Indicate whether each of the following statements is true or false. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. Acid strength in a series of H-A molecules increases with increasing size of A. The strongest acid known is HF because flourine iss the most ellectronegative element. For oxyacids of the same general structure but differing electronegativities of the central atoms, acid strength decreases with increasing electronegativity of the central atom. ResetHelp True False
Answers
The first statement is false. The second statement is true.
Acid strength in a series of H-A molecules does not necessarily increase with increasing size of A. The strength of an acid depends on various factors such as the stability of the resulting conjugate base and the ease of proton donation. While larger atoms may have a more polarizable electron cloud, leading to stronger acids in some cases, it is not a general trend.
The second statement is true. The strongest acid known is not HF. In fact, HF is a weak acid. The strength of an acid is determined by its ability to donate protons. While fluorine is the most electronegative element, which affects the polarity of the bond, it does not necessarily make HF the strongest acid.
The strongest known acid is often considered to be fluoroantimonic acid (HSbF6), which is much stronger than HF.
The third statement is not mentioned and does not require an explanation as it was not provided in the question.
To learn more about acid click here: brainly.com/question/29796621
#SPJ11
Related Questions
"As a 14-carbon fatty acid is oxidized in mitochondria; Blank 1β-cycles are performed, and Blank 2 acetyl-CoA molecules are produced." Fill the blanks with the correct numbers. Blank 1 Add your answer Blank 2 Add your answer
Answers
As a 14-carbon fatty acid is oxidized in mitochondria; 7 β-cycles are performed, and 8 acetyl-CoA molecules are produced.
The β-oxidation of fatty acids is a process that takes place in mitochondria. Fatty acids are oxidized by the stepwise removal of two-carbon units in the form of acetyl-CoA. The fatty acids are first activated in the cytoplasm by combining with coenzyme A (CoA) to form a fatty acyl-CoA. Acyl-CoA is transferred to the mitochondrial matrix by carnitine. The CoA is released again in the mitochondrial matrix, and β-oxidation takes place there. The β-oxidation pathway occurs in four successive steps.
The initial step is the oxidation of the fatty acid to an enoyl-CoA, which is then hydrated to β-hydroxyacyl-CoA. The β-hydroxyacyl-CoA is then oxidized again to a β-ketoacyl-CoA and eventually cleaved to acetyl-CoA and a shortened fatty acyl-CoA, which undergoes the next round of the cycle.
In a 14-carbon fatty acid, seven such cycles would be required to convert it into seven acetyl-CoA molecules, each consisting of two carbons. These acetyl-CoA molecules may be used in the citric acid cycle to produce ATP via oxidative phosphorylation.
Learn more about mitochondrial matrix from the given link:
https://brainly.com/question/32435789
#SPJ11
what does Le châteliers principle state?
Answers
Hope this helps!
What is the range of accuracy for food temperature?.
Answers
Answer:
+ 2 degrees Fahrenheit
Explanation:
When investigating whether or not the substance dibromoethane (ethylene dibro- mide) is carcinogenic, we follow the survival history of 161 white employees of 2 factories who were exposed to dibromoethane. Among them, we observe 7 can- cer deaths in the period 1940-1975. On the other hand, the mean number of cases over that period in that general population is expected to be 5.8. Do those 7 cases provide a reason to consider the substance as carcinogenic?
Answers
When investigating whether or not the substance dibromoethane (ethylene dibromide) is carcinogenic, we follow the survival history of 161 white employees of 2 factories who were exposed to dibromoethane.
Among them, we observe 7 cancer deaths in the period 1940-1975. On the other hand, the mean number of cases over that period in that general population is expected to be 5.8. Do those 7 cases provide a reason to consider the substance as .Yes, the seven cases provide a reason to consider the substance dibromoethane as carcinogenic.
Since the number of cancer deaths observed in the 161 white employees exposed to dibromoethane is 7 which is greater than the expected cancer deaths in the general population, which is 5.8. Therefore, the excess cases may suggest that dibromoethane has some carcinogenic potential.
