Answers
Hair loss is a common issue during pregnancy time. It is occurring dur to the hormonal changes during this time. Hence, option c is correct.
What is hair loss during pregnancy ?The excessive hair loss that happens one to five months after delivery is a common issue . Between 40 and 50 percent of women experience hair loss during pregnancy, so it is not uncommon and like most pregnancy-related changes, hair loss is only temporary.
Three months following delivery is when hair loss tends to be most prevalent. The increase in hormones that occurs during pregnancy prevents hair loss.
After birth, the hormone levels return to normal, allowing the hair to fall out and the cycle to resume as usual. The typical hair loss that was postponed during pregnancy can suddenly stop.
Find more on hair loss:
https://brainly.com/question/10512520
#SPJ9
Related Questions
1) A net force of 75.5 N is applied horizontally to slide a 225 kg crate across the floor.
a. Compute the acceleration of the crate?
Answers
Answer:
The acceleration of the crate is \(0.3356\,\frac{m}{s^2}\)
Explanation:
Recall the formula that relates force,mass and acceleration from newton's second law;
\(F=m\,a\)
Then in our case, we know the force applied and we know the mass of the crate, so we can solve for the acceleration as shown below:
\(F=m\,a\\75.5\,N=225\,\,kg\,\,a\\a=\frac{75.5}{225} \,\frac{m}{s^2} \\a=0.3356\,\,\frac{m}{s^2}\)
Which statement is true
Cells usually take in large food molecules
Cells can get energy by breaking down molecules from food
Cells use energy to help an organism grow and live
Breaking down molecules does not release energy
Answers
Cells usually take in large food molecules. In order to get the nutrients and energy they need, cells have to take in large molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. These molecules are too big to pass through the cell membrane, so cells have to use specialized structures like lysosomes and vacuoles to break them down into smaller molecules.
Cells can get energy by breaking down molecules from food. When cells break down molecules from food, they release energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This energy can be used by the cell to power its functions, such as growth and metabolism.
Cells use energy to help an organism grow and live. The energy that cells get from
breaking down molecules from food is essential for maintaining the functions of the organism. Without this energy, cells would not be able to perform essential tasks like building new tissue, repairing damaged cells, and fighting off infections.
Breaking down molecules does not release energy.
Breaking down molecules actually requires energy, not releases it. In order to break down large molecules into smaller ones, cells have to use enzymes and other specialized structures. These processes require energy in the form of ATP, which is why cells need to take in energy from food in the first place.
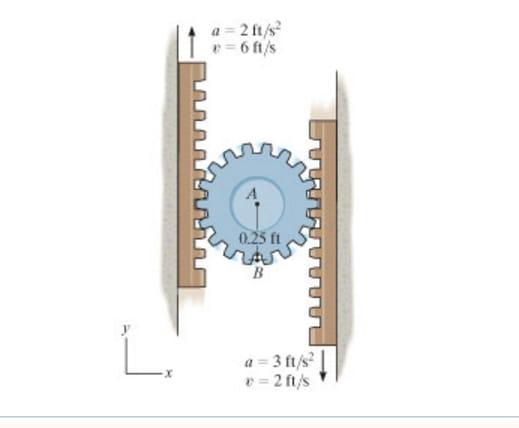
At a given instant, the gear racks have the velocities and accelerations shown.
Determine the acceleration of point A.
Enter the x and y components of the acceleration
Determine the acceleration of point B.
Enter the x and y components of the acceleration
Answers
The acceleration of both points A and B can be determined from the given velocities and accelerations of the gear racks.
Point A:
x-component of acceleration = 0 m/s^2
y-component of acceleration = 6 m/s^2
Point B:
x-component of acceleration = 0 m/s^2
y-component of acceleration = -6 m/s^2
The acceleration of both points A and B can be determined from the given velocities and accelerations of the gear racks. The x-component of the acceleration of both points is equal to 0 m/s^2 since the gear racks are not moving horizontally. The y-component of the acceleration of both points is equal to 6 m/s^2 in the upward direction for point A, and -6 m/s^2 in the downward direction for point B. Therefore, the acceleration of point A is (0, 6) m/s^2 and the acceleration of point B is (0, -6) m/s^2.
