WIll give brainliest! : In the following Punnett square, what is the phenotypic percentages of the offspring? From dwarfism slideshow - length of legs.

Answers
Answer:
75% will have long legs and 25% will have short legs
Explanation:
Related Questions
identify the best reagents to convert 1-hexyne into (e)-1,2-dibromo-1-hexene.select answer from the options belowxs br2, ccl41 equiv hbr, roorxs hbr1 equiv. br2, ccl41 equiv hbr
Answers
The best reagents to convert 1-hexyne into (e)-1,2-dibromo-1-hexene are 1 equiv. Br2 in CCl4, followed by NaOH to convert the mixture of (Z)- and (E)-isomers to the desired (E)-isomer.
This reaction is called the Vicinal Dibromination reaction. Option A: xs Br2 in CCl4 is a good choice of reagents, but it will give a mixture of (Z)- and (E)-isomers. Option B: 1 equiv. HBr will result in the formation of (Z)-1-bromo-1-hexene. Option C: ROOR is a radical initiator and will not result in the desired product.
To know more about different reagents and isomers : https://brainly.com/question/29713522
#SPJ11
If you have 100. 0g of O2, how many grams of Al2O3 will be produced?
Answers
If we have 100 g of O₂, the mass in grams of Al₂O₃ will be produced is 477.8 g.
The chemical equation is as follows :
4Al (s) + 3O₂ (g) ==> 2Al₂O₃ (s)
The mass of the O₂ = 100 g
The molar mass of the O₂ = 32 g/mol
The moles of the O₂ = 100 g / 32 g/mol
The moles of the O₂ = 3.125 mol
The 3 moles of the O₂ produces the 2 moles of the Al₂O₃
The moles of the Al₂O₃ = (2/3 ) 3.125
The moles of the Al₂O₃ = 4.687 mol
The mass of the Al₂O₃ = moles × molar mass
The mass of the Al₂O₃ = 4.687 × 101.96
The mass of the Al₂O₃ = 477.8 g
To learn more about moles here
https://brainly.com/question/20486415
#SPJ4
please help and give an explanation i don’t get it

Answers
The mass (in grams) of water, H₂O produced from 6.00 moles of hydrogen gas, H₂, is 108 g (last option)
How do i determine the mass of water produced?We'll begin by obtaining the mole of water produced from the reaction. Details below:
2H₂(g) + O₂ -> 2H₂O
From the balanced equation above,
2 moles of H₂ reacted to produce 2 moles of H₂O
Therefore,
6 moles of H₂ will also react to produce 6 moles of H₂O
Finally, we shall determine the mass of water, H₂O produced. Details below:
Molar mass of water, H₂O = 18 g/mol Mole of water, H₂O = 6 molesMass of water, H₂O = ?Mole = mass / molar mass
6 = Mass of water, H₂O / 16
Cross multiply
Mass of water, H₂O = 6 × 18
Mass of water, H₂O = 108 g (last option)
Learn more about mass produced:
https://brainly.com/question/9526265
#SPJ1
A sample of gas has an initial volume of 3.62 L at a pressure of 0.987 atm. If the volume of the gas decreases to 2.50 L, what will the pressure be
Answers
Answer: 1.43 atm
Explanation:
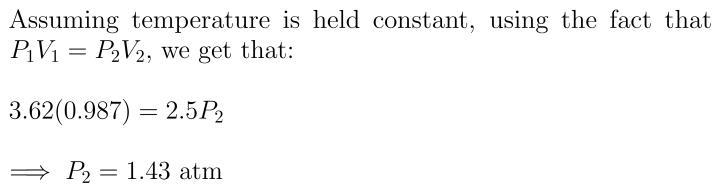
all about Henry Mosléy?
Answers
Answer:
Henry Moseley was an English physicist whose contribution to the science of physics was the justification from physical laws of the previous empirical and chemical concept of the atomic number.