Hence, we can consider dibromoethane as carcinogenic.
To know more about carcinogenic visit:
https://brainly.com/question/30763696
#SPJ11
given the reaction: 4 fe (s) 3 o2 (g) → 2 fe2o3 (s) identify the oxidizing and reducing agents and the oxidation and reduction half-reactions.
Answers
In the given reaction, iron (Fe) is oxidized to form iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3), while oxygen (O2) is reduced to form water (H2O).
Oxidizing agent can be defined as a substance that oxidizes other substance and help carry out oxidation while reducing agent helps to reduce other element or compound present in a reaction. Both these processes, that is oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously.
The oxidizing agent in this reaction is oxygen (O2), which accepts electrons from iron (Fe). The reducing agent is iron (Fe), which donates electrons to oxygen (O2).
The oxidation half-reaction is:
4Fe(s) → 4Fe3+(aq) + 12e-
The reduction half-reaction is:
3O2(g) + 12e- → 6O2-(aq)
Overall reaction:
4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s)
What is reduction oxidation reaction :https://brainly.com/question/21851295
#SPJ11
Review glycolysis and gluconeo on paper copy
Answers
Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis are two metabolic pathways. Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose to produce energy, while gluconeogenesis is the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
What are glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, and how do they differ from each other?Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and involves the breakdown of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate.
This process occurs in two phases: the preparatory phase and the payoff phase.
In the preparatory phase, glucose is phosphorylated twice, creating fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, which is then split into two three-carbon molecules.
In the payoff phase, each three-carbon molecule is converted into pyruvate, which produces a net gain of two ATP molecules and two NADH molecules.
Gluconeogenesis, on the other hand, is the metabolic pathway that occurs primarily in the liver and involves the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources such as amino acids, lactate, and glycerol.
This pathway is important because it enables the body to maintain blood glucose levels during periods of fasting or low carbohydrate intake.
The pathway is essentially the reverse of glycolysis, with a few extra enzymes to bypass the irreversible steps of glycolysis.
Overall, glycolysis and gluconeogenesis are both essential metabolic pathways in the body, playing opposite roles in the regulation of blood glucose levels.
While glycolysis breaks down glucose to produce energy, gluconeogenesis produces glucose to maintain blood glucose levels when there is a shortage of glucose in the body.
Learn more about glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
brainly.com/question/14596936
#SPJ11
In this nuclear reaction equation, oxygen decays to form nitrogen. Which equation describes this decay? Choices in the picture

Answers
In this nuclear reaction equation, oxygen decays to form nitrogen, the equation that correctly describes it is Oxygen-15 -> Nitrogen-15 + electron + anti-neutrino, i.e., \(^1^5_8O--- > ^{15}_7N+^0_1e\).
Nuclear decay is a process that occurs when the nucleus of an atom is unstable and releases particles or energy in order to become more stable.
There are three main types of nuclear decay: alpha decay, beta decay, and gamma decay.
The equation that describes the decay of oxygen to form nitrogen is:
Oxygen-15 -> Nitrogen-15 + electron + anti-neutrino
\(^1^5_8O--- > ^{15}_7N+^0_1e\).
This is an example of beta decay, where a neutron in the nucleus of the oxygen-15 atom is converted into a proton, releasing an electron and an anti-neutrino.
Thus, the oxygen-15 nucleus is transformed into a nitrogen-15 nucleus.
For more details regarding nuclear decay, visit:
https://brainly.com/question/12224278
#SPJ1
which element has the lowest atomic mass in group 6A
Answers
2 al(s) 3 br2(l) ----> 2 albr3(s) suppose the actual yield of the reaction is 42.0 grams of albr3 and the percent yield is 75%. what is the theoretical yield?
Answers
By multiplying the theoretical yield, or the amount that the process should theoretically produce, by 100.
