Wind can help make ________.
Answers
Answer:
Energy
Explanation:
Related Questions
What is the difference between a guard cell and a white blood cell?
Answers
Blood cells can guard body btw.
Guard cells are found in plants and white blood cells are found in animals.
What are guard cells?Guard cells are specialised plant cells that regulate gas exchange in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs. They are created in pairs, with a stomatal orifice separating them. What are white blood cells?The immune system's white blood cells, also known as leukocytes or leucocytes, are responsible for defending the body against both infectious diseases and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are created and developed from hematopoietic stem cells, which are multipotent cells found in the bone marrow. All parts of the body, including the blood and lymphatic system, include leukocytes.Guard cells function to allow gaseous exchange and white blood cells are responsible for the functioning of the immune system.
Learn more about guard cells here:
https://brainly.com/question/7145238
#SPJ2
The natural extinction of a predator can negatively affect the
Environment by leading to
-unrestricted prey species growth.
- major climate change.
-harmful human pollution.
-increased sediment deposits.
Answers
Explanation: the less predators the more the prey will reproduce, hence the fact that no one is there to consume them they will increase at a very accelerated speed
Question 3
Which statement below is correct?
A. Photosynthesis produces ATP, and cellular respiration requires light
energy
B. Photosynthesis produces carbon dioxide, and cellular respiration
produces sugars.
C. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration occur in both plant and
animal cells.
D. Photosynthesis produces the oxygen required for cellular respiration.
Answers
Answer:
B is the correct answer.
A is incorrect because respiration is always occuring in animals and plants, therefore it means it does not require the presence of light. Photosynthesis does produce ATP, though.
Not C because photosynthesis does not occur in animals
Not D because they both are different processes. They don't really depend on each other, though they could occur at the same time.
what are the precautions that should be token when using a photometer? please help me
Answers
Answer:
PRECAUTIONS FOR USING A SPECTROPHOTOMETER :
1 . By allowing the lamps and electronics to warm up
2.By cleaning up any spills inside the cuvette compartment
3.By carrying out the set-up procedure in the correct order
4.By ensuring that %T or transmission is used as appropriate
5.By closing the door to the cuvette compartment before reading the result
6.By performing calibration checks after set up
7.By wiping fingerprints and spilt sample off the outside of the cuvette before measuring
8.By using the correct wavelength
PRECAUTIONS FOR USING A FRAME PHOTOMETER:
1. Do not move or Carry the unit when in use or connected to the mains electricity supply
2. There should be sufficient time for the chimney to cool before handling
3. Do not use acetylene with the flame photometer
4. Over adjustment of the fuel valve will cause excess flame
Do not position the product so that it is difficult to disconnect from the mains supply
5. Do not cover the chimney whilst in use.
6. Do not block or obstruct ventilation slots /airways
7. Do not operate or handle any part of the product with wet hands
I HOPE THIS WILL HELP AND IF NOT LET ME KNOW
1. Discuss the importance of each of the following edaphic (soil) factors to living organisms. Water, Air, Mineral nutrients
Answers
The edaphic factor includes a range of proprieties of the soil, physical, chemical, and biological that are result from biological and geological phenomena. In the case of living organisms, we have those chemical and physical properties, such as minerals and water, as well as soil aeration influence ecology and evolution of plants and in consequence, associated biota, this is because plants are the base of the food chain as well as pioneers in many cases of ecosystem structure.
Following this line of thought, we have that soil is very important, factors as simple as the consistency, very different sand from mud, impact texture and chemical composition, and in consequence the type of organisms that can settle there, we can see that in deserts (sandy soil, limited water, good nutrients), the type of plants that grow have certain characteristics, for example, they live with very few water, and in turn, they provide refuge and food for other animals in the desert, on the other hand, we have places like confers forests, where the soil is rich and water is available in the subsoil, also tend to be mountainous sites, those plants are adapted to other conditions, their roots retain soil preventing erosion, also the kind of animals that depend on them are different.
Plant cells can produce glucose.
Suggest why yeast cells cannot produce glucose.
Answers
Answer:
Glucose can still be broken down in the absence of oxygen in order to meet the cells energy requirements. In plant and yeast cells pyruvate is converted into carbon dioxide and a type of alcohol called ethanol.
Explanation:
Explanation:
This was what I saw on the internet
Glucose can still need broken down in the absence of oxygen in order to meet the cells' energy requirements. In plant and yeast cells, pyruvate is converted into carbon dioxide and a type of alcohol called ethanol.
which type of gland consists of a secretory region and a duct running to a surface? multiple choice question.
Answers
Answer: sweat glands
Explanation: these glands secrete a big quantity of water with toxines on your skin, so in a surface.