I have two solutions. In the first solution, 1.0 moles of sodium chloride is dissolved to make 1.0 liters of solution. In the second one, 1.0 moles of sodium chloride is added to 1.0 liters of water. Is the molarity of each solution the same? Explain your answer.
Answers
Answer:4.0 liters of everything
Explanation: i just know...
How many grams of copper nitrate can be produced from 0.78 grams of silver nitrate and excess copper?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
This link will take you to a work sheet that I think might help.
Hydrogen gas caught fire quickly in the Hindenberg accident. In comparison, neon gas and helium gas are nonreactive. This is why helium is safe for aircraft and neon is safe for electrical signs. Which statement best explains why helium and neon have similar chemical properties?
Answers
Answer:
Helium and Neon have similar chemical properties because both of them completely fill the outer shell of their atoms' electrons, so there is nothing to share with other atoms, neither with the same element nor with any other element.
Explanation:
Helium and Neon are both noble gases . As elements react, their atoms, by losing, acquiring, or sharing electrons, complete their outer shells. Noble gas atoms already have full outer shells, so there is no tendency for them to lose, gain, or share electrons. There are incomplete outer shells of atoms of group 1 and 7 elements (so they are reactive)
Chemical properties of HELIUM and NEON -:
In group 8(or 0) of the periodic table, on the far right side, the Noble Gases are contained. Helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon and radon are their names. They are extremely colourless and unreactive. They do not form bonds, so they still remain as single (monatomic) atoms. There is very little chemical reactivity in them.Hence, helium and neon have similar chemical properties as they are the most stable due to having the maximum number of valence electrons their outer shell can hold.
Convert 3,124,991 centimeters (cm) to miles (mi) rounding to 4 sig figs
Answers
Answer:
19.417794 mi
Explanation:
Answer:
19.41
Explanation:
Select all examples that apply as a physical changes in properties (please help)

Answers
What is the [H+] if the pH of a
solution is 11.3?
[H+] = [? ] × 10^[?]]
Answers
Answer:
5.01 x 10^-12
Explanation:
Formula [H+]=10^-ph 》》 10^-11.2
-Hope this helps!!
Which will change will cause the gravitational force between a baseball and a soccerball
Answers
Pls mark as brainliest
4. How much heat is required to raise the
temperature of 250.0 g of mercury by 52°C?
Answers
The heat is required to raise the temperature of 250.0 g of mercury by 52 °C is 1820 J.
given that :
mass = 250 g
ΔT = 52 °C
specific heat capacity of mercury = 0.14 J/g °C
the specific heat capacity expression is given as:
Q = mc ΔT
where,
Q = heat
m = mass = 250 g
ΔT = change in temperature = 52 °C
putting the values in the formula, we get :
Q = mc ΔT
Q = 250 × 0.14 × 52
Q = 1820 J
Thus, The heat is required to raise the temperature of 250.0 g of mercury by 52 °C is 1820 J.
To learn more about specific heat here
https://brainly.com/question/16531422
#SPJ1
Mg + H2O → Mg(OH)2 + H2
Answers
ASAP PLEASE! Mostly just need the data and conclusion answers please!!!
Electromagnetic Spectrum Lab Report
Instructions: In this virtual lab, you will use a virtual spectrometer to analyze astronomical bodies in space. Record your hypothesis and spectrometric results in the lab report below. You will submit your completed report to your instructor.
Name and Title:
Include your name, instructor's name, date, and name of lab.
Objectives(s):
In your own words, what is the purpose of this lab?
Hypothesis:
In this section, please include the predictions you developed during your lab activity. These statements reflect your predicted outcomes for the experiment.
Procedure:
The materials and procedures are listed in your virtual lab. You do not need to repeat them here. However, you should note if you experienced any errors or other factors that might affect your outcome. Using your summary questions at the end of your virtual lab activity, please clearly define the dependent and independent variables of the experiment.
Data:
Record the elements present in each unknown astronomical object. Be sure to indicate “yes” or “no” for each element.