What do you mean reaction?Resistance or resistance to a force, impact, or movement is a reactionary act, process, or occurrence. especially: a reaction to the a particular treatment, condition, or stimulus; inclination toward a past but typically antiquated political or social system or policy.
What is meaning of reaction in chemistry?One or more chemicals, also referred to as reactants, are transformed into one or more other substances, often referred to as products, in a chemical reaction. Substances are built up of active compounds or chemical elements. Burning is one of the five basic types of chemical reactions, along with combining, breakdown, only one, double-replacement, and replacement.
To know more about reaction visit:
brainly.com/question/28984750
#SPJ4
which theory explains how glacial material can be observed today near sea level at the equator, even though sea level glaciers probably never existed there
Answers
The theory that explains how glacial material can be observed today near sea level at the equator, even though sea level glaciers probably never existed there, is called glacial erratics.
Glacial erratics are large rocks that have been transported from their place of origin by glaciers and deposited far away. During the Pleistocene era, glaciers covered much of the earth, including areas near the equator. As these glaciers retreated, they left behind glacial erratics that can still be observed today. These rocks provide evidence of the extent of past glaciation and help scientists understand the history of the earth's climate.
The theory that explains the presence of glacial material near sea level at the equator is Plate Tectonics. This theory describes Earth's crust as being composed of large, moving plates that interact with one another. Over millions of years, these plates have shifted continents, leading to the distribution of glacial material in various locations, including equatorial regions. Glaciers likely formed at higher latitudes and altitudes during past ice ages, and as the plates moved, the glacial deposits were carried along, eventually reaching their current positions near sea level at the equator. This process demonstrates the dynamic nature of Earth's surface and its geological history.
To know about glaciers :
https://brainly.com/question/19709729
#SPJ11
PLEASE HELP ME QUICK 22 POINTS RIGHT ANSWERS ONLY!! :)
Will mark brainliest if its right
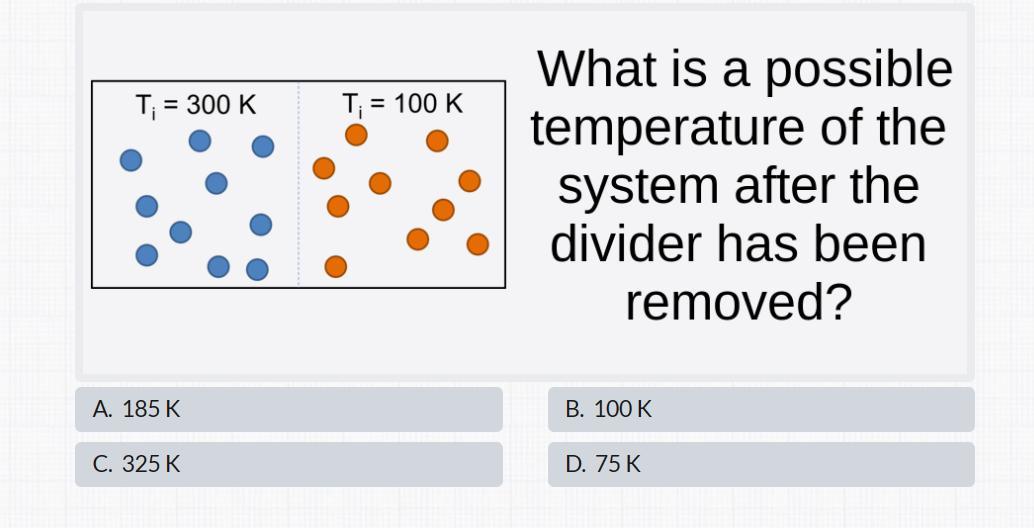
Answers
The correct final temperature after the divider is removed is 200K, amongst the options, the closeset is 185K option A.
The temperature equilibriumTo determine the possible temperature of a system after the divider has been removed, we need to consider the principle of thermal equilibrium and the conservation of energy.