A salivary gland is a type of gland consisting of a secretory area and a tube running over the surface
Salivary glands that produce the saliva, which aids in the digestion, keeps the mouth moist, and supports healthy teeth. Under and behind the chin are her three major salivary glands: the parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands. Salivary glands lubricate the mouth, aid in swallowing, aid digestion, and protect teeth from harmful bacteria. There are three main types of salivary glands: the sublingual, submandibular, and parotid glands. . They are divided into two main types: Major salivary glands, including the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands; minor salivary glands that line the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts and predominantly cover the entire mouth
To know more about Salivary glands visit:
https://brainly.com/question/27139668
#SPJ1
Explain how these individuals can carry a fusion gene that is transcriptionally active and yet do not develop CML.
CML is actually developing in a latent form.
A single gene alteration is not the only requirement for CML.
Developing CML after the gene fusion can take a long time.
None of the above
Answers
These individuals can carry a fusion gene that is transcriptionally active and yet do not develop CML as : A single gene alteration is not the only requirement for CML.
What is meant by CML?A rare kind of cancer of the bone marrow, the spongy tissue found inside bones where blood cells are formed, is chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). The amount of white blood cells in the blood rises as a result of CML.
A condition known as chronic myelogenous leukemia causes an excessive production of white blood cells in the bone marrow. Chronic granulocytic leukemia, often known as chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), is a slowly growing blood and bone marrow condition that primarily affects adults in or after middle age and very infrequently affects children.
To know more about CML, refer
https://brainly.com/question/10373918
#SPJ4
What makes up the sides of the backbone of DNA?
and
What makes up the inside or the steps of a DNA molecule?
Answers
Answer:
The sides of the backbone of DNA are made up of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. The inside of the DNA molecule, or the "steps" as you put it, consists of the bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. These bases pair up with each other in specific ways: adenine always pairs with thymine, and guanine always pairs with cytosine. This is what gives DNA its unique double-helical structure and allows it to store genetic information.
Answer:
The backbone of a DNA molecule consists of the phosphate groups and the deoxyribose sugars, whereas the base of the DNA molecule consists of nitrogenous bases, therefore, the backbone of DNA is made up of phosphate groups and pentose sugars. Adenine is a part of the base of the molecule.
What is the function of proteins in muscles?
Answers
Answer: Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell
Explanation:
which of the following is not a level of organization?
1)individual
2)population
3)community
4)ecosystem
5)ecology
Answers
Ecology is the study of relationships in their environment, so it cannot be a level of organization.
A rat has 42 chromosomes in eath somatic call. How many chromosomes are in each gamete
Answers
Answer:
21 chromosomes
Explanation:
Somatic cells are a diploid which have 2 sets of chromosomes. If two sets are 42 chromosomes, one set must be 21 chromosomes. Gametes are a haploid which have only 1 set of chromosomes. So in each gamete, there should be 21 chromosomes.
blood is an example of
Answers
Answer:
Blood is both tissue and a fluid. It is because it is a collection of similar specialized cells that serve particular functions. These cells are suspended in a liquid matrix (plasma) which makes blood a fluid
Explanation:
I majored in Biology.
What can cause an abrupt appearance of stasis in the fossil record?
Answers
Answer: new information about said fossil could have been found to add to the stasis
give an explanation about the importance of these processes (photosynthesis and cellular respiration) in cycling nutrients through the ecosystem of the earth
Answers
Answer: because it is
Explanation:
right?
Explain the processes involved in the transportation of absorbed
nutrients throughout the body.
Answers
Answer:
Absorption: The process of absorbing nutrients occurs primarily in the small intestine. Once the food is broken down into smaller molecules through digestion, these molecules are absorbed into the bloodstream. For example, carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, proteins into amino acids, and fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Circulatory System: The circulatory system, composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, plays a crucial role in transporting absorbed nutrients. The blood vessels form an extensive network that reaches all tissues and organs in the body.
Hepatic Portal System: After absorption, most of the nutrients are transported to the liver through a specialized system called the hepatic portal system. This system ensures that the liver, which performs various metabolic functions, receives a concentrated supply of nutrients before they are distributed throughout the body.
Bloodstream Transport: Once in the bloodstream, nutrients are carried by the plasma, the liquid component of blood. Different nutrients use specific mechanisms for transport:
Glucose: It is transported by facilitated diffusion or active transport, depending on the concentration gradient, with the help of insulin.
Amino Acids: They are transported through the bloodstream by specific carrier proteins.
Fats: Dietary fats are initially packaged into structures called chylomicrons and transported through the lymphatic system before entering the bloodstream. Once in the bloodstream, fats are carried by lipoproteins such as low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Distribution to Tissues: As the blood circulates, nutrients are distributed to various tissues and organs according to their specific needs. Nutrients are delivered to cells through the capillaries, the smallest blood vessels in the body, which have thin walls that allow for the efficient exchange of nutrients and waste products.
