A balloonist begins a trip in a helium-filled balloon in early morning when the temperature is 15°C. By mid-afternoon, the temperature is 30.°C. Assuming the pressure remains at 1.00 atm, for each mole of helium, calculate the following:
(f) Explain the relationship between the answers to parts (d) and (e).
Answers
The relationship between the answers to parts (d) and (e) is given that the system doesn't have constant pressure, ΔH(enthalpy change) and Q(heat transferred) can be stated to be equal to one another.
A thermodynamic system's enthalpy, which is one of its properties, is calculated by adding the system's internal energy to the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function that is frequently employed in measurements of chemical, biological, and physical systems at constant pressure, which the sizable surrounding environment conveniently provides.
Q (Heat) is referred to as energy in motion. On the other hand, enthalpy (ΔH) represents the system's condition and total heat content. The change in internal energy is equal to the heat transmitted to, less the work done by, the system, according to the law of energy conservation. The enthalpy change(ΔH) is precisely equal to the heat transferred(Q) to the system if the sole work performed is a change in volume at constant pressure.
To know more about enthalpy refer to: https://brainly.com/question/13996238
#SPJ4
Related Questions
6
What is the density of a substance that has a mass of 2.0 g, and when placed in a graduated cylinder
the volume changed from 70 mL to 75 mL?
A 2.5 g/mL
B 7.0 g/mL
C 10. g/mL
D 0.40 g/mL
Answers
The density of the substance having a mass of 2.0 g is 0.4 g/mL (Option D)
How do I determine the density of the substance?First, we shall obtain the volume of the substance. This can be obtained as follow:
Volume of water = 70 mL Volume of water + substance = 75 mL Volume of substance =?Volume of substance = (Volume of water + substance) - (Volume of water)
Volume of substance = 75 - 70
Volume of substance = 5 mL
Finally, we shall determine the density of the substance. This is illustrated below:
Mass of substance = 2.0 gVolume of substance = 5 mLDensity of substance = ?Density = mass / volume
Density of substance = 2 / 5
Density of substance = 0.4 g/mL
Thus, the density is 0.4 g/mL (Option D)
Learn more about density:
https://brainly.com/question/952755
#SPJ1
You need to prepare an acetate buffer of pH5.54 from a 0.659M acetic acid solution and a 2.42MKOH solution. If you have 780 mL of the acetic acid solution, how many milliliters of the KOH solution do you need to add to make a buffer of pH5.54 ? The pKa of acetic acid is 4.76. Be sure to use appropriate significant figures.
Answers
The volume of the KOH solution needed to make the buffer is also 780 mL. To prepare an acetate buffer of pH 5.54, we need to calculate the amount of acetic acid and potassium hydroxide required.
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to determine the ratio of the concentration of the acid (HA) to its conjugate base (A⁻) in the buffer solution:
pH = pKa + log([A⁻]/[HA])
Given that the pKa of acetic acid is 4.76 and the desired pH is 5.54, we can rearrange the equation to solve for the ratio [A⁻]/[HA]:
5.54 = 4.76 + log([A⁻]/[HA])
0.78 = log([A⁻]/[HA])
By taking the antilog of both sides, we can find the ratio [A⁻]/[HA]:
[A⁻]/[HA] = 10^0.78
[A⁻]/[HA] = 6.02
Now, let's consider the initial concentration of acetic acid (HA) in the acetic acid solution. We have 0.659 M acetic acid, which means that the concentration of the acetate ion (A⁻) will be 0 M initially.
To achieve the desired ratio of [A⁻]/[HA] = 6.02, we need to add potassium hydroxide (KOH) to convert some of the acetic acid to acetate ion. The reaction between acetic acid and KOH is as follows:
CH3COOH + KOH ⇌ CH3COOK + H2O
The stoichiometry of the reaction is 1:1, meaning that equal volumes of acetic acid and KOH solutions are needed to achieve the desired ratio. Since we have 780 mL of the acetic acid solution, we will need an equal volume of the KOH solution.
In summary, to prepare an acetate buffer of pH 5.54, you will need to add 780 mL of the 2.42 M KOH solution to 780 mL of the 0.659 M acetic acid solution. This will result in a buffer solution with the desired pH, maintaining the appropriate ratio of acetate ion to acetic acid as required by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
To learn more about Henderson-Hasselbalch equation click here:
brainly.com/question/31732200
#SPJ11
Hey. Can someone, please help me with the following questions:
Satellites
Satellites ___________the earth.