When the divider is removed, the two sides of the system will start to exchange heat until they reach a common temperature. This common temperature is called the final equilibrium temperature.
According to the principle of thermal equilibrium, heat flows from a higher-temperature region to a lower temperature region until the temperatures are equalized.
In this case, the higher-temperature region initially has a temperature of 300K, and the lower-temperature region initially has a temperature of 100K.
To find the final equilibrium temperature, we can use the concept of heat transfer. Heat transfer occurs until the two sides reach the same temperature, so the heat lost by the higher-temperature side must be equal to the heat gained by the lower temperature side.
The heat transferred is given by the equation:
Q = mcΔT
where Q is the heat transferred, m is the mass of the system, c is the specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
Since the masses and specific heat capacities are not given in the question, we can assume that they are equal on both sides, canceling out these variables.
Therefore, we can calculate the change in temperature:
300K - ΔT = 100K + ΔT
Simplifying the equation:
400K = 2ΔT
ΔT = 200K/2
ΔT = 100K
The change in temperature is 100K. Since the initial lower-temperature side was at 100K, the final equilibrium temperature will be:
Final temperature = 100K + ΔT = 100K + 100K = 200K
Learn more on temperature equilibrium here https://brainly.com/question/9459470
#SPJ1
help help pleaseeeee

Answers
T/F: in a titration, the indicator is used to signal when the endpoint has been reached.
Answers
The given statement "In a titration, an indicator is added to the solution being titrated to signal when the endpoint has been reached." is true because the endpoint is the point at which the titrant has completely reacted with the analyte.
An indicator is a substance that undergoes a visible change, such as a color change, at a specific point in the titration process. This change occurs when the stoichiometrically equivalent amounts of the reactants have reacted, indicating that the desired reaction has been completed.
The indicator is chosen based on its ability to undergo a noticeable and distinct color change within a specific pH range or at a specific point in the titration. It allows the experimenter to visually detect when the endpoint, or the point of complete reaction, has been achieved. This information is crucial for accurately determining the concentration of the unknown analyte solution being titrated.
Therefore, in titration, the indicator serves as a visual signal for the endpoint of the reaction.
Learn more about titration on:
https://brainly.com/question/186765
#SPJ11
An atom of Bismuth (Bi) having an atomic mass of 209 amu has an atomic numbr of 83. How many neutrons are present in this atom of Bismuth? (show the calculations)
Answers
Answer:
There are 126 neutrons in the bismuth atom.
Explanation:
Pre-SolvingWe are given that a Bi atom has an atomic mass of 209 amu and an atomic number of 83.
We want to find how many neutrons the bismuth atom has.
SolvingThe atomic mass of an atom is equal to the mass of the protons + mass of neutrons (n.b. the electrons are part of the mass too, however they are very, very small. Therefore, we tend to count the mass of the electrons as 0 when calculating the atomic mass).
Recall that protons and neutrons both have a mass of about 1 amu.
Also recall that the proton number is also the atomic number. Because of this, the bismuth atom has 83 protons. And since that protons have a mass of about 1 amu, the atomic mass of the protons will be:
83 protons × \(\frac{1 amu}{1 proton}\) = 83 amu
That means that if the atomic mass is 209 amu, it is equal to the proton mass (83 amu) + an unknown mass of neutrons (let's say it is x amu).
As an equation, it will be:
83 + x = 209
Subtract 83 from both sides.
x = 126
This means that the neutrons will weigh 126 amu.
Since every neutron is about 1 amu, the amount of neutrons will be:
126 amu × \(\frac{1 neutron}{1 amu}\) = 126 neutrons
Answer:
126
Explanation:
To calculate for neutron #, subtract atomic # from atomic mass.
t hus 09- 83= 126
Calculate the temperature when a 2.51L sample of gas at 25.0 °C is reduced to 1.75 L? (answer must be in K)
\Large \frac{V1}{T1}=\frac{V2}{T2}
Answers
Answer:
208 K
Explanation:
youre welcome
According to the Charle's law, when pressure is constant the temperature when a 2.51 L sample of gas at 25.0 °C is reduced to 1.75 L is 207.76 K.