The complete question is:
At a given instant, the gear racks have the velocities and accelerations shown.
Determine the acceleration of points A and B.
Enter the x and y components of the acceleration
the complete question is :
At a given instant, the gear racks have the velocities and accelerations shown ( attached below ).
Determine the acceleration of point A.
Enter the x and y components of the acceleration
Determine the acceleration of point B.
Enter the x and y components of the acceleration
learn more about acceleration here
https://brainly.com/question/12550364
#SPJ4
Has anyone read the book Third level
Answers
A submarine dove hundreds of feet from the surface of the ocean toward the oceans floor what is the potential energy stored
Answers
Potential energy is a form of accumulated energy that an item or set of objects may have depending on their size, shape, location, or even substance.
What is a simple definition of potential energy?Potential energy is the energy retained by an object as a result of its location relative to other objects, internal stresses, electric charge, or other variables. Although it has ties to the old Greek philosopher Aristotle's idea of potentiality, the word potential energy was coined by the 19th-century Scottish engineer and physicist William Rankine.
The gravitational potential energy of an object, the elastic potential energy of a stretched spring, and the electric potential energy of an electric charge in an electric field are all examples of common kinds of potential energy.
Learn more about potential energy
https://brainly.com/question/24284560
#SPJ1
A flat sheet of paper of area 0.450 m2 is oriented so that the normal to the sheet is at an angle of 600 to a uniform electric field of magnitude 18 N C-1. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the sheet? A. 3.22 N m2 C-1 B. 21.42 N m2 C-1 C. 5.04 N m2 C-1 D. 11.72 N m2 C-1 E. 4.05 N m2 C
Answers
The magnitude of the electric flux through the sheet is 4.05 N m² C⁻¹ (Option E).
The electric flux through a surface is given by the product of the electric field strength and the area of the surface projected perpendicular to the electric field.
In this case, the electric field strength is 18 N C⁻¹, and the area of the sheet projected perpendicular to the electric field is 0.450 m²
(since the normal to the sheet makes an angle of 60° with the electric field). Multiplying these values gives the electric flux:
Electric flux = Electric field strength × Area
Electric flux = 18 N C⁻¹ × 0.450 m²
Electric flux = 8.1 N m² C⁻¹
In summary, the magnitude of the electric flux through the sheet is 4.05 N m² C⁻¹. This value is obtained by multiplying the given electric field strength by the projected area of the sheet perpendicular to the electric field.
The angle of 60° is taken into account to determine the effective area for calculating the flux.(Option E).
for such more questions on electric
https://brainly.com/question/1100341
#SPJ8
Describe a situation in which these two velocity vectors are different. Use complete sentences.
Answers
When acceleration is equal to zero average velocity and the instantaneous velocity vectors are identical.
Types of velocity
Velocity is defined as the rate of displacement of an object with respect to time. It is measured in meter/ seconds and is a vector quantity.
Acceleration is defined as the rate at which velocity changes with time.
There are two types of velocity which includes:
Average velocity: This is the average rate of change of position of particles with respect to time over an interval.
Instantaneous velocity: This is defined as the specific rate of change of position with respect to time at a particular point.
The situation that will make the average velocity and the instantaneous velocity vectors to be equal or identical is when acceleration is equal to zero.