You can see _____________ _______________ without a telescope.
An example of a man made satellite is the _____________ _____________ _____________.
The only natural satellite of the earth is the __________.
Choose from: moon, orbit, natural satellites, international space station
Planets
There are ________ planets you can see with the __________ __________.
The five planets are, _________, ___________, ___________, ___________, ___________.
The planets are part of the ___________ ___________.
Light from Saturn takes around ___________ hours to reach earth.
Choose from: 1,5, naked eye, solar system, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn
Comets and Meteors
A _________ is a spectacular sight in the _________ sky.
They are _______ to see and could be described as giant ___________ that orbit the _______.
__________ are bits of dust and _________ that _______ up as they move through the earth’s ____________. A meteor that makes it to earth is called a ______________.
Galaxies
1. What are most of the dots of light that we see in the sky?
2. What is the name of our home galaxy?
3. What is the name of our nearest star?
4. How long does it take the light from the sun to reach the earth?
5. Can you say what some of the other dots of light in the night sky might be?
6. How many stars might there be in one galaxy?
7. What is the name of our nearest neighbor galaxy?
8. State how long it takes for the light from our neighbor galaxy to reach the earth
Answers
5, naked eye, Mercy, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, solar system, 1
I would need to see the choices for this section
1.Stars
2. The Milky Way
3. The sun
4.8 minutes
5. Satellites
6. 100 thousand million
7. Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy
8. 10s of thousands of years
3
2.035g of hydrogen gaz prockset)
a pressure of 1.015 atm in a 9.00.
Container at -211.76 °c . what will be
be the temperature in °c If an
additional
be the 2.099 gram of hydrogen
gas is added to the container and
the pressure increases to 20.15 atm
Answers
The final temperature is 280.59 degrees Celsius.
Who or what is putting pressure on the ATM?The term atmospheres (atm), defined as follows: A mercury column one millimetre high would impose a pressure of one atm, or 1.01325 x 105 Pa. millimetres of mercury (mmHg). One atmosphere of pressure is generated by a mercury column that is 760 mm high. Because pressure and force are connected, you may use the physics equation to compute one if you know the other.
P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
Where P1, V1, and T1 are the initial pressure, volume, and temperature, and P2, V2, and T2 are the final pressure, volume, and temperature.
Given:
Initial pressure (P1) = 1.015 atm
Initial volume (V1) = 9.00 L
Initial temperature (T1) = -211.76 °C (62.39 K)
Mass of hydrogen gas initially (m1) = 2.035 g
Additional mass of hydrogen gas added (m2) = 2.099 g
Final pressure (P2) = 20.15 atm
PV = nRT
n1 = m1/MH2 = 2.035 g / 2.016 g/mol = 1.011 mol
n2 = m1/MH2 + m2/MH2 = 2.035 g / 2.016 g/mol + 2.099 g / 2.016 g/mol = 2.059 mol
We can assume that the volume of the container is constant, so we can set V1 = V2 in the combined gas law equation:
P1/T1 = P2/T2
Solving for T2:
T2 = P2T1V1 / (P1*V2)
Substituting the values:
V2 = V1 = 9.00 L
T2 = (20.15 atm)(62.39 K)(9.00 L) / (1.015 atm)(2.059 mol)(8.314 J/(mol*K))
T2 = 553.75 K or 280.59 °C
To know more about temperature visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/30863015
#SPJ1
Question:
A container holds 2.035 grams of hydrogen gas at a pressure of 1.015 atm and a temperature of -211.76 °C. What will be the temperature in °C if an additional 2.099 grams of hydrogen gas is added to the container and the pressure increases to 20.15 atm?
A 1.35 m aqueous solution of compound X had a boiling point of 101.4C. Which one of the following could be compound X? The boiling point elevation constant for water is .52C/m.
a. CH3CH2OH
b.C6H12O6
c. KCl
d. CaCl2
e. Na3PO4
Answers
The boiling point of a solution is related to the molality of the solution (the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent) by the equation: The Correct option is \(Na_{3} PO_{4}\)
ΔTb = Kb x molality
where ΔTb is the change in boiling point, Kb is the boiling point elevation constant, and molality is the molality of the solution.
We can calculate the molality of compound X using the given information:
ΔTb = Tb - Tb°
where Tb is the boiling point of the solution and Tb° is the boiling point of the pure solvent, which is 100°C for water at standard pressure.