Hydrogen Helium Lithium Sodium Carbon Nitrogen
Moon One
Moon Two
Planet One
Planet Two
Conclusion:
Your conclusion will include a summary of the lab results and an interpretation of the results. Please answer all questions in complete sentences using your own words.
Using two to three sentences, summarize what you investigated and observed in this lab.
Astronomers use a wide variety of technology to explore space and the electromagnetic spectrum; why do you believe it is essential to use many types of equipment when studying space?
If carbon was the most common element found in the moons and planets, what element is missing that would make them similar to Earth? Explain why. (Hint: Think about the carbon cycle.)
We know that the electromagnetic spectrum uses wavelengths and frequencies to determine a lot about outer space. How does it help us find out the make-up of stars?
Why might it be useful to determine the elements that a planet or moon is made up of?
Answers
Answer: This lab's goal is to investigate the absorbance patterns created by recently discovered moons and planets.
The first moon consists of Lithium and carbon, the second moon consists of sodium and nitrogen. Moving onto the planets, the first planet consists of hydrogen and carbon, and lastly, the second planet is consistent with helium and carbon.
How to explain the lab report
The theory was right; there have been no flaws in the outcome. The astronomical item observed by the spectrometer is the independent variable. The spectrum of any astronomical object is the dependent variable.
Space consists of bodies with different types of the electromagnetic spectrum. This includes high-energy bodies emitting radiation in short wavelengths and extremely short wavelengths such as in UV spectrum, X rays, and gamma rays. Conversely, other bodies might be emitting radiations in the longer wavelengths such as Microwaves and Radio waves.
The element missing from the moons and the planets would be Oxygen. It is to be remembered that Oxygen forms the base of the sustenance of life forms on Earth and forms an indispensable part of the carbon cycle. In the absence of oxygen, these planets and moons remain lifeless.
Stars emit heat and light. Along with the heat and light, radiations are emitted by the star. These radiations travel outward from stars and work as the signature of the stars. By analyzing the radiations from the stars, scientists back on Earth could deduce the physical conditions in the heart of a star including its constitution, temperature, and surface conditions.
The knowledge of the constitution of the elements making up the moon or planet is necessary to ascertain the life-sustaining capability of the same.
Answer: This lab's goal is to investigate the absorbance patterns created by recently discovered moons and planets.
The first moon consists of Lithium and carbon, the second moon consists of sodium and nitrogen. Moving onto the planets, the first planet consists of hydrogen and carbon, and lastly, the second planet is consistent with helium and carbon.
How to explain the lab report
The theory was right; there have been no flaws in the outcome. The astronomical item observed by the spectrometer is the independent variable. The spectrum of any astronomical object is the dependent variable.
Space consists of bodies with different types of the electromagnetic spectrum. This includes high-energy bodies emitting radiation in short wavelengths and extremely short wavelengths such as in UV spectrum, X rays, and gamma rays. Conversely, other bodies might be emitting radiations in the longer wavelengths such as Microwaves and Radio waves.
The element missing from the moons and the planets would be Oxygen. It is to be remembered that Oxygen forms the base of the sustenance of life forms on Earth and forms an indispensable part of the carbon cycle. In the absence of oxygen, these planets and moons remain lifeless.
Stars emit heat and light. Along with the heat and light, radiations are emitted by the star. These radiations travel outward from stars and work as the signature of the stars. By analyzing the radiations from the stars, scientists back on Earth could deduce the physical conditions in the heart of a star including its constitution, temperature, and surface conditions.
The knowledge of the constitution of the elements making up the moon or planet is necessary to ascertain the life-sustaining capability of the same.
Calculate the mass of hydrogen produced when 72 g of magnesium
reacts with sulfuric acid.
Answers
Since this is a single replacement reaction, the equation for the reaction is:
\(\text{Mg}+\text{H}_{2}\text{SO}_{4} \longrightarrow \text{MgSO}_{4}+\text{H}_{2}\)
From this, we know that for every mole of magnesium consumed, 1 mole of hydrogen is produced.