What is pressure?Pressure is defined as the force applied on an object perpendicular to it's surface per unit area over which it is distributed.Gauge pressure is a pressure which is related with the ambient pressure.
There are various units by which pressure is expressed most of which are derived units which are obtained from unit of force divided by unit of area . The SI unit of pressure is pascal .
It is a scalar quantity which is related to the vector area element with a normal force acting on it.It is distributed over solid boundaries and across arbitary sections of fluid normal to the boundaries at every point.As per Charle's law substitution of values gives T₂=298×1.75/2.51=207.76 K.
Learn more about pressure,here:
https://brainly.com/question/18431008
#SPJ3
Now the engineering students have placed a 50 kg lump of copper at 140 C into an insulated tank containing 90 L of water. The initial temperature of the tank was 10 C. What is the entropy change of the copper for this process in kJ/K
Answers
The mass of the copper is 50 kg and the change in temperature (ΔT) is 130 C (140 C - 10 C). Therefore, the entropy change of the copper is 6.5 kJ/K (50 kg × 130 C × 0.05 kJ/K).
What is copper ?Copper is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal that is naturally found in the Earth's crust. It is an essential element for all forms of life, and it is used in a variety of ways in the modern world. Copper is one of the oldest metals used by humans and has been used for thousands of years in the production of jewelry, coins, and statues. It is also used in the production of electrical wiring, plumbing pipes, and other components used in the construction of buildings. Copper is also used in many industrial applications, such as in the production of semiconductors, motors, and other electronic components.
To learn more about copper
https://brainly.com/question/24540382
#SPJ4
What is the mass of 8.12 × 1023 molecules of CO2 gas? (Atomic mass of carbon = 12.011 u; oxygen = 15.999 u.)
Answers
Answer:
8306.76
Explanation:
you just calcuate 8.12 x 1023 and that will give you the answer
PLZ mark me as a BRAINLIESTConsider an energy diagram of two energy levels, one at 0 cm-1 and one at 300 cm-1. a. At what temperature will the probability of occupying the second energy level be 0.15? b. Consider the same situation but imagine you could locate two particles now in the second energy level (imagine the spin in an electronic system, where you can place 2 electrons per energy level, from 152). Do you expect the temperature to be higher or lower than in case a? Why? (no calculations needed)
Answers
The probability of occupying the second energy level in an energy diagram of two energy levels, one at 0 cm-1 and one at 300 cm-1, will be 0.15 when the temperature is 874 K (600°C)
We can write the formula as, Substituting the values: E2 - E1 = 300 cm-1 (which equals to 3 × 104 m-1 or 3.96 × 10-19 J).Then the probability of occupying the second level be 0.15 when the temperature is 874 K (600°C).
If two particles are in the second energy level, then the temperature will be higher than in case a. This is because having two particles in the second energy level (instead of none) indicates that there is an external source of energy that has raised the temperature of the system, since at lower temperatures, particles will occupy the lowest possible energy level.
To know more about temperature visit:-
https://brainly.com/question/7510619
#SPJ11
On the basis of Rutherford's experimental observations, which of the following statements predicts the
structure of the atom?
Check all that apply.
► View Available Hint(s)
In an atom, all of the positive and negative charges are randomly distributed.
In an atom, negatively charged electrons are small particles held within a positively charged
sphere.
In an atom, negatively charged electrons are dispersed in the space surrounding the positively
charged nucleus of an atom.
In an atom, most of the mass and the positive charge are located in a small core within the
atom called the nucleus.
Answers
Answer:
3 and 4
Explanation:
After Rutherford did the alpha particle scattering experiment, he realised that most of the atom must be empty space, and the positive charge needed to be concentrated in the middle of the atom (in the nucleus).