ΔTb = 101.4°C - 100°C = 1.4°C
molality = ΔTb / Kb
For water, Kb = 0.52°C/m, so:
molality = 1.4°C / 0.52°C/m = 2.7 m
Now we need to identify which of the given compounds could form a 1.35 m solution with water, resulting in a boiling point elevation of 1.4°C.
ΔTb = Kb x molality = 0.52°C/m x 2.7 m = 1.4°C
Therefore, the compound that could be X is \(Na_{3} PO_{4}\).
Learn more about molality
https://brainly.com/question/26921570
#SPJ4
Who formed the first atomic theory?
The answers is John Dalton FYI I’m just letting people know just incase they don’t know
Answers
Answer:
Leucippus and Democritus
Explanation:
Hope this helps~ :D
Thank you so much! :D
I NEED HELP PLS ILL GIVE BRAINLY

Answers
The correct statement about Dunite is that it is formed when magma cooled slowly below the ground; Option B.
What are rocks?Rocks are large aggregates of minerals that occur in the earth's crusts as a result of the cooling ad solidification of molten magma or the deposition of the remains of dead organic matter which changes from pressure ad heat.
There are three types of rocks, and they are:
Igneous rocks - formed by the cooling of molten magma e.g. Dunite, a light yellowish-green, intrusive igneous rockSedimentary rocks - formed from the remains of dead organic matterMetamorphic rocks - are formed from changes that occur in sedimentary rocks.Learn more about igneous rocks at: https://brainly.com/question/18297174
#SPJ1
A 1-kg block of phosphorus-32, which has a half life of 14.3 days is stored for 100.1 days. At the end of this period, how much phosphorus-32 remains?
Answers
The half-life of phosphorus-32 is 14.3 days, which means that after each 14.3-day period, the amount of phosphorus-32 remaining will be reduced by half. We can use the following equation to calculate the amount of phosphorus-32 remaining after a certain number of half-lives:
N = N0 * (1/2)^(t/t1/2)
where:
N = the amount of radioactive material remaining
N0 = the initial amount of radioactive material
t = the time elapsed
t1/2 = the half-life of the radioactive material
In this case, we know that:
N0 = 1 kg (the initial amount)
t1/2 = 14.3 days (the half-life)
t = 100.1 days (time elapsed)
Plugging these values into the equation, we get:
N = 1 kg * (1/2)^(100.1/14.3)
Simplifying this expression yields:
N = 1 kg * 0.0684
Thus, the amount of phosphorus-32 remaining after 100.1 days is:
N = 0.0684 kg
Therefore, at the end of the 100.1-day period, approximately 68.4 grams of phosphorus-32 remains.
When matter undergoes a physical change, mass is
a
always conserved.
b
sometimes conserved.
c
never conserved.
Answers
what does le chateliter's principle state
Answers
when is an object in free fall
Answers
Answer:
a free-falling object is an object that is falling under the sole influence of gravity. That is to say that any object that is moving and being acted upon only be the force of gravity is said to be "in a state of free fall." Such an object will experience a downward acceleration of 9.8 m/s/s.
Help me with this question please

Answers
Answer:
a. Oxidising agent: Cl₂
b. Reducing agent: NaBr
c. Oxidised: NaBr
d. Reduced: Cl₂
e. Oxidation numbers before reaction: Cl= 0, Na= +1, Br= -1
f. Oxidation numbers after reaction: Cl= -1, Na= +1, Br= 0
Explanation:
Oxidising agents reduces themselves, oxidising other elements/compounds.
Reducing agents oxidise themselves, reducing other elements/compounds.
Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation number.
Reduction is the gain of electrons or decrease in oxidation number.
Convert 3.5mol of CO2 to grams.
Answers
molar mass of dinitrogen triphosphate?
Answers
The molar mass of dinitrogen triphosphide is 121 grams per mole.
What is the molar mass of dinitrogen triphosphate?The molar mass of dinitrogen triphosphide (N₂P₃) can be calculated by adding up the atomic masses of its constituent elements:
2 x atomic mass of nitrogen (N) + 3 x atomic mass of phosphorus (P)
The atomic mass of nitrogen is 14 g/mol and the atomic mass of phosphorus is 31 g/mol.