How does the work needed to stretch a spring 2 cm compare to the work needed to stretch it 1 cm.A.Same amount of workB.twice the workC.4 times the work D.8 times the work
Answers
The work required to stretch a string is given by the following equation:
\(W=\frac{1}{2}kx^2\)Where:
\(\begin{gathered} k=\text{ string constant} \\ x=\text{ distance the string is stretched} \end{gathered}\)If the string is stretched 2 cm then we substitute the value of "x = 2" in the formula, we get:
\(W_2=\frac{1}{2}k(2)^2\)Solving the square and simplifying:
\(W_2=2k\)Now, if the string is stretched 1 cm we get:
\(W_1=\frac{1}{2}k(1)^2\)Solving the operations:
\(W_1=\frac{1}{2}k\)Now, we determine the quotient between W2 and W1:
\(\frac{W_2}{W_1}=\frac{2k}{\frac{1}{2}k}\)Simplifying we get:
\(\frac{W_2}{W_1}=4\)Now, we multiply both sides by W2:
\(W_2=4W_1\)Therefore, the work required to stretch the string 2 cm is 4 times the work to stretch it 1 cm.
The anomalous expansion characteristics of liquid water are crucial to many biological systems. Rather than an approximately constant value for the coefficient of volume expansion, the value for water changes drastically, as illustrated in the figure.
Below what temperature T
does water shrink when heated?
If the temperature of water at 30 ∘C
is raised by 1 ∘C
, the water will expand. At approximately what initial temperature T
will water expand by twice as much when raised by 1 ∘C
?
Answers
(A) The water will shrink when is heated above 4°C. (B).water at an initial temperature of 33.3°C will be expand by twice as much when it is raised by 1°C compared to water at 30°C.
The anomalous expansion of water refers to the fact that its volume increases upon cooling from 4°C to 0°C, and then contracts upon further cooling to 0°C, and continues to contract upon further cooling. Similarly, when water is heated, its volume first contracts until it reaches 4°C, and then expands upon further heating.
To determine at what temperature water shrinks when heated, we need to find the point at which the coefficient of volume expansion, β, becomes negative. The coefficient of volume expansion is defined as the fractional change in volume per degree Celsius change in temperature, i.e.,
β = (1/V) (dV/dT)
where V is the volume of the water and dV/dT is the rate of change of volume with respect to temperature.
At temperatures below 4°C, the coefficient of volume expansion is positive, indicating that water expands upon heating. However, at temperatures above 4°C, the coefficient of volume expansion becomes negative, indicating that water contracts upon heating.
Therefore, water will shrink when heated above 4°C.
To determine the initial temperature at which water will expand by twice as much when raised by 1°C, we can use the formula for the coefficient of volume expansion:
β = (1/V) (dV/dT)
We want to find the initial temperature T such that
(dV/dT)T = 2 (dV/dT)30
where (dV/dT)T is the rate of change of volume with respect to temperature at temperature T, and (dV/dT)30 is the rate of change of volume with respect to temperature at 30°C.
Using the coefficient of volume expansion for water, we have
β = 3α
where α is the coefficient of linear expansion, which is approximately constant for small temperature changes. Therefore, we can write
(dV/dT) = V × 3α
Substituting this into the equation above and simplifying, we get
T = 30 + 10/3 = 33.3°C
Therefore, water at an initial temperature of 33.3°C will expand by twice as much when raised by 1°C compared to water at 30°C.
To know more about water
https://brainly.com/question/29668257
#SPJ1

What is the acceleration of a 4,000 kg car pushed with a
force of 12,000 N?
Answers
Answer:
3 m/s
Explanation:
A= F/m
12,000/ 4000 = 3
Answer:
3 m/s^2
Explanation:
The equation you have to use is F=ma because the problem is a Newton's 2nd law problem.
Our known values are:
F ( Force ) = 12,000 N
m ( mass ) = 4,000 kg
a ( acceleration ) = ?
Now we plug in the known values into the equation and solve
F=ma
12,000=4,000a
We have to divide 4,000 by both sides to isolate the a value
12,000/4,000=4,000/4,000a
The 4,000s on the right of the equation cancel.
And 12,000 divided by 4,000 equals 3
The acceleration (a) is 3 meters per second squared (m/s^2)
Next, check to make sure 3 does work by plugging it back into the equation.