Cellular Uptake: Nutrients are taken up by cells through various mechanisms. For instance, glucose enters cells with the help of insulin, while amino acids are transported into cells through specific carrier proteins. Fats are taken up by cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis or by diffusion.
Metabolism: Once inside the cells, nutrients undergo metabolic processes to produce energy or build new molecules. Glucose, for example, can be metabolized through glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation to generate ATP, the cell's energy currency.
Waste Removal: Metabolic byproducts, such as carbon dioxide and urea, are generated during nutrient metabolism. These waste products are transported back into the bloodstream and eventually eliminated from the body through the lungs (carbon dioxide) or the kidneys (urea).
It's important to note that different nutrients may have different transport mechanisms and pathways. The body's ability to efficiently transport and utilize absorbed nutrients is vital for maintaining proper functioning and overall health.
2. Describe the property of water that is indicated by the data. How is this property explained by the structure of water molecules and the bonds between them? Type your answer here. FIED
Answers
Answer:
Water molecules are polar, so they form hydrogen bonds. This gives water unique properties, such as a relatively high boiling point, high specific heat, cohesion, adhesion and density.
Why is honesty an important component of bargaining.
Answers
The picture below shows some features of the ocean floor. (1 point)
At which of these locations does the ocean floor spread apart to form new oceanic crusts?
Location A
Location B
Location C
Location D
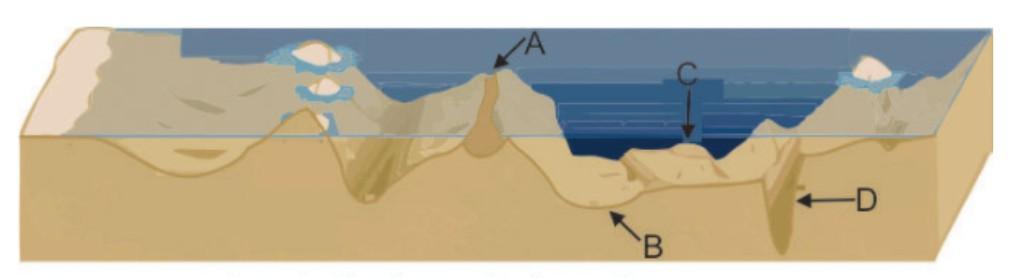
Answers
Answer:
I think the answer should be D
Explanation:
Answer:
It is D
Explanation:
New oceanic crust will form
QUICK PLS
Body cells have
____ the number of chromosomes as sex cells.
a: 4times
b: one half
c: one fourth
d: twice
Answers
Answer:
Body cells have twice the number
A cosmetologist can prescribe medicated shampoo
Answers
A cosmetologist is not legally authorized to prescribe medicated shampoo.
Can a cosmetologist prescribe medicated shampoo?A cosmetologist is not legally authorized to prescribe medicated shampoo. Only licensed healthcare professionals, such as physicians, nurse practitioners, and physician assistants, are authorized to prescribe medications, including medicated shampoos.
Cosmetologists are trained to provide beauty and cosmetic services, such as hair styling, makeup application, and skincare treatments. While they may have knowledge of different types of shampoos and their benefits for the hair and scalp, they do not have the medical training and expertise to diagnose and treat medical conditions that require the use of medicated shampoos.
Learn more about a cosmetologist:https://brainly.com/question/14645414
#SPJ1
Identify the 6 steps jaguar would use to forecast for the new S-type jaguar
Answers
Jaguar would use the following six steps to forecast for the new S-type Jaguar:
1. Environmental Scanning: This process involves the gathering of information on all external factors that might affect the production and sale of the S-type Jaguar. This can include economic trends, political factors, and social factors such as changing lifestyles or consumer trends.
2. Market Segmentation: This process involves dividing the target market for the S-type Jaguar into smaller, more manageable groups based on specific demographic, geographic, and psychographic variables.
3. Forecasting Demand: This process involves using statistical tools and market research data to estimate the level of demand for the S-type Jaguar.
4. Setting Objectives: This process involves setting clear objectives for the production and sale of the S-type Jaguar, such as sales targets or market share goals.
5. Developing a Marketing Plan: This process involves developing a marketing plan that outlines the steps that will be taken to achieve the objectives set out in the previous step.
6. Implementing and Monitoring the Plan: This final step involves putting the marketing plan into action and monitoring its effectiveness to ensure that the objectives are being met and any necessary adjustments can be made if necessary.