The molar mass of dinitrogen triphosphide is calculated as;
2(14 g/mol) + 3(31 g/mol)
= 121 g/mol
Learn more about molar mass here: https://brainly.com/question/21334167
#SPJ1
Which of the following is an example of a learned response?
A.
A bird avoids moths that make it sick after eating one.
B.
A person's leg moves when a doctor taps his or her leg with a mallet.
C.
A plant turns to follow the sun during the day.
D.
An adult salmon is able to return to the river where it hatched.
Answers
Explanation: learned response - a reaction that has been acquired by learning. (a bodily process occurring due to the effect of some antecedent stimulus or agent)
the foul odor of rancid butter is due largely to butryic acid, a compound containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen-produces 14.08 g co2 and 4.32 g h2o. determine the empirical formula of tartaric acid
Answers
The empirical formula of tartaric acid is C₄H₆O₆.
Tartaric acid is a compound that contains carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). To determine its empirical formula, we need to analyze the given information about the production of carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O). From the data, we can calculate the mole ratios of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in the compound.
Using the molar masses of carbon (12.01 g/mol), hydrogen (1.008 g/mol), and oxygen (16.00 g/mol), we can convert the given masses of CO₂ and H₂O to moles. From the balanced chemical equation of the reaction, we know that 1 mole of butyric acid produces 4 moles of CO₂ and 2 moles of H₂O.
By dividing the number of moles of carbon and hydrogen by the smallest number of moles obtained, we find that the empirical formula of tartaric acid is C₄H₆O₆. This means that tartaric acid consists of four carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms, and six oxygen atoms in its simplest, empirical form.
To learn more about empirical formula, click here:
brainly.com/question/32125056
#SPJ11
An atom of an element contains 4 electrons, 4 protons and 6 neutrons. In which group of the Periodic Table is this element placed?
Answers
the element is in group 2
if you toward the right of the periodic table is it harder or easier to remove valence electrons?
Answers
Answer:
harder
Explanation:
Answer:
The increased distance weakens the nuclear attraction to the outer-most electron, and is easier to remove
Explanation:
The diagram shows the electron configuration of an atom of an element for the electrons in the s and p orbitals.
What is the group number of the element in the periodic table?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 13
D) 15
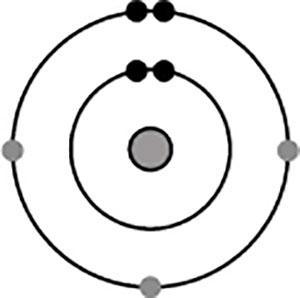
Answers
Answer:
The answer would be 15, letter D.
Explanation:
Since it has 5 electrons in its outermost shell, it will be located in group 15 in the periodic table.
The electron configuration of an atom of an element for the electrons in the s and p orbitals 15th group number of the element in the periodic table option D is correct.
What is electronic configuration of 15th group?Tha common electronic configuration of 15th group elements in ns2 np3, Group 15 elements in the modern periodic table are known as the pnictogens which means suffocation in Greek language.
This group consists of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb) and bismuth (Bi).
The group 15 elements consist of five valence electrons. Due to this the elements can either lose five electrons or gain three electrons in order to attain the stable configuration. The general electronic configuration of nitrogen family is ns 2 np 3.
therefore , because of ns2 np3 option D is correct.
Learn more about electronic configuration , here :
https://brainly.com/question/13497372
#SPJ2
What is the mass of 0.2 mole of sodium.
Answers
We know that 1 mole of sodium contains Avogadro number of atoms. - But we have to find the number of atoms in 0.2 mole of sodium. - Therefore 0.2 moles of sodium (Na) contains 12.046×1023atoms in it.
Two materials A and B are heated separately in air. The product formed is dissolved in water. How will you identify which one is metal?
Answers
a sodium hydroxide solution is 19 M. What will the strength of the solution formed if 25 ml of this NaOH solutio nis diluted to 5.0 Liters
Answers
the strength of the solution formed is 3.8.
What is the strength of the solution?The amount of solute dissolved in grammes per litre of the solution is used to determine the solution's strength. It stands for the solution's potency or concentration. It uses grammes per litre of expression.