The atomic mass of magnesium is 24.305 g/mol, so 72 grams of magnesium is 72/24.305 = 2.9623534252211 moles.
This means we need to find the mass of 2.9623534252211 moles of hydrogen.
Hydrogen has an atomic mass of 1.00794 g/mol, so doubling this to get the formula mass of of \(\text{H}_{2}\), we get 2.01588 g/mol, which his a mass of:
(2.01588)(2.9623534252211). which is about 5.97 g
define the term inertia
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Enertia is an integral part of Newton's first law of motion.
It is the tendency of an object to stay at rest or to continue moving until and unless any external unbalanced force, (like, applied force or force of tension or frictional force ) is applied to either move it from rest or change its speed(in other words, accelerate it!!).
Example below, is of ball at rest (fig1) and if this ball is moving straight on a frictionless surface(like ice) it will keep moving!! until, we push it or pull it.

Write the equation for the equilibrium contant, K, for the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin
Answers
Equilibrium constant K for the reaction can be written as,
K = [C]c [D]d / [A]a [B]b
In the absence of oxygen, cells cannot carry out their biochemical responsibilities. Oxygen moves to the cells attached to hemoglobin. Equilibrium constant is the value of its reaction quotient. The equilibrium constant, K, expresses the relationship between products and reactants of a reaction at equilibrium with respect to a specific unit. The equilibrium constant K is the ratio of the mathematical product of the concentrations of the products of a reaction to the mathematical product of the concentrations of the reactants of the reaction. protein hemoglobin which binds oxygen in your lungs and carries it to other tissues of your body. hemoglobin bind oxygen tightly so that a large fraction of the hemoglobin will pick up an oxygen before cycling back through the other tissues. However, in the other tissues, one wants hemoglobin to bind oxygen loosely so that it can be easily relinquished for use in respiration. Each concentration is raised to the power of its coefficient in the balanced chemical equation.
suppose a general reaction written,
aA + bB---> cC + dD
For the reaction equilibrium constant can be written as,
Keq = [C]c [D]d / [A]a [B]b
The reaction of equilibrium of hemoglobin is,
Hb(CO)4 + 4O2 ⇌ Hb(O2)4 + 4CO
To know more about Equilibrium constant please visit :
https://brainly.com/question/3159758
#SPJ4
why would a metal house not be a good idea in Florida or Alaska?
Answers
Answer: Maybe, It could be a good and bad idea.
Explanation:
This is beacuse Metal does not absorb and can block sunlight.
I need help calculating the Kc for both of these reactions.

Answers
Given the equation :
CH3OH +Cl2 →← 2 CH3CL + 2OH ^-1
at equilibrium concentration, we have:
(1.5 -2x )/ 5L + (1.0 -x )/5L =2x /5L + 2x /5L
→ (1.5-2x+ 1 -x )/ 5L = 4x /5L
→(0.5 -3x)/5L = 4x/5L (5L in the Left hand side cancels 5L inthe right hand side)
→ 0.5 = 4x +3x
0.5 = 7x
x = 0.5/7
x = 0.071
( Extra note : Now lets test and see if this balances ):
LHS : (1.5 -2x )/ 5L + (1.0 -x )/5L = 0.5 -3x)/5L
= 0.5 - 3(0.071)/5
= 0.287 /5 = 0.05
RHS :4(x) /5 = 4(0.071) /5
= 0.28/5 = 0.05
at equlibrium , LHS = RHS therefore our x value is 0.07
Explain how energetic coupling with the hydrolysis reaction of atp can replace a chemical reaction that:______.
Answers
Energetic coupling with the hydrolysis reaction of ATP can replace a chemical reaction that requires a high activation energy.