This was because most of the alpha particles went straight through the gold sheet but some were deflected to the side or straight back.
This led to the nuclear model, where Rutherford concluded that most of the mass and all of the positive charge was concentrated in the middle of the atom in the nucleus, and the electrons existed in a sort of negatively charged cloud around the nucleus.
hope this makes sense!
A 0.674m cobalt (ii) chloride (cocl2) solution is prepared with a total volume of 0.0750l. the molecular weight of cocl2 is 128.9 g/mol. what mass of cocl2 in grams is needed for this solution?
Answers
The mass of CoCl₂ is 6.515 g.
Calculation:
Given,
Molarity of the solute (CoCl₂) = 0.674 M
Volume of solution = 0.0750 L
Molecular weight of solute (CoCl₂) = 128.9 g/mol
Molarity formula is used to solve this question.
Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
\(Molarity = \frac{number of moles }{volume (in L)}\) .......(i)
We know that,
\(number of moles = \frac{weight of given solute }{molecular mass if the solute}\) ........(ii)
Put the above values in equation (i)
\(0.674 = \frac{number of moles}{0.0750}\)
\(number of moles = 0.674 (0.0750)\)
\(number of moles = 0.05055\)
Put the number of moles in equation (ii)
\(0.05055 = \frac{weight of given solute}{128.9}\)
\(weight of given solute = 0.05055 (128.9)\)
\(weight of given solute = 6.515 g\)
Therefore, 6.515 g of CoCl₂ is needed.
Learn more about molarity here:
https://brainly.com/question/13386686
#SPJ4
Select the weaker acid from each of the following pairsI. HI or HBr II. H3AsO3 or H2SeO3 III. HNO3 or HNO2A. I. HBr II. H3AsO3 III. HNO2B. I. HNO2 II.H3AsO3 III. HBrC. I. HI II. H3AsO3 III. HNO3D. I. HBr II. H2SeO3 III.HNO2E. I. HI II. H2SeO3 III. HNO2
Answers
The weaker acid in pair I is HBr because it has a higher atomic radius than HI. \(H_2SeO_3\) is the weaker acid in pair II because it has a higher atomic radius than \(H_3AsO_3.\) \(HNO_2\) is the weaker acid in pair III because it has a higher atomic radius than \(HNO_3\).
A. I. HBr II.\(H_3AsO_3\) III. \(HNO_2\)
B. I. \(HNO_2\) II. \(H_3AsO_3\) III. HBr
C. I. HI II. \(H_3AsO_3\) III. \(HNO_3\)
D. I. HBr II. \(H_2SeO_3\) III. \(HNO_2\)
E. I. HI II. \(H_2SeO_3\) III. \(HNO_2\)
In each of the given pairs, the weaker acid is the one with the larger atomic radius, as the larger atom has a weaker hold on its electrons and thus a weaker ability to donate a proton. In pair I, HBr has a larger atomic radius than HI, making it the weaker acid. In pair II, \(H_2SeO_3\) has a larger atomic radius than \(H_3AsO_3\), making it the weaker acid. In pair III, \(HNO_2\) has a larger atomic radius than \(HNO_3\), making it the weaker acid.
Learn more about weaker acid here
https://brainly.com/question/15579188
#SPJ11
Equation balancing
a. S(s) + O2(g) → SO3(g)
b. 2Al(s) + 3Cl2(g) ► 2AICI3(s)
E. 2NaOH(s) + H2SO4(ac) —Na2So (ac) + H2O(l)
d. C3H8(g) + 50(g) -3C02(g) + 4H2O(g)
Answers
Answer:
For a: The balanced equation is \(2S(s)+3O_2(g)\rightarrow 2SO_3(g)\)
For c: The balanced equation is \(2NaOH(s)+H_2SO_4(aq)\rightarrow Na_2SO_4(aq)+2H_2O(l)\)
Explanation:
A balanced chemical equation is one where all the individual atoms are equal on both sides of the reaction. It follows the law of conservation of mass.
