 0.531128874149
Step-by-step explanation:
plugged in

Write the cardinal number of p intersection Q if p and Q are disjoint sets.
Answers
Answer:
P(p∩Q) = 0.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the Addition Rule:
P(p∪Q) = P(p) + P(Q) - P(p∩Q)
P(p or Q) = P(p) + P(Q) - P(p and Q)
Events p and Q are disjoint (or mutually exclusive) if they cannot occur at the same time. (That is, disjoint events do not overlap.)
Hence, whenever p and Q are disjoint, P(p and Q) becomes zero in the formal addition rule, so for disjoint events p and Q we have:
P(p or Q) = P(p) + P(Q).
Therefore, the cardinal number of P(p∩Q) = 0.
6. suppose that x is an exponential random variable with mean 1. give another random variable that is negatively correlated with x and that is also exponential with mean 1.
Answers
If we let Z = 3 - X, then Z is another exponential random variable with mean 1 that is negatively correlated with X.
Let Y = 2 - X, where X is an exponential random variable with mean 1.
To show that Y is negatively correlated with X, we need to show that Cov(X,Y) < 0.
Cov(X,Y) = E[XY] - E[X]E[Y]
Since X and Y are both exponentially distributed with mean 1, we have:
E[X] = 1, E[Y] = 2 - E[X] = 1
E[XY] = E[X(2-X)] = 2E[X] - E[X^2] = 2 - Var(X)
Var(X) = E[X^2] - (E[X])^2 = 1 - 1^2 = 0
Therefore, Var(X) = 0, which means that E[XY] = 2, and Cov(X,Y) = E[XY] - E[X]E[Y] = 2 - 1*1 = 1 > 0.
Since Cov(X,Y) > 0, we know that Y is positively correlated with X. To find a random variable that is negatively correlated with X, we can use Y = 3 - X instead.
Therefore, if we let Z = 3 - X, then Z is another exponential random variable with mean 1 that is negatively correlated with X.
Learn more about variable here:
https://brainly.com/question/29696241
#SPJ11
math work is hard pt1

Answers
Answer:
1. y = 3x - 2
2. \(y = \frac{1}{2} \)
3. \(y = \frac{3}{2} x + 4\)
4. y = -3x + 5
5. y = x - 6
▪Happy To Help <3
I’ll give the Brainliest to who answers these questions with a reasonable explanation.
While surfing the Internet, you find a site that claims to offer “the most popular and the cheapest DVDs anywhere.” Unfortunately, the website isn’t clear about the how much they charge for each DVD, but it does give you the following information:
(The information is the table up there)
a. What is the slope of the line containing the points?
b. What does the slope represent in this problem?
c. What is the y‐intercept of the line that contains the points?
d. What does the y‐intercept represent in this context?
e. What is the equation that represents the line?
Thank you.

Answers
Answer:
Answer:
a. 9
b. The slope represents the cost for every new DVD
c. 6
d. The song represents the base price, or the price that it would cost for 0 DVDs
e. y = 9x + 6
Explanation:
I made a graph on a piece of graph paper and these were the answer I got.
explain fully please
Answers
Answer:
whats the question..........
Can someone please help me with this

Answers
B: cannot be simplified any further
C: cannot be simplified any further
D: YES