When a chemical reaction occurs, it typically requires a certain amount of energy to overcome the activation energy barrier and initiate the reaction. However, in some cases, this activation energy is too high for a reaction to proceed efficiently or spontaneously. This is where energetic coupling with the hydrolysis reaction of ATP comes into play.
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a molecule commonly referred to as the "energy currency" of cells. It stores and releases energy in living organisms. When ATP is hydrolyzed, it is converted into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and inorganic phosphate (Pi), releasing a significant amount of free energy. This energy can be harnessed and utilized to drive other energy-requiring processes.
By coupling an energetically unfavorable reaction with the hydrolysis of ATP, the high-energy phosphate bonds in ATP can be broken, liberating the energy needed to overcome the activation energy of the target reaction. This coupling occurs through the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to a reactant molecule, effectively activating it and enabling the reaction to proceed.
The transferred phosphate group acts as a chemical handle, facilitating the bonding of the reactant with other molecules or participating in other chemical transformations necessary for the desired reaction. This energetic coupling mechanism allows reactions that would otherwise be thermodynamically unfavorable or too slow to occur efficiently within the cellular environment.
Learn more about Energetic coupling
brainly.com/question/29735117
#SPJ11
How many moles of water can be produced with 4.3 moles of H2 and 5.6 moles of O2? Which reactant is limiting? How many moles of the excess reactant will be left after the reaction? 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O
Answers
Answer:
Hydrogen H₂ will be the limiting reagent.
The excess reactant that will be left after the reaction is 3.45 moles.
4.3 moles of water can be produced.
Explanation:
The balanced reation is:
2 H₂ + O₂ → 2 H₂O
By reaction stoichiometry (that is, the relationship between the amount of reagents and products in a chemical reaction), the following amounts of each compound participate in the reaction:
H₂: 2 moles O₂: 1 mole H₂O: 2 molesTo determine the limiting reagent, you can use a simple rule of three as follows: if by stoichiometry 1 mole of O₂ reacts with 2 moles of H₂, how much moles of H₂ will be needed if 5.6 moles of O₂ react?
\(moles of H_{2} =\frac{5.6 moles of O_{2} *2 mole of H_{2} }{1 mole of O_{2}}\)
moles of H₂= 11.2 moles
But 11.2 moles of H₂ are not available, 4.3 moles are available. Since you have less moles than you need to react with 5.6 moles of O₂, hydrogen H₂ will be the limiting reagent and oxygen O₂ will be the excess reagent.
Then you can apply the following rules of three:
If by reaction stoichiometry 2 moles of H₂ react with 1 mole of O₂, 4.3 moles of H₂ will react with how many moles of O₂?\(moles of O_{2} =\frac{1 mole of O_{2} *4.3 mole of H_{2} }{2 mole of O_{2}}\)
moles of O₂= 2.15 moles
The excess reactant that will be left after the reaction can be calculated as:
5.6 moles - 2.15 moles= 3.45 moles
The excess reactant that will be left after the reaction is 3.45 moles.
If by reaction stoichiometry 2 moles of H₂ produce 2 moles of H₂O, 4.3 moles of H₂ produce how many moles of H₂O?\(moles of H_{2}O =\frac{2 moles of H_{2}O *4.3 mole of H_{2} }{2 mole of H_{2}}\)
moles of H₂O= 4.3 moles
4.3 moles of water can be produced.
i hope someone can help me here please don't answer nonsense

Answers
Answer:
4560 torr
Explanation:
PV = K
4 x 1.5 = k
k = 6
V = k / p
V = 6 / 1
V = 6
atm to torr = 1 to 760
760 x 6 = 4560
Answer:
4560 Torr
Explanation:
Boyle's Law
\(\sf P_1 \cdot V_1=P_2 \cdot V_2\)
where:
\(\sf V_1\) = initial volume\(\sf V_2\) = final volume\(\sf P_1\) = initial pressure\(\sf P_2\) = final pressureGiven:
\(\sf V_1\) = 4 L\(\sf V_2\) = 1 L\(\sf P_1\) = 1.5 atmSubstituting the given values into the formula:
\(\implies \sf 1.5 \cdot 4=P_2 \cdot 1\)
\(\implies \sf P_2=6\:atm\)
To convert atm to Torr, multiply atm by 760:
\(\implies \sf P_2=6\cdot 760=4560\:Torr\)
How many mL of 3,0 M HNO₂ can be completely
neutralized by 75 mL of 1.5 M Mg(OH)2 solution?