Concentration of NaOH = 19 M
Initial volume of NaOH = 25 mL= 0.025 L
Moles of NaOH = 19*0.025
= 0.475 moles
Final volume of NaOH solution = 5 L
Final concentration = 0.475/5
= 0.095 M
so, the strength is 19/5
= 3.8
to know more about strength of the solution go to - https://brainly.com/question/15848974
#SPJ4
gas is contained in a closed pi ston-cylinder device and undergoes the following three processes. process 1-2: a constant pressure process from 100 kpa and 0.002 m3 (state 1) to a volume of 0.004 m3 (state 2) process 2-3: a constant volume process with heat transfer to state 3 process 3-1: a polytropic compression process pv1.4
Answers
For the given data , (a) the process cannot reach State 3. Thus, it is impossible to determine the pressure and volume at this state ; (b) Work done is : W1-2 = 0.1005 kJ ; W2-3 = 0.1435 kJ ; W3-1 = 2.019 kJ.
(a) To determine the pressure and volume at State 3 :
For, process 1-2: P1V1 = P2V2
At state 2 :
V2 = 0.004m
P1V1/P2 = V2 = 0.004m
=> P2 = P1V1/V2
=> P2 = 100 kPa * 0.002 m / 0.004 m = 50 kPa
For process 3-1: It is Polytropic compression process
PVn = C where n = 1.4
State 3 = Initial state and State 1 = final state
Let the pressure and volume at state 3 be P3 and V3.
P3V3n = P1V1n
=> P3 = P1(V1/V3)^n= 100 kPa(0.002 m / V3)^1.4
Now, to find V3: V1 = V2 + V3
∴ V3 = V1 − V2
=> V3 = 0.002 m − 0.004 m = -0.002 m (unacceptable)
Volume at state 3 is negative. It is an unacceptable value.
Therefore, the process cannot reach State 3.
Therefore, it is not possible to determine the pressyre and volume at this state.
(b) To determine : work for each process :
We know, Process 1-2: constant pressure process
Q1-2 = ΔH1-2 = H2 − H1
=> Q1-2 = CpΔT = Cp(T2 − T1)
where Cp = specific heat at constant pressure = 1.005 kJ/kgK
ΔT = T2 − T1
For a constant pressure process, work done, W1-2 = Q1-2 = Cp(T2 − T1)
Now, P1V1 = P2V2 = mRT1
P2/P1 = T2/T1 = V1/V2 = 0.5
At state 2, P2 = 50 kPa
Process 2-3: constant volume process
Work done during a constant volume process is :
W2-3 = Q2-3 = ΔU2-3 =
=> W2-3 = U3 − U2= CvΔT = Cv(T3 − T2)
where Cv = specific heat at constant volume = 0.718 kJ/kgK
ΔT = T3 − T2
Now, Process 3-1: Polytropic compression process
Work done during a polytropic compression process is :
W3-1 = Q3-1 = ΔH3-1
=> W3-1 = H1 − H3 = Cp
ΔT + V(P1 − P3)= Cp(T1 − T3) + V(P1 − P3)
where ΔT = T1 − T3 ; V = (V1V3)^0.5
State 3 = Initial state and State 1 = final state
As, PVn = CP1V1n = C,
P3V3n = CP3V3n = C
∴ P1V1n = P3V3n
V1/V3 = (P3/P1)^(1/n) = (50 kPa / 100 kPa)^(1/1.4) = 0.883
At state 3, P3V3 = P1V1(V1/V3)^n= 100 kPa * 0.002 m * (0.002 m / 0.004 m)^1.4= 3.925 kJ/kgK
=> W3-1 = Cp(T1 − T3) + V(P1 − P3)
= 1.005 kJ/kgK(T1 − T3) + 0.002 m(100 kPa − 3.925 kPa)
= 2.019 kJ
The pressure and volume at this state is not possible to determine.
Therefore, the work done by all the processes is :
W1-2 = 0.1005 kJ
W2-3 = 0.1435 kJ
W3-1 = 2.019 kJ.
Thus, the required answers are given above.
To learn more about specific heat :
https://brainly.com/question/29792498
#SPJ11
Which is one source of the sediments that form sedimentary rocks?
Answers
Answer:
Sandstone, limestone, and shale
Explanation:
The rocks are most likely to start as sediments carried in rivers and end up in lakes and oceans
Answer:
D - materials dissolved in solutions
Explanation:
EDGE 2021
Carbon dioxide molecules (select all that apply)
Group of answer choices
Protect the Earth from all of the harmful Ultraviolet (UV) radiation
Absorb most of the shortwave radiation emitted from the Sun
Are one of the most abundant constituents of Earth's atmosphere
Can move in many ways, thus absorbing and emitting infrared radiation
Answers
Carbon dioxide molecules can absorb and emit infrared radiation, and they are one of the most abundant constituents of Earth's atmosphere.