For (a):The given unbalanced equation follows:
\(S(s)+O_2(g)\rightarrow SO_3(g)\)
To balance the equation, we must balance the atoms by adding 2 infront of both \(S(s)\) and \(SO_3\) and 3 in front of \(O_2\)
For the balanced chemical equation:
\(2S(s)+3O_2(g)\rightarrow 2SO_3(g)\)
For (b):The given balanced equation follows:
\(2Al(s)+3Cl_2(g)\rightarrow 2AlCl_3(s)\)
The given equation is already balanced.
For (c):The given unbalanced equation follows:
\(2NaOH(s)+H_2SO_4(aq)\rightarrow Na_2SO_4(aq)+H_2O(l)\)
To balance the equation, we must balance the atoms by adding 2 infront of \(H_2O(l)\)
For the balanced chemical equation:
\(2NaOH(s)+H_2SO_4(aq)\rightarrow Na_2SO_4(aq)+2H_2O(l)\)
For (d):The given balanced equation follows:
\(C_3H_8(g)+5O_2(g)\rightarrow 3CO_2(g)+4H_2O(g)\)
The given equation is already balanced.
A mixture of helium and neon gases is collected over water at 0 oC and 745 mmHg. If the partial pressure of helium is 368 mmHg, what is the partial pressure of neon in mmHg
Answers
The partial pressure of neon in the mixture can be calculated using Dalton's law of partial pressures. According to this law, the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each gas in the mixture.
In this case, the total pressure of the mixture is given as 745 mmHg, and the partial pressure of helium is given as 368 mmHg. To find the partial pressure of neon, we can subtract the partial pressure of helium from the total pressure:
745 mmHg - 368 mmHg = 377 mmHg
Therefore, the partial pressure of neon in the mixture is 377 mmHg.
Dalton's law of partial pressures states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of non-reacting gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each gas. This law is based on the assumption that gases behave ideally, meaning they do not interact with each other and occupy the entire volume available to them.
In this specific case, the mixture of helium and neon gases is collected over water, which means that the total pressure measured (745 mmHg) is the sum of the partial pressure of helium and the vapor pressure of water at 0 oC. Since we are only interested in the partial pressure of neon, we subtract the known partial pressure of helium (368 mmHg) from the total pressure to find the partial pressure of neon (377 mmHg).
By using Dalton's law of partial pressures, we can determine the individual contributions of each gas in a mixture, allowing us to understand and manipulate gas mixtures in various scientific and practical applications.
Learn more about partial pressure of neon here:-
https://brainly.com/question/29132593
#SPJ11
Question 28
Which component of clean, dry air has the smallest volume?
a. Carbon monoxide
b. Nitrogen dioxide
c. Ammonia
d. Sulfur dioxide
Answers
The component of clean, dry air that has the smallest volume is: a. Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is toxic to humans and animals. It is produced by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, such as gasoline, natural gas, propane, and coal.
Carbon monoxide is dangerous because it binds to the hemoglobin in red blood cells, reducing the amount of oxygen that can be carried throughout the body. This can lead to symptoms such as headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, and confusion, and can eventually lead to unconsciousness and death.
Carbon monoxide can be produced by a wide range of sources, including vehicles, generators, furnaces, water heaters, and fireplaces. It is important to ensure that these sources are properly installed, maintained, and vented to prevent the buildup of carbon monoxide indoors.
Carbon monoxide detectors are also an important safety measure to detect the presence of carbon monoxide in indoor spaces. These detectors work by sounding an alarm when the concentration of carbon monoxide in the air reaches a certain level, allowing occupants to evacuate and ventilate the area.
Visit here to learn more about Carbon monoxide brainly.com/question/22530423
#SPJ11
2NaOH + CO₂ = Na₂CO3 + H₂O
Is this equation balanced?