12,000=4,000*3
12,000=12,000 ✔
As you can see, the acceleration will be 3 m/s^2
Identical metal spheres are initially charged as shown. Spheres P and Q are touched together and then separated. Then spheres Q and R are touched together and separated. Afterward, the charge on sphere R is A)-1 nC or less . B)-0.5 nC C) 0 nC D) +0.5 nC E) +1 nC or more +4 nC-2
Answers
The potential of the two aluminum spheres will be equal when they come into contact. identical radius, therefore equal potential results in charges. Hence, sphere C will have a final charge of q c = +1.125q.
Why does a sphere not have a charge?All charges in a circular conductor are at suitable intervals from one another because the energy in a sphere conductor will travel about until it is evenly distributed across its surface. As a result, there's an equal and opposite charge for every charge. Electric fields produced by these charges cancel each other out.
In a spherical, how is the charge distributed?This is just Qr40r if the charge is evenly dispersed throughout the sphere. The charge contained inside radius r in this instance is Qr, and if the charge is Q(r3/a3) is uniformly distributed around the sphere. Hence, Qr240a3 represents that portion of the potential.
To know more about conductor visit :
https://brainly.com/question/8426444
#SPJ1
if an object sinks in water its density is greater than that of water
Answers
What are the total positive charge and total negative charge in a solid copper penny that is electrically neutral
Answers
Answer:
a spark
Explanation:
a spark would be the most smartest
A baseball is hit almost straight up into the air with a speed of 22 m/s. Estimate (a) how high it goes, and (b) how long it is in the air. (c) What factors make this an estimate ?
Answers
(a) The ball goes up to the height of 31.89 m. (b) The ball stays for 5.1 s in the air. (c) The acceleration due to gravity and wind resistance can affect the estimation.
What is Acceleration due to gravity?Acceleration owing to gravity is the term used to describe the rate at which a body's velocity changes as a result of the earth's gravitational pull. In general, it is assumed that the acceleration caused by gravity is in the downward direction.
The acceleration caused by gravity has been calculated as, however as it changes from location to location, it may have an impact on the estimation.
You may have thought that the wind has no impact, but it can actually generate drag and even cause the ball to shift course.
Therefore, (a) The ball goes up to the height of 31.89 m. (b) The ball stays for 5.1 s in the air. (c) The acceleration due to gravity and wind resistance can affect the estimation.
To learn more about acceleration due to gravity, refer to the link:
https://brainly.com/question/13860566
#SPJ1
The series circuit in the figure contains an ideal battery with a constant terminal voltage V_B=52 V, an ideal inductor L=42 H, a R=20-ohm resistor, and a switch S. Initially, the switch is open, and there is no current in the inductor. At time t=0 s, the switch is suddenly closed. What is the current in the circuit when the voltage across the resistor is equal to the voltage across the inductor?

Answers
The current in the circuit when the voltage across the resistor is equal to the voltage across the inductor is given by:
i(t) = [V_B / R] (1 - e^(-Rt/L)) where t is the time after the switch is closed.
The series circuit in the figure contains an ideal battery with a constant terminal voltage V_B=52 V, an ideal inductor L=42 H, a R=20-ohm resistor, and a switch S. Initially, the switch is open, and there is no current in the inductor. At time t=0 s, the switch is suddenly closed. What is the current in the circuit when the voltage across the resistor is equal to the voltage across the inductor-If the voltage across the resistor and the voltage across the inductor are equal, then the voltage across the inductor is V = IR, where I is the current in the circuit.
According to Kirchhoff's law, the voltage across the resistor is equal to the voltage of the battery minus the voltage across the inductor, i.e., V = V_B - L (di / dt), where di/dt is the rate of change of current, and L is the inductance of the inductor. Equating these two expressions for V, we have: IR = V_B - L (di / dt). Rearranging this equation gives us the following differential equation:di / dt + (R/L) i = (V_B / L)The solution of this differential equation is given by: i(t) = [V_B / R] (1 - e^(-Rt/L)).
for such more questions on resistor
https://brainly.com/question/30611906
#SPJ8
In the above example, the 9.012 represents the
Answers
The medium in which electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves travel is one of their primary distinctions. Light and other electromagnetic waves, including radio waves, can move through void space without the aid of a physical medium.