Learn more about jaguar visit:
brainly.com/question/32398311
#SPJ11
I mark Branliest for the correct answer quickly please listen to me Eyes Blue

Answers
Answer:
1(i think)
Explanation:
The nucleus controls and regulates the activities of the cell (e.g., growth and metabolism) and carries the genes, structures that contain the hereditary information. Nucleoli are small bodies often seen within the nucleus. The gel-like matrix in which the nuclear components are suspended is the nucleoplasm.
alewife populations undergo extreme fluctuations sometimes experiencing large scale die-offs from unknown causes. this is an example of what population growth pattern? a. predator and prey b. irregular c. stable d. illogical
Answers
The alewife population growth pattern is an example of an irregular pattern. Alewife populations are known to undergo extreme fluctuations, with large-scale die-offs occurring from unknown causes.
This irregular pattern is due to a variety of factors, including changes in water temperature, availability of food sources, and predation. Additionally, human activities such as overfishing and the construction of dams can also impact the population. Despite these fluctuations, alewife populations play a vital role in the aquatic ecosystems in which they live, serving as an important food source for a variety of predators.
To know more about population growth pattern visit:
https://brainly.com/question/4414152
#SPJ11
Which group, named from their cuplike sexual reproductive asocarp, make up 75% of know fungi?
Answers
Answer: Sac Fungi, or Ascomycota.
Explanation: This type of fungi has cupcake asocarp.
Sar and Dagon are the same distance from the equator, and they are
both near the ocean. Using the information in the map, how does the air
temperature of Sar compare to the air temperature of Dagon? Why The
air at Sar is?
Answers
Answer:colder
Explanation:colder than Dagon. The winds push ocean water that turns and follows the coasts. Energy is transferred from the air to the ocean at Sar and energy is transferred from the ocean to the air at Dagon.
A type of protein the immune system produces to neutralize a threat of some kind, such as an incompatible substance in the blood, is called an
Answers
A type of protein the immune system produces to neutralize a threat of some kind, such as an incompatible substance in the blood, is called an antibody.
Antibodies are specifically designed to recognize and bind to unique molecules on the surface of these foreign substances, known as antigens. By binding to antigens, antibodies help neutralize or eliminate the invading pathogens and activate other cells of the immune system to eliminate them.
There are several different types of antibodies, each with unique properties and functions. The five main classes of antibodies are IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG, and IgM. Each class has a different structure and function, and is produced in response to different types of antigens and at different stages of an immune response.
To know more about antibody: https://brainly.com/question/15382995
#SPJ11
A researcher is examining a data set. She sums the total of all of the data points and then divides that value by the number of data points.
A. the standard deviation
B. the mode
C. the range
D. the mean
Answers
the formula to calculate the mean:
total data / number of data = the total mean
What can be done to quickly produce large numbers of identical plants with this same trait
Answers
Answer:
Plants can be cloned to quickly produce large numbers of identical plants with similar traits.
Explanation:
Fred was diagnosed 6 months ago with liver cancer. His liver is no longer able to make the necessary amount of proteins needed by the body. What effect, if any, would this have on the net glomerular filtration rate
Answers
The correct answer is b. Blood colloid osmotic pressure would be decreased, decreasing the net glomerular filtration rate. This is because the liver plays an important role in producing proteins such as albumin, which is a major contributor to blood colloid osmotic pressure.
When the liver is no longer able to produce enough proteins, there is a decrease in blood colloid osmotic pressure, leading to a decrease in the net glomerular filtration rate. This is because blood colloid osmotic pressure opposes the hydrostatic pressure in the glomerular capillaries, which is one of the three forces contributing to the net filtration rate. Therefore, a decrease in blood colloid osmotic pressure results in a decrease in the net filtration rate. It is important to note that liver cancer and its treatment can also have other effects on kidney function, such as damage to the nephrons or obstruction of the urinary tract, which may further affect the glomerular filtration rate.
learn more about glomerular filtration rate Refer: https://brainly.com/question/29676967
#SPJ11
complete question: Fred was diagnosed 6 months ago with liver cancer. His liver is no longer able to make the necessary amount of proteins needed by the body. What effect, if any, would this have on the net glomerular filtration rate?
(Hint, decide which of the 3 forces contributing to the net filtration rate is affected. Then adjust numbers in the equation to determine if there is an increase, decrease, or no change to the net filtration rate).
a. Blood colloid osmotic pressure would be decreased, increasing the net glomerular filtration rate.
b. Blood colloid osmotic pressure would be decreased, decreasing the net glomerular filtration rate.
c. Capsular hydrostatic pressure would be decreased, increasing the net glomerular filtration rate.
d. Capsular hydrostatic pressure would be decreased, decreasing the net glomerular filtration rate.
e. There would be no effect on the net glomerular filtration rate.