Answers
Answer: approximately 18.75 mL of 3.0 M HNO₂ solution can be completely neutralized by 75 mL of 1.5 M Mg(OH)₂ solution.
Explanation:
To determine the volume of 3.0 M HNO₂ solution that can be neutralized by 75 mL of 1.5 M Mg(OH)₂ solution, we can set up an equation based on the stoichiometry of the balanced chemical equation.
The balanced chemical equation for the neutralization reaction between HNO₂ and Mg(OH)₂ is:
2 HNO₂ + Mg(OH)₂ → Mg(NO₂)₂ + 2 H₂O
From the equation, we can see that it takes two moles of HNO₂ to react with one mole of Mg(OH)₂.
First, let's calculate the number of moles of Mg(OH)₂ present in 75 mL of 1.5 M solution:
Number of moles of Mg(OH)₂ = Volume (in L) × Concentration (in mol/L)
= 75 mL × (1 L / 1000 mL) × 1.5 mol/L
= 0.1125 mol
Since the stoichiometry ratio is 2:1 (HNO₂:Mg(OH)₂), we can conclude that 0.1125 moles of Mg(OH)₂ can neutralize 0.1125/2 = 0.05625 moles of HNO₂.
Now, let's determine the volume of 3.0 M HNO₂ required to contain 0.05625 moles:
Volume (in L) = Number of moles / Concentration (in mol/L)
= 0.05625 mol / 3.0 mol/L
≈ 0.01875 L
Finally, we convert the volume from liters to milliliters:
Volume (in mL) = Volume (in L) × 1000
≈ 0.01875 L × 1000
≈ 18.75 mL
In double replacement reactions, why will two metals not combine with each other when products are formed?.
Answers
When pieces of two ionic compounds are exchanged, creating two new compounds, this reaction is known as a double replacement reaction (also known as a double displacement, exchange, or metathesis reaction).
What is Double Displacement Reaction?
When one reactant is partially replaced by another, the reaction is referred to as a twofold displacement reaction.
Double displacement reactions can be described as follows:
AD = CB + CD + AB
In a double replacement process, the ions in two reactant ionic compounds are exchanged for the same ions in two new product compounds.
When two reactants swap cations or anions to produce two new products, the process is known as a double replacement reaction.
Double displacement reactions and metathesis reactions are other names for double replacement processes.
Double replacement reactions include neutralisation, precipitation, and gas production.
Learn more about Double Displacement Reaction from given link
https://brainly.com/question/23918356
#SPJ4
24. A hypothesis cannot be considered a
a. possible explanation,
b. preliminary conclusion.
c. good guess.
d. concept
Answers
Answer:
B. Preliminary conclusion
Explanation:
The answer is B because a hypothesis is really an educated guess you make in regards to a question, usually before performing an experiment, so it can't be a preliminary conclusion because you don't really have any solid evidence to support your hypothesis, you only have background information. You will either be able/not be able to support your hypothesis after your expirement has concluded.
Calculate the total binding energy, and the binding energy per nucleon, for 73Li37Li . The masses of the atoms of 73Li37Li and 11H11H are 7.016004 uu and 1.007825 uu , respectively. The mass of a neutron is 1.008665 uu . Express your answe
Answers
The total binding energy for lithium is 39.25 Mev
The binding energy per nucleon for lithium is 5.61 Mev / nucleon
BINDING ENERGYBinding energy is the total energy required for the breakdown of a nucleus to its component nucleons
TOTAL BINDING ENERGYTotal binding energy is the amount of energy released when the atom is formed from its constituent electron, protons and neutrons.