They may move through vacuum, air, or other materials and are made up of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. The propagation of mechanical waves, such as sound or water waves, on the other hand, depends on a physical medium.
To transport energy, they rely on particle interactions and displacements in the medium. Since mechanical waves need a physical medium to carry their energy, they cannot move through a vacuum.
To know more about wave :
brainly.com/question/27511773
#SPJ1.
Which of the following is a vector quantity
weight
temperature
acceleration
distance
Answers
Answer:
weight, acceleration
Explanation:
weight = mass x gravity(meaning the direction of the mass)
acceleration = v-u/t
v-u is the change in velocity
A hockey puck slides off the edge of a horizontal platform with an initial velocity of 28.0 m/s horizontally. The height of the platform above the ground is 2.00 m. What is the direction of the velocity of the puck just before it hits the ground? Neglect air resistance. Give the angle with the + x-axis
Answers
* **Step 1: Identify the relevant information.**
We are given the following information:
* The initial velocity of the puck is 28.0 m/s horizontally.
* The height of the platform above the ground is 2.00 m.
* We can neglect air resistance.
* **Step 2: Set up the equations.**
We can use the following equations to solve for the direction of the velocity of the puck just before it hits the ground:
* $v_y = v_0y + at$
* $y = y_0 + v_0yt + \frac{1}{2}at^2$
Where:
* $v_y$ is the final velocity in the vertical direction
* $v_0y$ is the initial velocity in the vertical direction
* $a$ is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s^2)
* $t$ is the time
* $y$ is the vertical position
* $y_0$ is the initial vertical position
* **Step 3: Solve for the unknowns.**
We can solve for the final velocity in the vertical direction using the following equation:
```
v_y = v_0y + at
```
Plugging in the known values, we get:
```
v_y = 0 + (-9.8) t
```
```
v_y = -9.8t
```
We can solve for the time using the following equation:
```
y = y_0 + v_0yt + \frac{1}{2}at^2
```
Plugging in the known values, we get:
```
2 = 0 + (0) t + \frac{1}{2}(-9.8)t^2
```
```
4 = -4.9t^2
```
```
t^2 = -0.816
```
```
t = -0.90
```
We can now solve for the final velocity of the puck using the following equation:
```
v_y = -9.8t
```
Plugging in the known value for $t$, we get:
```
v_y = -9.8(-0.90)
```
```
v_y = 8.82 m/s
```
The final velocity of the puck in the vertical direction is 8.82 m/s downward.
* **Step 4: Find the angle.**
The angle of the velocity of the puck can be found using the following equation:
```
\theta = \tan^{-1} \left ( \frac{v_y}{v_x} \right )
```
Plugging in the known values for $v_y$ and $v_x$, we get:
```
\theta = \tan^{-1} \left ( \frac{8.82}{28.0} \right )
```
```
\theta = 12.6^\circ
```
Therefore, the direction of the velocity of the puck just before it hits the ground is 12.6 degrees below the horizontal.
which statements describe the Gironde ecosystem
Answers
Answer:
Gironde Ecosystem is an important biological and cultural area.
Explanation:
A stone is dropped from a bridge 45 meters above the surface of a river. What is the time required for the stone to reach the water’s surface?
Answers
Answer:
C. 3.0 s
Explanation:
Well, I've taken this question before, so I went back and this was the answer I put, which was correct.
Hope this helps! <3 May I have brainliest if it helps you enough?
It will take 3 s for the stone to get to the surface of the water.