Thus, the correct options are:d) Are one of the most abundant constituents of Earth's atmospheree) Can move in many ways, thus absorbing and emitting infrared radiation
Carbon dioxide is a trace gas present in the Earth's atmosphere. It's a vital component of Earth's carbon cycle, which helps to regulate Earth's temperature and support life as we know it. Carbon dioxide molecules are one of the most common gases in the atmosphere, accounting for around 0.04% of the Earth's atmosphere.
The greenhouse effect is caused by carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases. When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's surface, it is absorbed and then radiated back into space as infrared radiation. Greenhouse gases absorb this radiation and trap it in the atmosphere, which causes the Earth's temperature to rise and the climate to change.
Carbon dioxide molecules are capable of absorbing and emitting infrared radiation due to their molecular structure, which consists of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. This property of carbon dioxide is the main reason it's classified as a greenhouse gas.
To know more about Carbon dioxide molecules visit:
https://brainly.com/question/12770212
#SPJ11
What product results from the reaction of CH2==CH2 with Br2?
A. CHBrCHBr
B. CH2CHBr
C. CH3CH2Br
D. CH2BrCH2Br
Answers
The correct option is:D. CH2BrCH2Br. The product that results from the reaction of CH2=CH2 (ethylene) with Br2 (bromine) is CH2BrCH2Br (1,2-dibromoethane). The reaction of CH2==CH2 with Br2 is a halogenation reaction, which involves the addition of a halogen to an unsaturated organic compound.
The product that results from this reaction is CH2BrCH2Br, which is option D. This product is formed by the addition of one Br atom to each of the carbon atoms in the double bond of ethene. The resulting molecule is a dibromoalkane, which is a type of organic compound that contains two bromine atoms attached to adjacent carbon atoms. This reaction is an example of an addition reaction, where the unsaturated organic compound undergoes a reaction with a halogen to form a saturated organic compound. In summary, the correct answer is D, CH2BrCH2Br. This reaction is an example of an addition reaction, in which the bromine atoms are added to the carbon atoms in the double bond, resulting in a single bond between the carbon atoms and a bromine atom attached to each carbon.
Learn more about halogenation reaction here
https://brainly.com/question/31477102
#SPJ11
WILL GIVE BRAINLIEST!

Answers
Answer:
I believe the Answer is B, as time is not dependent on growth, but growth is dependent on time.
Explanation:
Atoms of arsenic (As) are often added to silicon (Si) in a process called doping to change the conductivity of the silicon. How does the addition of arsenic change the conductivity of silicon?
An atom of arsenic has one fewer valence electron and more electron shells than an atom of silicon, so the conductivity decreases because the arsenic atom gains an electron.
An atom of arsenic has one more valence electron and more electron shells than an atom of silicon, so the conductivity decreases because the arsenic atom loses the electron.
An atom of arsenic has one fewer valence electron and fewer electron shells than an atom of silicon, so the conductivity increases because the arsenic atom gains an electron.
An atom of arsenic has one more valence electron and more electron shells than an atom of silicon, so the conductivity increases because the arsenic atom loses the electron.
Answers
Answer:
B.) An atom of arsenic has one more valence electron and more electron shells than an atom of silicon, so the conductivity decreases because the arsenic atom loses the electron.
Explanation:
Silicon is located in the 3rd row and 14th column in the periodic table. Arsenic is located in the 4th row and 15th column in the periodic table. This means that arsenic has one more valence electron than silicon. Since arsenic is located one row down from silicon, its valence electrons occupy higher energy orbitals.
Silicon maintains a crystal-like lattice structure. Each silicon atom is covalently connected to assume this shape. When silicon gains one extra electron from arsenic, it experiences n-type doping. This new electron is not tightly bound in the lattice structure. This allows it to move more freely and conduct more electricity. This can also be explained using band gaps. Silicon, which previously had an empty conduction band, now has one electron in this band. This lowers the band gap between the conduction and valence bands and increases conductivity.
Answer:
its d
Explanation:
One of the problems that occurs as a consequence of chlorofluorocarbon (cfc) pollution is ________.
Answers
One of the problems that occurs as a consequence of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) pollution is ozone depletion. CFCs are synthetic compounds that were commonly used in refrigerants, aerosol propellants, and foam-blowing agents.