Answers
Balanced chemical equation :
A balanced equation is a chemical reaction equation in which the total charge and the number of atoms for each element in the reaction are the same for both the reactants and the products.
Given Equation :
\(2NaOH_{}\) + \(CO_{2}\) = \(Na_{2}CO_{3}\) + \(H_{2}O\)
Here, we have 2 sodium (Na) atoms, 4 Oxygen (O) atoms, 2 Hydrogen (H) atoms and 1 Carbon (C) atom on the left hand side of the equation (reactants).
Also we have 2 sodium (Na) atoms, 4 Oxygen (O) atoms, 2 Hydrogen (H) atoms and 1 Carbon (C) atom on the right hand side of the equation (products).
Hence , the given equation, \(2NaOH_{}\) + \(CO_{2}\) = \(Na_{2}CO_{3}\) + \(H_{2}O\) is a balanced chemical equation.
To know more about balanced chemical equations, visit,
https://brainly.com/question/14072552
#Balanced chemical equations
what sea animals have moveable spines that they use for protection
Answers
Answer:
sea urchins
Explanation:
Answer:
sea urchins
Explanation:
i took the test
. a 23.74 ml volume of 0.0981 m naoh was used to titrate 25.0 ml of a weak monoprotic acid solution to the stoichiometric point. determine the molar concentration of the weak acid solution
Answers
The molar concentration of the weak acid solution is 0.09308 M.
To determine the molar concentration of the weak acid solution, we need to use the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between the weak acid and the strong base NaOH:
HA + NaOH → NaA + H2O
where HA is the weak monoprotic acid and NaA is its corresponding sodium salt.
At the stoichiometric point of the titration, all of the weak acid has reacted with the strong base, and the number of moles of NaOH used is equal to the number of moles of weak acid present in the original solution:
n(HA) = n(NaOH)
We can use the molarity and volume of NaOH used to calculate the number of moles of NaOH used:
n(NaOH) = M(NaOH) × V(NaOH)
= 0.0981 mol/L × 23.74 mL / 1000 mL/L
= 0.002327 moles
Since the molar ratio of HA to NaOH in the balanced equation is 1:1, the number of moles of HA in the original solution is also 0.002327 moles.
To calculate the molar concentration of the weak acid solution, we divide the number of moles of HA by the volume of the original solution used in the titration:
M(HA) = n(HA) / V(HA)
= 0.002327 moles / 25.0 mL / 1000 mL/L
= 0.09308 mol/L
Therefore, the molar concentration of the weak acid solution is 0.09308 M.
Learn more about molar concentration
https://brainly.com/question/13385951
#SPJ4
A person has a 342.41 mL sample of gas at a pressure of 21.31kPa If the person increases the volume to 1.42L what will the new pressure of the gas be in kPa?
Answers
Answer:
\(\text{5.14 kPa}\)
Explanations:
Here,we want to get the new pressure of the gas
To get this, we have to use the gas law that relates volume and pressure
This is the Boyle's law and it can be represented as follows:
\(P_1V_1=P_2V_2\)Where 1 represents the initial values and 2 represents the final values
We have to convert the volumes to the same scale
We have to convert the liters to ml by multiplying by 1000
We have this as 1.42 * 1000 = 1420 mL
The values are:
Initial
Pressure = 21.31 kPa
Volume = 342.41 mL
Final
Pressure =?
Volume = 1420 mL
We substitute the values as follows:
\(\begin{gathered} 21.31\text{ }\times\text{ 342.41 = P }\times\text{ 1420} \\ P\text{ = }\frac{21.31\times342.41}{1420}\text{ = 5.14 kPa} \end{gathered}\)how electronegativity relates to polar bonding
Answers
2. Which of the following best describes temperature? *
O Number of molecules
Motion of molecules
O Size of molecules
O Type of molecules
Answers
Answer:
motion of molecules because we gonna see which one is in a solid state and what's so ever