We'll begin by listing out what was given from the question. This includes:
Height (h) = 45 m
Time (t) =?NOTE: Acceleration due to gravity (g) is 10 m/s²
From the data above, we can obtain the time taken for the stone to get to the surface of the water as follow:
H = ½gt²45 = ½ × 10 × t²
45 = 5 × t²
Divide both side by 5\(t^{2} = \frac{45}{5} \\\\t^{2} = 9\)
Take the square root of both side\(t = \sqrt{9}\)
t = 3 sTherefore, it will take 3 s for the stone to get to the surface of the water.
Learn more: https://brainly.com/question/19339518
What type of tv uses a VfL for backlighting
Answers
A VfL (Vertical Field LED) backlighting system is commonly used in LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) televisions.
LCD TVs rely on a backlight to illuminate the liquid crystal layer, which controls the passage of light to create the visual image. The VfL technology is a specific type of LED backlighting arrangement used in certain LCD TV models. In a VfL backlighting system, the LEDs (Light-Emitting Diodes) are positioned vertically along the edges of the LCD panel.
The light emitted by these LEDs is directed across the panel using light guides or optical films, illuminating the liquid crystal layer uniformly. One advantage of VfL backlighting is its ability to provide consistent illumination across the LCD panel, reducing any potential inconsistencies in brightness or color uniformity. The vertical orientation of the LEDs allows for more precise control over light distribution, improving overall image quality.
Additionally, VfL backlighting offers potential advantages in terms of power efficiency. By selectively dimming or turning off specific zones of LEDs, local dimming techniques can be employed to enhance contrast and black levels, resulting in improved picture quality while conserving energy. It's important to note that VfL backlighting is just one of several backlighting technologies available for LCD TVs.
know more about Liquid Crystal Display here:
https://brainly.com/question/30047287
#SPJ8
Airflow lifts a 3.6 kg bird 50 m up. How much work was done by the flow?
Answers
If airflow lifts a 3.6 kg bird 50 m up, then the work done by the airflow is 1764 joules.
Given,
Mass of the bird = 3.6 kg,displacement covered by the bird due to airflow d) = 50 m,Work done against the friction (W) =?
We know that :
Work done against the friction (W) = force × displacement
W = F × d
W = m × g x d [ Force = mass × acceleration due to gravity ]
W = 3.6 × 9.8 × 50 [ g = 10 m/s2 ]
W = 1764 joules
Hence, the work done by the airflow is 1764 joules.
A force is an influence that has the power to alter an object's motion. A force can cause an object with mass to accelerate when it changes its velocity, for as when it moves away from rest.
Learn more about force here : https://brainly.com/question/25573309
#SPJ1
Consider a double-paned window consisting of two panes of glass, each with a thickness of 0.500 cm and an area of 0.760 m2 , separated by a layer of air with a thickness of 1.65 cm . The temperature on one side of the window is 0.00 ∘C; the temperature on the other side is 23.0 ∘C. In addition, note that the thermal conductivity of glass is roughly 36 times greater than that of air. Approximate the heat transfer through this window by ignoring the glass. That is, calculate the heat flow per second through 1.65 cm of air with a temperature difference of 23.0 ∘C . (The exact result for the complete window is 24.4 J/s .)
Answers
The approximate heat transfer through 1.65 cm of air with a temperature difference of 23.0 °C is approximately 24.4 J/s.
To approximate the heat transfer through the air layer in the double-paned window, we can assume that the glass layers have a negligible impact on the heat flow. The heat transfer can be calculated using Fourier's Law of Heat Conduction, which states that the heat flow (Q) is proportional to the temperature difference (ΔT) and inversely proportional to the thickness (L) and thermal conductivity (k) of the material.
First, we need to calculate the effective thermal conductivity of the air layer due to its thickness and the thermal conductivity ratio between air and glass. Let's denote the thermal conductivity of air as k_air and the thermal conductivity of glass as k_glass. Since glass has a thermal conductivity roughly 36 times greater than air, we have k_glass = 36 * k_air.