When released into the atmosphere, CFCs rise to the stratosphere, where they are broken down by ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This process releases chlorine atoms that catalytically destroy ozone molecules, leading to a reduction in the ozone layer.
Ozone depletion has significant environmental consequences, including increased exposure to harmful UV radiation, which can have detrimental effects on human health, ecosystems, and agricultural productivity.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are chemical compounds that were widely used in various industries due to their stability, non-toxicity, and non-reactivity.
However, when CFCs are released into the atmosphere, they eventually reach the stratosphere, where they undergo photodissociation by high-energy UV radiation. This photodissociation process breaks down CFC molecules and releases chlorine atoms.
The released chlorine atoms are highly reactive and act as catalysts in the destruction of ozone molecules. Each chlorine atom can participate in a series of reactions that lead to the destruction of thousands of ozone molecules before it is eventually deactivated. This process is known as ozone depletion.
Ozone depletion is a critical environmental issue because the ozone layer in the stratosphere plays a vital role in protecting life on Earth from harmful UV radiation.
UV radiation can cause various health problems in humans, including skin cancer, cataracts, and weakened immune systems. It can also have adverse effects on marine ecosystems, agricultural productivity, and the overall balance of ecosystems.
To address the problem of ozone depletion, the international community came together and took action through the Montreal Protocol in 1987. This agreement aimed to phase out the production and use of CFCs and other ozone-depleting substances.
As a result, the production and consumption of CFCs have significantly decreased, leading to a gradual recovery of the ozone layer. However, it will take several more decades for the ozone layer to fully heal.
In conclusion, the release of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) into the atmosphere causes ozone depletion, leading to a reduction in the protective ozone layer in the stratosphere.
This depletion increases the levels of harmful UV radiation reaching the Earth's surface, posing risks to human health, ecosystems, and agriculture.
International efforts to reduce CFC production and consumption have been successful in mitigating ozone depletion, but continued vigilance and adherence to protocols are necessary to ensure the full recovery of the ozone layer.
To learn more about, chlorofluorocarbon :-
brainly.com/question/14523807
#SPJ11
Choose one of the following topics:
Acids and Bases
Chemical and physical properties of matter
Kinetic and potential energy
Electricity and magnetism
Newton's Laws of Motion
Heat energy
Gravity
Create a brochure, flyer, PowerPoint, Prezi, or other creative endeavor that visually describes/explains the topic and how this topic can be observed or applied in everyday life or your career field.
Assignment checklist: Before you submit your assignment, ask yourself these questions:
Did you include a minimum of one full page (or 10 slides if a PowerPoint is used)?
Did you fully describe the topic?
Did you make sure to include all references that you used?
Did you complete the CARS checklist to evaluate the references?
Answers
Understanding the properties of acids and bases is critical for everyday life and several career fields.
Topic: Acids and Bases
Acids and bases are two major branches of chemistry that deal with the behavior of acids and bases in solutions and the properties of their aqueous solutions. Acids and bases can be found all around us, from the foods we eat to the products we use in our daily lives. The pH scale is used to measure the acidity or basicity of solutions.
Solutions with pH less than 7 are acidic, while solutions with pH greater than 7 are basic. A solution with a pH of 7 is neutral.
A few examples of acids and bases in everyday life are:
Acids
Vinegar: Acetic acid is a weak acid found in vinegar.
Citrus fruits: Citric acid is a weak acid found in citrus fruits.
Carbonated drinks: Carbonic acid is a weak acid found in carbonated drinks.
Stomach acid: Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid found in the stomach.
Base
Soap: Sodium hydroxide is a strong base found in soaps.
Ammonia: Ammonia is a weak base found in cleaning products.
Antacids: Antacids are basic compounds used to neutralize stomach acid.
So, in everyday life, people can observe and apply the properties of acids and bases while cooking, cleaning, and consuming food and drinks. The use of acids and bases is also critical in several professions, including healthcare, agriculture, and manufacturing.
In healthcare, pH regulation is critical for maintaining homeostasis in the body. In agriculture, pH regulation is critical for soil fertility and plant growth. In manufacturing, acids and bases are used in the production of various products.
Therefore, understanding the properties of acids and bases is critical for everyday life and several career fields.
To learn more about acids and bases,
https://brainly.com/question/9836972
#SPJ4