The given mass are lithium is 7.016004 u and hydrogen is 1.007825
There are 3 hydrogen and 4 neutrons
To calculate the Total binding energy
3 ( 1.0782) + 4 ( 1.008665 ) = 7.058135 u
Mass of neutron is 1.008665 u
1 atomic mass unit is 931.5 Mev
The total binding energy isTBe = ( 7.058135 - 7.016004 ) × 931.5
= 39.25 Mev
Total binding energy is 39.25 Mev
To calculate the binding energyBE= 39.25 / 7
= 5.61 Mev / neucleon
Hence, The total binding energy is 39.25 Mev.
The binding energy is 5.61 Mev / neucleon.
Learn more about the binding energy on
https://brainly.com/question/4334375
#SPJ4
Copper turns a green-brown when it is exposed to oxygen in air. What chemical property of oxygen causes this effect? A. its reactivity B. its volume C. its mass D. its flammability
Answers
Answer:
A. its reactivity
Explanation:
It's reactivity because copper was exposed to air and if it is reactivity it must be exposed to air
Answer:
A. reactivity
Explanation:
3. Calculate the concentration in g/dm3 of solution of NaOH containing 0.25 mole in 1dm3
Answers
The concentration of the NaOH solution is 10.00 g/dm³.
To calculate the concentration in g/dm³ of a solution of NaOH containing 0.25 moles in 1 dm³, we need to know the molar mass of NaOH.
The molar mass of NaOH is calculated as follows:
Na (Sodium) = 22.99 g/mol
O (Oxygen) = 16.00 g/mol
H (Hydrogen) = 1.01 g/mol
Molar mass of NaOH = 22.99 g/mol + 16.00 g/mol + 1.01 g/mol = 40.00 g/mol
Now, we can calculate the concentration (C) using the formula:
C = (moles of solute) / (volume of solution in dm³)
C = 0.25 moles / 1 dm³
C = 0.25 mol/dm³
To convert moles to grams, we can multiply the molar mass by the number of moles:
Concentration in g/dm³ = (0.25 mol/dm³) * (40.00 g/mol)
Concentration in g/dm³ = 10.00 g/dm³
To know more about Hydrogen
https://brainly.com/question/31018544
#SPJ11
Complete and balance the following redox reaction in acidic solution.Sn+HNO3→SnO2+NO2+H2O
Answers
The complete and balanced redox reaction in an acidic solution is: Sn + 2HNO₃ + 6H+ → SnO₂ + 2NO₂ + H₂O
To complete and balance the redox reaction in an acidic solution using the given terms. The reaction is: Sn + HNO₃ → SnO₂ + NO₂ + H₂O.
1: Separate the reaction into half-reactions:
Oxidation half-reaction: Sn → SnO₂
Reduction half-reaction: HNO₃ → NO₂
2: Balance the atoms in each half-reaction:
Oxidation: Sn → SnO₂ (Oxygen atoms are already balanced)
Reduction: 2HNO₃ → 2NO₂ + H₂O (Oxygen atoms are balanced by adding H2O)
3: Balance the charges in each half-reaction by adding electrons:
Oxidation: Sn → SnO₂ + 4e- (Charge is balanced)
Reduction: 2HNO₃ + 6H+ + 4e- → 2NO₂ + H₂O (Charge is balanced by adding H+ ions)
4: Make the number of electrons lost and gained equal by multiplying the half-reactions:
Oxidation: Sn → SnO₂ + 4e-
Reduction: 2HNO₃ + 6H+ + 4e- → 2NO₂ + H₂O
5: Add the half-reactions and simplify:
Sn + 2HNO₃ + 6H+ → SnO₂ + 2NO₂ + H₂O
You can learn more about redox reactions at: brainly.com/question/13293425
#SPJ11