Next, we calculate the effective thermal conductivity of the air layer as:
k_eff = (k_air * L_air) / (L_air + k_glass)
Substituting the given values, we have:
k_eff = (k_air * 0.0165 m) / (0.0165 m + 0.005 m) = 0.01309 * k_air
Now, we can calculate the heat flow per second through the air layer using the formula:
Q = (k_eff * A * ΔT) / L_air
Substituting the given values, we get:
Q = (0.01309 * k_air * 0.760 m^2 * 23.0 K) / 0.0165 m = 24.4 J/s
Therefore, the approximate heat transfer through 1.65 cm of air with a temperature difference of 23.0 °C is approximately 24.4 J/s.
For more questions on temperature, click on:
https://brainly.com/question/27944554
#SPJ8
a car is moving 5.82 m/s when it accelerates at 2.35 m/s2 for 3.25, what is its final velocity
Answers
The final velocity of the car can be calculated using the formula: final velocity = initial velocity + acceleration * time. Plugging in the values you provided, we get: final velocity = 5.82 m/s + 2.35 m/s² * 3.25 s = 13.44 m/s.
1When you look through a magnifying glass, the objects you are looking at
seem larger and you can see them in morsetail. The lenses in a magnifying
glass are
Answers
convex lenses.
eyeglasses with convex lenses increase refraction, and accordingly reduce the focal lenght
Vector A has a magnitude of 75.0 cm and points at 30° above the positive x-axis. Vector B has a magnitude of 25.0 cm and points along the negative x-axis. Vector C⃗ has a magnitude of 40.0 cm and points at 45° below the negative x-axis.
(a) Determine the x and y components of Vector A
(b) Determine the x and y components of Vector B .
(c) Determine the x and y components of Vector C .
(d) Determine x and y components of the sum of these three vectors.
(e) Determine the magnitude of the sum of these three vectors.
(f) Determine the direction of the sum of these three vectors.
Answers
(a)
A = (75.0 cm) (cos(30°) i + sin(30°) j)
A = (75.0 cm) (√3/2 i + 1/2 j)
A ≈ (64.95 i + 37.5 j) cm
The x component is the coefficient of the i unit vector, while the y component is the coefficient of the j unit vector.
(b) "points along the negative axis" in other words means that B makes an angle of 180° with the positive x-axis in the counterclockwise direction. In particular this tells you that B is parallel to the x-axis, so its y component would be zero.
B = (25.0 cm) (cos(180°) i + sin(180°) j)
B = (25.0 cm) (-1 i + 0 j)
B = (-25.0 i) cm
(c) If the negative x-axis corresponds to 180°, then 45° below this would make an angle of 180° + 45° = 225° with the positive x-axis.
C = (40.0 cm) (cos(225°) i + sin(225°) j)
C = (40.0 cm) (-1/√2 i - 1/√2 j)
C ≈ (-28.28 i - 28.28 j) cm
(d) The sum A + B + C has components that are the sums of the components of each of A, B, and C.
A + B + C ≈ (11.67 i + 9.22 j) cm
(e) The magnitude of the vector sum is
||A + B + C|| = √((11.67 cm)² + (9.22 cm)²) ≈ 14.87 cm
(f) Since both components of the vector sum are positive, you know that it's a vector that terminates in the first quadrant of the x,y-plane, so it makes an angle with the positive x-axis of
arctan(9.22/11.67) ≈ 38.3°
How are reflectivity and solubility related?
Answers
Answer:
they are related because..
Explanation:
Physical properties can be observed or measured without changing the composition of matter. Physical properties include: appearance, texture, color, odor, melting point, boiling point, density, solubility, polarity, and many others
The relation is ; Reflectivity and solubility are both physical properties of substances and are measured in relation to given variable ( i.e. incident ray for reflectivity and solvent for solubility )
Reflectivity ( aka optical property ) and solubility are both physical properties of any substance. while reflectivity of an object is measured as the amount of light an object reflects in relation to the light incident on it ( incident ray ), solubility is the amount of a substance that will dissolve in a given solvent at a given temperature. a
Hence we can conclude that the relation between reflectivity and solubility is that they are both physical properties of substances and are measured in relation to given variable ( i.e. incident ray for reflectivity and solvent for solubility ).
Learn more : https://brainly.com/question/20499668

Solenoid 2 has twice the radius and six times the number of turns per unit length as solenoid 1. The ratio of the magnetic field in the interior of 2 to that in the interior of 1 is:___________A. 2B. 4C. 6D. 1E. 1/3
Answers
Given :
Solenoid 2 has twice the radius and six times the number of turns per unit length as solenoid 1.
To Find :
The ratio of the magnetic field in the interior of 2 to that in the interior of 1.
Solution :
We know, magnetic field in the interior of a solenoid is given by :
\(B = \dfrac{\mu ni}{L}\)
Let, length of solenoid 2 is L.
Therefore, length of solenoid 1 is 6L.
\(B_a=\dfrac{\mu (6n)i}{L}\\\\B_b = \dfrac{\mu n i}{L}\)
Dividing \(B_a\) by \(B_b\) :
\(\dfrac{B_a}{B_b}=\dfrac{\dfrac{\mu (6n)i}{L}}{\dfrac{\mu n i}{L}}\\\\\dfrac{B_a}{B_b}=6\)
Therefore, the correct answer is C. 6.
Which observation is evidence that electromagnetic radiation (EMR) has particle-like
properties? (1 point)
O EMR refracts as it moves into a different medium.
O
A diffraction pattern is observed when EMR passes through a narrow slit.
O Some EMR is blocked when it passes through a polarized lens.
O EMR with energy above a certain value can eject electrons out of a metal.
Answers
The observation that electromagnetic radiation with energy above a certain value can eject electrons out of a metal is a piece of evidence that they have particle-like properties.
Electromagnetic radiations as particlesThe observation that electromagnetic radiation with energy above a certain value can eject electrons out of a metal is a piece of evidence that they have particle-like properties.
This observation that electromagnetic radiation behaves like particles is known as the photoelectric effect.
It provides evidence that electromagnetic radiation exhibits particle-like properties. When EMR with sufficient energy (above a certain threshold) interacts with a metal surface, it can cause the ejection of electrons from the metal.
This behavior indicates that EMR behaves as discrete packets of energy called photons, which transfer their energy to the electrons and cause their release. The photoelectric effect supports the particle nature of EMR and is a fundamental concept in the field of quantum mechanics.
More on electromagnetic radiation can be found here: https://brainly.com/question/29646884
#SPJ1
for each case, derive an expression for the change in gravitational potential energy, and compare it to the work done by gravity. (take the ground as the reference level (where gpe
Answers
U = mgh is result of the expression calculating gravitational potential energy elevation (h). R + h = R + g = GM/R2 follow when hR. should be noted as g no value near the earth's centre, a body's weight is also zero .
Why is gravity a force?But in a wider sense, gravity is a force since it explains the interaction of two masses. Fundamentally, the stretching of space and the motion of things through the deformed spacetime are what create gravitational effects. But the outcome appears to be the effect of applying force.
– Derive ΔU = mgh. When, h<<R, then, R + h = R and g = GM/R2. ⇒
What are the three different types of gravity?There will be only one kind of gravity. In nature, there are only two types of gravity. This indicates that there is just one kind of gravitational pull that draws the two bodies closer based on their.
U = – GMm / r
U = – GMm/r
U = mgh
Fdx = dw
dW = (GMm/x2)dx
W=SC.Mm ) dx00
W = - (GMm)- (-00• GMm
W=-GMm/r
U = - GMm(1/r1 - 1/r2)
if r1 >r2 so U is negative
To know more about gravitational visit:
https://brainly.com/question/3009841
#SPJ4
The correct question is
Define gravitational potential energy. Derive expression for gravitational potential in the gravitational field of earth at distance r from the centre of the earth.